

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
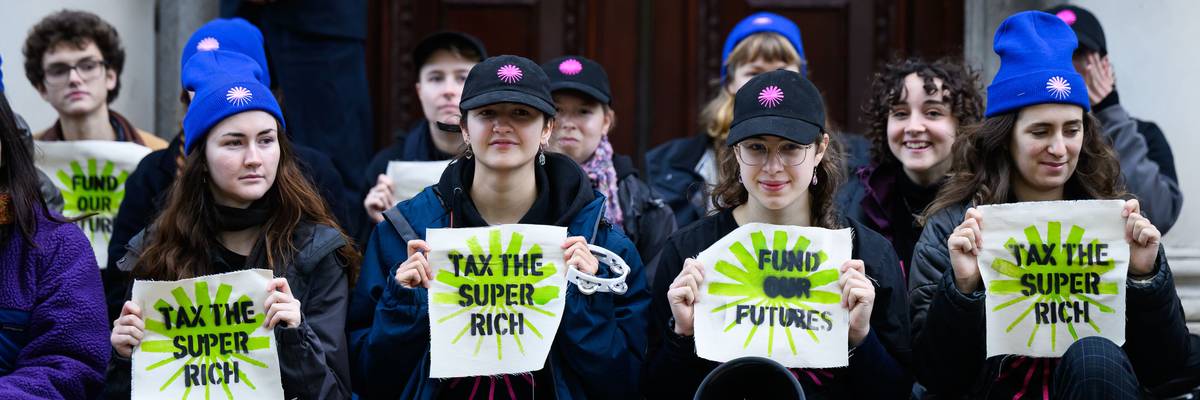
Protestors stage a demonstration, calling for US Chancellor Rachel Reeves to tax the superrich, outside the Treasury on October 27, 2025 in London, England.
"A fair billionaire tax could fund climate flood prevention, clean air, green cities, affordable housing, and nature protection," said one Greenpeace campaigner.
As Hurricane Melissa leaves a trail of destruction in the Caribbean and the world prepares for the next United Nations climate summit, campaigners this week are demanding taxes to make the superrich pay for creating a better future for all, including by transitioning away from planet-wrecking fossil fuels to renewable energy.
An Oxfam International report released Tuesday found that consumption-based carbon emissions of the richest 0.1% of the global population surged by 92 tonnes between 1990 and 2023, while CO2 pollution from the poorest half of humanity grew by just 0.1 tonnes.
The following day, the UK government released a new climate action plan for the next 12 years. The country aims to decarbonize its electricity supply by 2030 and reach net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The climate group 350.org responded by urging Chancellor Rachel Reeves to introduce a tax on ultrawealthy individuals and polluting companies.
"Ordinary people are already paying the price for a crisis they didn't cause—from failed harvests here in the UK to devastation from Hurricane Melissa overseas," 350.org UK campaigner Matilda Borgström said in a statement. "The government's plan will only work if it is funded fairly."
"There's more than enough wealth in this country to pay for affordable clean energy, warm homes, and secure jobs," Borgström argued. "The question for Rachel Reeves is simple: Whose side is she on, ordinary people or the superrich?"
BREAKING: 80+ young people are outside the Treasury right now to tell Rachel Reeves: make tax the super-rich PAY UP - or step down.This Budget, it's time for Reeves to pick a side: us or the billionaires. For wealth taxes to fund investment in a better future.
[image or embed]
— Green New Deal Rising (@gndrising.bsky.social) October 27, 2025 at 5:56 AM
Meanwhile, Greenpeace on Thursday took aim at the wealthiest person on the planet, Elon Musk. As of Thursday, his estimated net worth is $472-490.2 billion, though he could become the world's first trillionaire if shareholders of electric vehicle giant Tesla approve his proposed CEO pay package next week.
Noting Tesla's annual general meeting on November 6, Greenpeace called on governments "to lay the ground for a global tax reform" negotiations for a UN Framework Convention on International Tax Cooperation, scheduled to start in Nairobi, Kenya on November 10—the same day the climate summit, COP30, is set to begin in Belém, Brazil.
"Instead of enabling one person to become a trillionaire, governments should unlock that same scale of wealth—the $1.7 trillion, which a billionaire and multimillionaire tax could generate per year globally—to protect lives and secure our common future," said Fred Njehu, Greenpeace Africa political lead for the Fair Share campaign, in a statement.
"A fair billionaire tax could fund climate flood prevention, clean air, green cities, affordable housing, and nature protection," Njehu noted. "There is no lack of money, only a failure to make the richest of the rich pay their fair share. Governments must act on behalf of the majority of people and listen to what many economic experts suggest: Tax the superrich and their polluting corporations to finance a fair green transition."
A UN synthesis report published Tuesday shows that governments' climate plans, officially called Nationally Determined Contributions, would cut emissions by just 10% by 2035 compared to 2019 levels, dramatically short of what is needed to meet the Paris Agreement's goal of keeping global temperature rise this century at 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
"There is little mistaking the potential of the wealth tax to serve as a financial engine for environmental initiatives," Amir H. Khodadadi, an Iranian developmental economist focused on climate policy and green technology, wrote Wednesday for Earth.org. "Theoretically, a properly designed wealth tax could redistribute wealth and underwrite everything from renewable energy infrastructure to strategies for climate adaptation."
"Reality, however, is a good deal trickier," Khodadadi acknowledged. "As attractive as it is from those standpoints, using a wealth tax for climate action raises some very thorny questions about equity, effectiveness, and possible unintended consequences that will need to be thoughtfully weighed."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
As Hurricane Melissa leaves a trail of destruction in the Caribbean and the world prepares for the next United Nations climate summit, campaigners this week are demanding taxes to make the superrich pay for creating a better future for all, including by transitioning away from planet-wrecking fossil fuels to renewable energy.
An Oxfam International report released Tuesday found that consumption-based carbon emissions of the richest 0.1% of the global population surged by 92 tonnes between 1990 and 2023, while CO2 pollution from the poorest half of humanity grew by just 0.1 tonnes.
The following day, the UK government released a new climate action plan for the next 12 years. The country aims to decarbonize its electricity supply by 2030 and reach net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The climate group 350.org responded by urging Chancellor Rachel Reeves to introduce a tax on ultrawealthy individuals and polluting companies.
"Ordinary people are already paying the price for a crisis they didn't cause—from failed harvests here in the UK to devastation from Hurricane Melissa overseas," 350.org UK campaigner Matilda Borgström said in a statement. "The government's plan will only work if it is funded fairly."
"There's more than enough wealth in this country to pay for affordable clean energy, warm homes, and secure jobs," Borgström argued. "The question for Rachel Reeves is simple: Whose side is she on, ordinary people or the superrich?"
BREAKING: 80+ young people are outside the Treasury right now to tell Rachel Reeves: make tax the super-rich PAY UP - or step down.This Budget, it's time for Reeves to pick a side: us or the billionaires. For wealth taxes to fund investment in a better future.
[image or embed]
— Green New Deal Rising (@gndrising.bsky.social) October 27, 2025 at 5:56 AM
Meanwhile, Greenpeace on Thursday took aim at the wealthiest person on the planet, Elon Musk. As of Thursday, his estimated net worth is $472-490.2 billion, though he could become the world's first trillionaire if shareholders of electric vehicle giant Tesla approve his proposed CEO pay package next week.
Noting Tesla's annual general meeting on November 6, Greenpeace called on governments "to lay the ground for a global tax reform" negotiations for a UN Framework Convention on International Tax Cooperation, scheduled to start in Nairobi, Kenya on November 10—the same day the climate summit, COP30, is set to begin in Belém, Brazil.
"Instead of enabling one person to become a trillionaire, governments should unlock that same scale of wealth—the $1.7 trillion, which a billionaire and multimillionaire tax could generate per year globally—to protect lives and secure our common future," said Fred Njehu, Greenpeace Africa political lead for the Fair Share campaign, in a statement.
"A fair billionaire tax could fund climate flood prevention, clean air, green cities, affordable housing, and nature protection," Njehu noted. "There is no lack of money, only a failure to make the richest of the rich pay their fair share. Governments must act on behalf of the majority of people and listen to what many economic experts suggest: Tax the superrich and their polluting corporations to finance a fair green transition."
A UN synthesis report published Tuesday shows that governments' climate plans, officially called Nationally Determined Contributions, would cut emissions by just 10% by 2035 compared to 2019 levels, dramatically short of what is needed to meet the Paris Agreement's goal of keeping global temperature rise this century at 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
"There is little mistaking the potential of the wealth tax to serve as a financial engine for environmental initiatives," Amir H. Khodadadi, an Iranian developmental economist focused on climate policy and green technology, wrote Wednesday for Earth.org. "Theoretically, a properly designed wealth tax could redistribute wealth and underwrite everything from renewable energy infrastructure to strategies for climate adaptation."
"Reality, however, is a good deal trickier," Khodadadi acknowledged. "As attractive as it is from those standpoints, using a wealth tax for climate action raises some very thorny questions about equity, effectiveness, and possible unintended consequences that will need to be thoughtfully weighed."
As Hurricane Melissa leaves a trail of destruction in the Caribbean and the world prepares for the next United Nations climate summit, campaigners this week are demanding taxes to make the superrich pay for creating a better future for all, including by transitioning away from planet-wrecking fossil fuels to renewable energy.
An Oxfam International report released Tuesday found that consumption-based carbon emissions of the richest 0.1% of the global population surged by 92 tonnes between 1990 and 2023, while CO2 pollution from the poorest half of humanity grew by just 0.1 tonnes.
The following day, the UK government released a new climate action plan for the next 12 years. The country aims to decarbonize its electricity supply by 2030 and reach net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The climate group 350.org responded by urging Chancellor Rachel Reeves to introduce a tax on ultrawealthy individuals and polluting companies.
"Ordinary people are already paying the price for a crisis they didn't cause—from failed harvests here in the UK to devastation from Hurricane Melissa overseas," 350.org UK campaigner Matilda Borgström said in a statement. "The government's plan will only work if it is funded fairly."
"There's more than enough wealth in this country to pay for affordable clean energy, warm homes, and secure jobs," Borgström argued. "The question for Rachel Reeves is simple: Whose side is she on, ordinary people or the superrich?"
BREAKING: 80+ young people are outside the Treasury right now to tell Rachel Reeves: make tax the super-rich PAY UP - or step down.This Budget, it's time for Reeves to pick a side: us or the billionaires. For wealth taxes to fund investment in a better future.
[image or embed]
— Green New Deal Rising (@gndrising.bsky.social) October 27, 2025 at 5:56 AM
Meanwhile, Greenpeace on Thursday took aim at the wealthiest person on the planet, Elon Musk. As of Thursday, his estimated net worth is $472-490.2 billion, though he could become the world's first trillionaire if shareholders of electric vehicle giant Tesla approve his proposed CEO pay package next week.
Noting Tesla's annual general meeting on November 6, Greenpeace called on governments "to lay the ground for a global tax reform" negotiations for a UN Framework Convention on International Tax Cooperation, scheduled to start in Nairobi, Kenya on November 10—the same day the climate summit, COP30, is set to begin in Belém, Brazil.
"Instead of enabling one person to become a trillionaire, governments should unlock that same scale of wealth—the $1.7 trillion, which a billionaire and multimillionaire tax could generate per year globally—to protect lives and secure our common future," said Fred Njehu, Greenpeace Africa political lead for the Fair Share campaign, in a statement.
"A fair billionaire tax could fund climate flood prevention, clean air, green cities, affordable housing, and nature protection," Njehu noted. "There is no lack of money, only a failure to make the richest of the rich pay their fair share. Governments must act on behalf of the majority of people and listen to what many economic experts suggest: Tax the superrich and their polluting corporations to finance a fair green transition."
A UN synthesis report published Tuesday shows that governments' climate plans, officially called Nationally Determined Contributions, would cut emissions by just 10% by 2035 compared to 2019 levels, dramatically short of what is needed to meet the Paris Agreement's goal of keeping global temperature rise this century at 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
"There is little mistaking the potential of the wealth tax to serve as a financial engine for environmental initiatives," Amir H. Khodadadi, an Iranian developmental economist focused on climate policy and green technology, wrote Wednesday for Earth.org. "Theoretically, a properly designed wealth tax could redistribute wealth and underwrite everything from renewable energy infrastructure to strategies for climate adaptation."
"Reality, however, is a good deal trickier," Khodadadi acknowledged. "As attractive as it is from those standpoints, using a wealth tax for climate action raises some very thorny questions about equity, effectiveness, and possible unintended consequences that will need to be thoughtfully weighed."