

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
Daniela Durán González’s words felt less like a procedural objection and more like an oracle speaking truth in the court of self-appointed climate policy gods.
The final moments of United Nations climate summits usually follow a familiar script. In the closing plenary, decisions are gaveled through, despite several powerful objections stated by delegates from climate-vulnerable countries and quietly noted by the Conference of Parties presidency, and the appearance of full consensus by all governments is carefully preserved—no matter how compromised the outcome actually is.
At COP30 in Brazil, that script was nearly held with business as usual.
By the final plenary, meaningful references to fossil fuel phaseout, pushed by a growing number of countries, had already been stripped from the presented outcome text. Many months of organizing and campaigning by civil society, increasingly dire scientific warnings, and pressure from leaders in Brazil and some of the most climate-vulnerable nations had been erased. The fossil fuel omission left behind a painful awareness of the continued death and destruction of communities and land that will inevitably result from this inaction. The disappointing outcome was sadly to be expected, but that didn’t make the moment any less heavy.
Civil society engages in COPs year after year, not because we believe these negotiations will save us, but because they are sites of power, and nonengagement would signal the loss of resolve. We come to stop devastating outcomes from getting worse, to confront decision-makers face to face, to hold governments accountable in real time, and to intervene with sustainable and equitable solutions that are rising from frontline and grassroots communities.
The climate emergency is a mirror, reflecting back to humanity that how we are living with the Earth and each other is existentially flawed.
But something unusual happened in the final COP30 plenary that many of us were thrilled to witness. The climate negotiator from Colombia lifted her flag and spoke out.
Daniela Durán González, head of international affairs at the Colombian Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development, raised a procedural objection and disrupted the final conference procedures. The mood in the room shifted instantly, and what had felt preordained suddenly felt like a seismic eruption. I remember exchanging glances with my colleagues as we rose to our feet, cheering as the weight of the moment sank in. For a brief, electric moment in time, the machinery of managed consensus was forced to stop.
Throughout COP30, negotiators wrestled with the need to scale up finance—especially for adaptation; commitments to mitigation efforts; and deep political divisions over whether and how to confront the root causes of climate change, including by advancing just transition pathways. At the center of those divisions and heated discourses were fossil fuels—the source of most global greenhouse gas emissions. Despite support from roughly 80 countries for including language on a roadmap to phase out fossil fuels, opposition from major producing nations and others prevented the inclusion of any explicit mention of fossil fuels in the final outcome text.
Instead of addressing the source of the crisis, the agreed outcome text tinkered only on the margins with some vague commitment to tripling adaptation finance by 2035 and a focus on advancing voluntary implementation initiatives, while abandoning a direct confrontation of fossil fuel phaseout that many delegates had sought.
COP30 unfolded amid a growing and dangerous consolidation of power further aggravating and entrenching inequity. Many of the world’s wealthiest governments and global elites are well aware not only of the accelerating climate crisis, but simultaneously of biodiversity collapse and social instability. Because they are dependent on the fossil fuel economy for their wealth and power, these leaders are willing to do anything but stop the extraction of coal, oil, and gas. Rather than changing course (and exploring other energy sources), many major players are preparing to survive the polycrisis that they themselves are inciting, by escaping to fortified enclaves, privatized resilience, and militarized borders—while the rest of the world absorbs the fallout.
Science offers no room for denial about where all of this is heading. Under existing climate policies, global warming could reach nearly 2.8°C. While countries have strengthened current national climate pledges, even if honored, the world would still be moving toward 2.3-2.5°C of global warming. Any of these scenarios is a catastrophic overshoot. What we call “climate disasters” are, in truth, interlocking ecological, social, and economic crises unfolding simultaneously. Every fraction of a degree of warming deepens the wound that’s inflicted on forests, oceans, ice, and human communities alike. We are talking about forests that breathe life into the Earth, rivers that carry the water of life, soils that sustain our food.
The world’s richest corporations and governments have built their wealth on fossil fuel extraction and domination, and they will not suddenly stop these operations on their own. More than 1,600 fossil fuel lobbyists roamed the halls of COP30, their presence outnumbering every party’s delegation except Brazil’s and setting a new deplorable record. Throughout the conference, fossil fuel-producing countries worked to revert the negotiations back to narrow discussions of emission reductions alone, protecting their expansion agenda while presenting the appearance of action. This is why organizing and resistance by civil society are so essential.
The climate crisis is a symptom of deeper, interlocking crises—racial, economic, ecological, and spiritual—rooted in an ideology of supremacy that treats land, water, life, and people as disposable. Indigenous, Black, brown, and Global South communities have borne the brunt of this deadly logic for centuries, and climate breakdown is an acute and tragically visible manifestation of this ideology.
It was into this constructed reality that Daniela Durán González made her forceful intervention in the closing plenary, reminding us that Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva officially designated the COP30 climate summit in Belém as the "COP of Truth."
The "COP of the Truth" cannot support an outcome that ignores science. According to the IPCC, nearly 75% of global CO2 emissions come from fossil fuels. There is no mitigation if we cannot discuss transitioning away from fossil fuels with means of implementation in a just, orderly, and equitable manner… Denying the best available science requires us to not only put the climate regime at risk but also our existence.
The hall erupted as civil society cheered her on.
Her objection to adopting the mitigation text—registered through a formal point of order—caused the entire plenary proceedings to come to an abrupt stop, which is an exceptionally rare act in a space defined by diplomatic choreography. The COP Presidency temporarily halted the plenary to deliberate the point of order, which inevitably served to bring further attention to the powerful objection. But what followed, as the session reopened, exposed even more about the culture of power dynamics inside these negotiations.
Rather than engaging substantively, a senior Russian delegate took to the floor and admonished González and other objecting nations (who were also represented by women leaders) to “refrain from behaving like children who want to get your hands on all the sweets.” Delegates from Latin America (also women leaders) immediately rebuked the comment as offensive and inappropriate. The exchange laid bare how patriarchal and colonial logics continue to shape climate discourse—where women, particularly women from the Global South, are met with ridicule rather than respect when they speak truth to power.
In that moment, Daniela Durán González’s words felt less like a procedural objection and more like an oracle speaking truth in the court of self-appointed climate policy gods. To hear a strong woman, unbowed, articulate what Indigenous peoples, frontline communities, and global climate advocates have been demanding was to glimpse a different futurity—one not dictated by patriarchal, colonial inertia but shaped by those who have lived the consequences first or deeply care about our collective future.
The climate emergency is a mirror, reflecting back to humanity that how we are living with the Earth and each other is existentially flawed. To address it, we must also confront questions of leadership, equity, justice, and care. Every negotiation, every summit, every treaty is not merely a political event—it is a new opportunity to take part in writing and choosing our future by confronting power imbalances and inequities.
The UN climate process operates by consensus, meaning every party must agree before a decision is adopted. In theory, this is meant to protect equity. However, in practice, it amplifies the power of fossil fuel states and entrenched economic interests, diluting ambition and sidelining voices that challenge the status quo. In recent years, civil society has advocated for reform in the UN climate summit process to limit the power of the fossil fuel industry and elevate the solutions and advocacy of climate justice leadership.
Yet, González’s intervention did not disappear from the proceedings. When the closing plenary resumed, the COP30 President, Ambassador André Corrêa do Lago, acknowledged the need for further work on fossil fuel phaseout by proposing a Presidency-led one-year road map process. He suggested the same for deforestation, as both of these critical—and interconnected—issues were absent from the formal text.
This acknowledgment was also recognized and was in support of another significant breakthrough heralded at COP30. Colombia, alongside the Netherlands, announced an April 2026 international conference focused entirely on fossil fuel phaseout, informed by years of advocacy from climate justice movements and the vision of a civil society initiative called the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Throughout COP30 women leaders, including Daniela Durán González reminded us that leadership is not an inheritance of patriarchal privilege but responsibility to the living, those yet to be born, and the sacred agreement between humanity and Earth.
The April conference in Colombia comes at a pivotal time and demonstrates just how many countries are ready to move forward on a phase-out plan. At COP30, more than 80 countries called for language in support of a transition away from fossil fuels, and there are now 18 countries that have endorsed the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty. These countries recognize what is at stake, and the criticality of their upcoming dialogue cannot be overstated. To arrange this conference is to formally acknowledge that no matter how many technological solutions might be developed, if we do not stop the source of climate collapse—coal, oil, and gas—we will not be here to carry out the next steps toward rebuilding as a human community.
It needs to be stated that the parties’ adoption of a new Gender Action Plan and agreement to develop a Just Transition Mechanism were real victories at COP30, ones that were hard fought for and should be truly celebrated, even if details—and dedicated funding—for their successful implementation are yet to be elaborated. They are crucial mechanisms the climate justice movement can utilize to drive change from within the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change process, even as it seeks to reform the UNFCCC to better fulfill its mandate and promise. Nevertheless, what was delivered at COP30 is profoundly insufficient. It falls short of what is urgently needed in collective action for the millions already living through climate-fueled devastation and for ecosystems being irreversibly damaged by fossil fuel expansion and deforestation.
Whether we like it or not, and despite the shortcomings of the process, the COP negotiations remain an important part of how we show up and how we collectively work to make our way out of the climate disaster. They provide the access to governments we need to make our demands turn into action. Yet, we can also remember that hope does not live in negotiated text—it lives in people’s movements globally. Communities continue to rise with clarity and courage, advancing real solutions grounded in Indigenous knowledge, feminist principles, climate justice frameworks, and frontline leadership. Communities are insisting on a world shaped by care, consent, justice, and liberation.
Indigenous women leaders from Brazil were clear from the beginning that the COP30 conference should take place in the Amazon. The rainforest biome is at a critical tipping point, and the entire world ecologically depends on the survival of the Amazon. The women wanted the world to hear the voice of the forest and the voices of Indigenous Peoples calling for protection against fossil fuels and other extractive industries.
Specifically, Indigenous women explained that they wanted the global community to experience the spirit of the Amazon because it is time to reforest our minds. “We are here not only to negotiate,” they said, “but to remember.”
Reforesting the mind is an invitation to undo the dead matter logic that governs modern systems—the belief that separation from the Earth is natural, that endless extraction is progress, and that the future can be postponed. It is a call to restore relationship, memory, equity, reciprocity, and responsibility as living principles.
COP30 revealed the crisis with painful clarity. But it also revealed the power of women’s voices to interrupt dangerous narratives and insist on truth. Throughout COP30 women leaders, including Daniela Durán González reminded us that leadership is not an inheritance of patriarchal privilege but responsibility to the living, those yet to be born, and the sacred agreement between humanity and Earth.
Sitting in the plenary with colleagues from all over the world—vigorously applauding both González’s intervention and the COP30 president’s favorable acknowledgement of the First Conference on Transitioning Away from Fossil Fuels in Colombia (a process outside of the UNFCCC)—it was impossible not to feel that history had briefly opened, offering a pathway for new opportunities.
That is why, ahead of the upcoming conference in Colombia, the Women’s Earth and Climate Action Network is organizing the Women’s Assembly for a Just Fossil Fuel Phaseout on March 31, the last day of Women’s History Month. At the assembly over 20 global women leaders will convene to advance strategies, proposals, and projects to call for transformative action in Colombia. All are welcome. Now, we need to work toward reforesting our minds and using that opening to ensure a better, more just future.As people throughout the globe prepare for the First International Conference for the Phase-Out of Fossil Fuels in Santa Marta, Colombia, in April, a frontline-led just transition must be given center stage.
On February 12, 2026, the US Environmental Protection Agency repealed the Endangerment Finding, a key determination for regulating greenhouse gas emissions under the Clean Air Act. This decision follows the EPA’s January 2026 announcement that air quality protections will be determined based on corporations’ bottom lines, not people’s health. These harmful decisions join a dizzying number of other regulations essential for environmental justice that have been dismantled, deregulated, or destroyed.
In these times, it would be easy to despair about how the tireless movement organizing labor that made these strides possible over many years has now been eroded. However, we cannot accept defeat. My decades of frontline organizing with workers and environmental justice communities toward a just transition shows that transformations come from our collective power. No matter the obstacles, we have the real solutions needed for the crucial work ahead, including during the upcoming Santa Marta conference.
Last year marked a huge moment for just transition. This movement and the principles that inform it often took center stage in grassroots organizing and during the United Nations Climate Summit in Belém, Brazil, in November 2025. The popularity of this concept, practice, and process reveals both promising and harmful co-opted outcomes for Indigenous Peoples, frontline workers, and fenceline communities. The language can be amplified by those most impacted, used to communicate their demands and desires, and it can be used as a tool for trying to undermine the hard work of community organizations and frontline communities.
At COP30, while we welcomed progressive news media coverage and the labor of journalists to cover such an intense few weeks of climate justice and just transition advocacy, we also witnessed reporting by some Global North journalists and news outlets that worked to minimize the credibility of frontline groups and community-based organizations, while amplifying the voices and positions of false solutionists and disaster capitalists.
Unlike some researchers who argue that the negotiations can be improved by using generative artificial intelligence for creating treaty drafts, we know who has the real solutions and who must be centered in building pathways toward just transition.
Much mainstream coverage of COP30 has not adequately addressed the indispensable role of grassroots organizing in pushing toward the successful implementation of a Just Transition Mechanism within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Several days before the official start of COP30, the Movimiento de Afectados por Represas held the IV International Encuentro (Meeting) of People Affected by Dams and the Climate Crisis. This global gathering resulted in the launch of an international movement. Similarly, the Peoples’ Summit, including a just transition axis, was integral in building relationships and movement power. These mobilizations and knowledge sharing spaces worked synergistically with the Global Day of Action for Climate Justice, which occurred on November 15, with people of the world overflowing into the streets of Belém. It was these preceding and concurrent gatherings that energized Just Transition cross-constituencies and that shaped the direction of the Just Transition Work Programme negotiations and the resulting Just Transition Mechanism.
Many celebrate the institutionalization of just transition as one of the greatest successes at COP30. However, much work remains in the implementation process for the new mechanism to actually advance a just transition. Without a commitment to and practice of Indigenous Principles of Just Transition and Just Transition Principles, this mechanism will become another failed effort and abuse of the labor of frontline peoples and grassroots groups who have fought so hard for so long.
Unlike some researchers who argue that the negotiations can be improved by using generative artificial intelligence for creating treaty drafts, we know who has the real solutions and who must be centered in building pathways toward just transition. Groups practicing agroecology and Landback, as well as waste pickers and many other frontline workers, are creating collective power that brings together the most affected workers and environmental justice communities, rather than pitting them against each other.
Additionally, as knowledge holders, Indigenous Peoples and Afro-Indigenous Peoples hold inherent and collective rights; accordingly, they should not be conflated as part of “civil society.” We know that Indigenous Peoples and civil society members must be the ones consulted and centered in these key United Nations negotiations and texts, not the corporate profiteers and their political cronies who pollute just transition possibilities at every COP and at many other conferences.
This year marks 35 years since I served on the drafting committee of the Principles of Environmental Justice and 30 years since I contributed to the Jemez Principles for Democratic Organizing. These principles and the relationships and lived experiences that gave them life continue to inform and fortify our movements toward just transition and a livable world where we all can thrive. Let’s not forget these principles and the frontline peoples who made them possible.
"Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition."
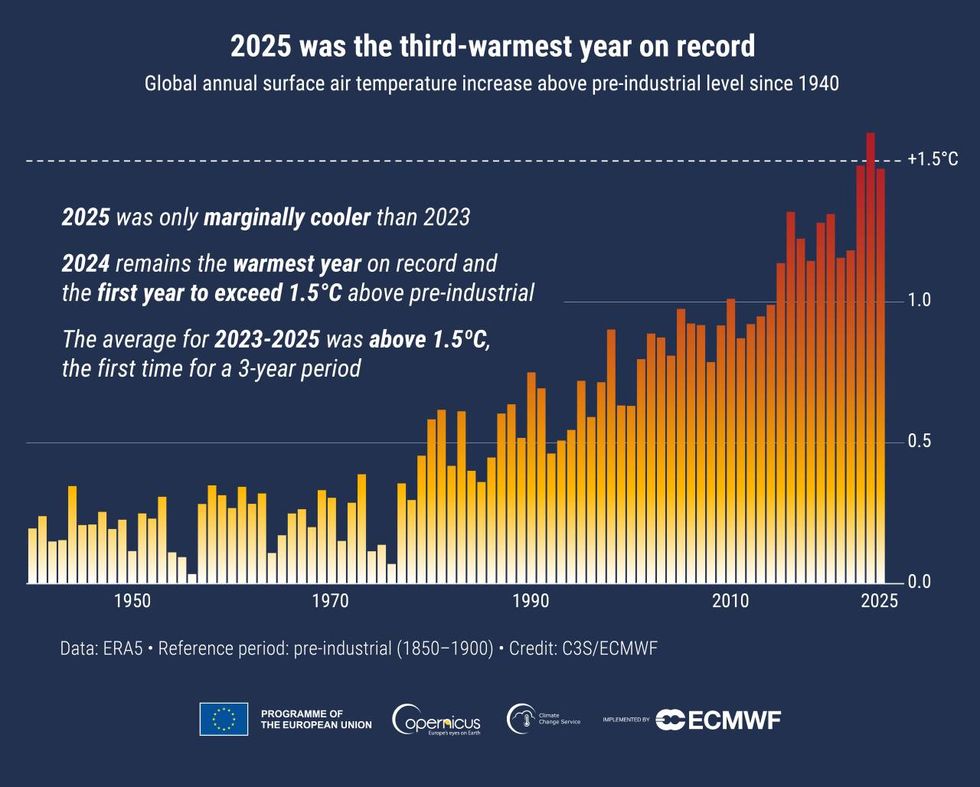
Increasing fossil fuel extraction helped make 2025 the third-hottest year on record and marked the third straight year of “extraordinary global temperatures,” according to a major new report on the climate crisis.
On Wednesday, the European Union's Copernicus climate agency published a report based on data from climate-monitoring organizations, including NASA and the World Meteorological Organization.
Based on billions of weather readings from satellites, ships, aircraft, and weather stations, the report found that, for the first time in recorded history, global temperatures over a three-year period have exceeded the critical threshold of 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
At current rates of heating, the report found, the Earth could surpass the Paris Climate Accord’s target of 1.5°C on a long-term basis by 2030, more than a decade sooner than scientists' projection when nations negotiated the pledge to reduce emissions back in 2015.
“Atmospheric data from 2025 paints a clear picture: Human activity remains the dominant driver of the exceptional temperatures we are observing,” said Laurence Rouil, the director of Copernicus’ Atmosphere Monitoring Service. “Atmospheric greenhouse gases have steadily increased over the last 10 years.”
As with previous years, 2025 was marked by a series of disasters fueled by rising temperatures: From a historic heatwaves that killed an estimated 24,000 people in Europe, to typhoons across Asia that displaced millions, to the wildfires that ravaged the Los Angeles area roughly a year ago and were one of a record 23 disasters in the US that exceeded more than a billion dollars in damage.
The Copernicus report was released as Australia suffered what DW News called possibly its "first megafire of the climate change age" in Victoria, which had charred over 350,000 hectares (more than 864,000 acres) of land as of Sunday and forced thousands to flee their homes.
(Video: Sky News Australia)
"Extreme weather isn’t rare anymore—it’s driving up food prices, insurance premiums, water shortages, and upending daily life across the globe," said Savio Carvalho, the managing director for campaigns and networks for the climate activist group 350. "Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition. We don’t have the luxury of wasting time or taking side paths—we are running out of time."
The past year was marked by yet more disappointment for those hoping to see collective global action to reduce carbon emissions.
The most glaring setbacks occurred in the United States—the globe's largest historic polluter—where President Donald Trump has virtually halted renewable energy expansion, pushed to crank up fossil fuel extraction, and sought to end the "endangerment finding" that allows carbon emissions to be regulated on the basis of their harm to the climate.
But even in the absence of Trump, the past year's global climate summit in Brazil, COP30, once again fell well short of a cohesive international action plan, ending with no global agreement to wind down the use of oil, gas, and coal. Eighty nations failed to submit global emissions pledges, and many of those that did failed to make commitments that would likely bend the global temperature curve in a favorable direction.
Where scientists once urged nations to take swift action in the hope of passing the 1.5°C tipping point, Carlo Buontempo, the director of Copernicus, said following Wednesday's report that "we are bound to pass it."
He said, "The choice we now have is how to best manage the inevitable overshoot and its consequences on societies and natural systems."
But an overshoot is intolerable to many on the front lines of the crisis.
"In the Pacific, climate disasters are costing us billions of dollars in recovery and rebuilding," said Fenton Lutunatabua, 350's program manager for the Pacific and Caribbean. "A world beyond 1.5°C would devastate our resources even more."
"Entire villages in Fiji are being uprooted and relocated, losing connection to traditional lands and fishing grounds," he added. "Atoll nations like Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands are grappling with both adaptation and addressing the reality of potential forced migration. To give up on 1.5°C is to say that any of these realities is acceptable."
In Indonesia, where unprecedented flash floods in November killed 1,100 people, Suriadi Darmoko, an activist in Bali who is suing his government following an International Court of Justice ruling allowing states to be held legally accountable over climate harms, agreed that complacency is not an option.
“Entire communities are still buried in mud. Thousands of families are still grieving and struggling to have their basic needs met. We refuse to be treated as mere climate disaster victims," he said. "Our leaders have kept the world hooked on fossil fuels even as they knew decades ago it would lead to such tragedies."
Carvalho, too, rejected the notion that extreme warming is something the Earth must accept. Despite setbacks to collective action, 2025 also saw certain actors on the global stage make great strides toward a renewable future.
In large part due to massive investments by China, renewable sources generated more power worldwide than coal for the first time, and solar energy generation grew by 31% in the first half of the year, outpacing demand growth.
"We need to do what’s right now: a global phase out of fossil fuels is urgent," said Carvalho. "We already have the renewable energy solutions we need—what’s missing is the political will. We can prevent the worst if we act now."