March, 31 2016, 09:45am EDT

Lawsuit Challenges FDA's Approval of Genetically Engineered Salmon
Coalition of fishing, consumer, and environmental groups say first-ever approval of laboratory-created food animal violated laws and ignored risks to wild salmon and fishing communities
SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.
A broad coalition of environmental, consumer, and commercial and recreational fishing organizations today sued the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for approving the first-ever genetically engineered -- GE -- food animal, an Atlantic salmon engineered to grow quickly. The man-made salmon was created by AquaBounty Technologies, Inc. with DNA from three fish: Atlantic salmon, Pacific king salmon, and Arctic ocean eelpout. This marks the first time any government in the world has approved a GE animal for commercial sale and consumption.
The plaintiff coalition, jointly represented by legal counsel from Center for Food Safety and Earthjustice, includes Pacific Coast Federation of Fishermen's Associations, Institute for Fisheries Resources, Golden Gate Salmon Association, Kennebec Reborn, Friends of Merrymeeting Bay, Ecology Action Centre, Food & Water Watch, Center for Biological Diversity, Friends of the Earth, Cascadia Wildlands, and Center for Food Safety.
In approving the GE salmon, FDA determined it would not require labeling of the GE fish to let consumers know what they are buying, which led Congress to call for labeling in the 2016 omnibus spending bill. FDA's approval also ignored comments from nearly 2 million people opposed to the approval because the agency failed to analyze and prevent the risks to wild salmon and the environment, as well as fishing communities, including the risk that GE salmon could escape and threaten endangered wild salmon stocks.
AquaBounty's GE salmon will undertake a 5,000-mile journey to reach U.S. supermarkets. The company plans to produce the GE salmon eggs on Prince Edward Island, Canada. The GE salmon will then be grown to market-size in a facility in Panama, processed into fillets, and shipped to the U.S. for sale. That complicated scheme is only for the initial approval, however. AquaBounty has publicly announced plans to ultimately grow its GE fish in the U.S. rather than Panama, and sell it around the world. Despite this, FDA's approval only considered the current plans for the far-flung facilities in Canada and Panama, leaving the risk of escape and contamination of U.S. salmon runs unstudied.
The lawsuit challenges FDA's claim that it has authority to approve and regulate GE animals as "animal drugs" under the 1938 Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Those provisions were meant to ensure the safety of veterinary drugs administered to treat disease in livestock and were not intended to address entirely new GE animals that can pass along their altered genes to the next generation. The approval of the GE salmon opens the door to other genetically engineered fish and shellfish, as well as chickens, cows, sheep, goats, rabbits and pigs that are reportedly in development.
The lawsuit also highlights FDA's failure to protect the environment and consult wildlife agencies in its review process, as required by federal law. U.S. Atlantic salmon, and many populations of Pacific salmon, are protected by the Endangered Species Act and in danger of extinction. Salmon is a keystone species and unique runs have been treasured by residents for thousands of years. Diverse salmon runs today sustain thousands of American fishing families, and are highly valued in domestic markets as a healthy, domestic, "green" food.
When GE salmon escape or are accidentally released into the environment, the new species could threaten wild populations by mating with endangered salmon species, outcompeting them for scarce resources and habitat, and/or introducing new diseases. Studies have shown that there is a high risk for GE organisms to escape into the natural environment, and that GE salmon can crossbreed with native fish. Transgenic contamination has become common in the GE plant context, where contamination episodes have cost U.S. farmers billions of dollars over the past decade. In wild organisms like fish, it could be even more damaging.
The world's preeminent experts on GE fish and risk assessment, as well as biologists at U.S. wildlife agencies charged with protecting fish and wildlife heavily criticized the FDA decision for failing to evaluate these impacts. FDA ignored their concerns in the final approval.
Statements from counsel and plaintiff coalition:
"FDA's decision is as unlawful as it is irresponsible," said George Kimbrell, senior attorney for Center for Food Safety and co-counsel for the plaintiffs. "This case is about protecting our fisheries and ocean ecosystems from the foreseeable harms of the first-ever GE fish, harms FDA refused to even consider, let alone prevent. But it's also about the future of our food: FDA should not, and cannot, responsibly regulate this GE animal, nor any future GE animals, by treating them as drugs under a 1938 law."
"FDA has not answered crucial questions about the environmental risks posed by these fish or what can happen when these fish escape," said Earthjustice attorney Brettny Hardy and co-counsel for plaintiffs. "We need these answers now and the FDA must be held to a higher standard. We are talking about the mass production of a highly migratory GE fish that could threaten some of the last remaining wild salmon on the planet. This isn't the time to skimp on analysis and simply hope for the best."
"Atlantic salmon populations including our endangered Gulf of Maine fish are hanging on by a thread- they can't afford additional threats posed by GE salmon," said Ed Friedman from Friends of Merrymeeting Bay, one of the parties who successfully petitioned to classify most Maine Atlantic salmon as endangered. "The law requires agencies like FDA, who aren't fisheries biologists, to get review and approval from scientists with that expertise. FDA's refusal to do this before allowing commercialization of GE salmon is not only irresponsible, it violates the law."
"On Prince Edward Island and across Atlantic Canada, indigenous peoples, anglers and community groups are working hard to protect and restore endangered salmon populations and rivers. Genetic contamination threatens all this work and in return there is little or no economic benefit to the region," said Mark Butler, policy director at Ecology Action Centre in Nova Scotia.
There's never been a farmed salmon that hasn't eventually escaped into the natural environment. Why should we believe that long term, these frankenfish won't be the same?" asked Golden Gate Salmon Association executive director John McManus.
"Once they escape, you can't put these transgenic fish back in the bag. They're manufactured to outgrow wild salmon, and if they cross-breed, it could have irreversible impacts on the natural world," said Dune Lankard, a salmon fisherman and the Center for Biological Diversity's Alaska representative. "This kind of dangerous tinkering could easily morph into a disaster for wild salmon that will be impossible to undo."
"FDA's action threatens and disrespects the wild salmon ecosystems, cultures and industries that are treasured here in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska," said Gabriel Scott, Alaska legal director for Cascadia Wildlands. "These folks think a salmon is just a packet of protein, but we in Salmon Nation know better. From Alaska to California, Americans are intimately related with diverse runs of salmon and we've learned their unique attributes and incredible value. We've worked very hard to be good stewards of our natural heritage, and refuse to allow that to be undone by one company's irresponsible experiment."
"The FDA has failed to adequately examine the risks associated with transgenic salmon," said Wenonah Hauter, executive director of Food & Water Watch. "The long term effects of people eating genetically modified foods have never been adequately addressed--and this GE salmon is no exception. This fish is unnecessary, so why take the risk?"
"It's clear that the market has rejected GE salmon despite FDA's reckless approval," said Dana Perls, food and technology campaigner for Friends of the Earth. "Major retailers including Costco, Safeway and Kroger won't sell it and polls show the vast majority of people don't want to eat it. Yet under this approval it won't be labeled, violating our fundamental right to know what we are feeding our families."
For more information, visit:
https://www.centerforfoodsafety.org/issues/309/ge-fish or
www.biologicaldiversity.org/campaigns/ge_seafood/
Center for Food Safety's mission is to empower people, support farmers, and protect the earth from the harmful impacts of industrial agriculture. Through groundbreaking legal, scientific, and grassroots action, we protect and promote your right to safe food and the environment. CFS's successful legal cases collectively represent a landmark body of case law on food and agricultural issues.
(202) 547-9359LATEST NEWS
Working Families Party Seeks Banner Year as Trump-Led GOP Appears Poised for ‘Landslide Electoral Defeat’
"I don't think there’s been a better and more right time for a third party to emerge in this country that speaks to the interest of everyday working people," said Maurice Mitchell, national director of the Working Families Party.
Dec 29, 2025
The Working Families Party is gearing up to have a banner year in the 2026 midterms at a time when political trends show the Republican Party led by President Donald Trump heading for a major loss.
The party, which is now active in 18 states, is preparing to "ramp up its involvement in primary elections, supporting candidates that emphasize working-class politics and seek to disrupt the political status quo," according to a Monday report in the Guardian.
The Working Families Party (WFP) had a number of victories in 2025, highlighted by its election of democratic socialist Zohran Mamdani as mayor of New York City.
Maurice Mitchell, national director of the WFP, told the Guardian that he thinks now is the right time for a populist progressive insurgency given that both Democrats' and Republicans' brands are underwater with US voters.
"Less and less people are identifying as being a Democrat or Republican," he said. "I don't think there’s been a better and more right time for a third party to emerge in this country that speaks to the interest of everyday working people. I believe that our time has come."
Although the WFP has traditionally worked within the confines of Democratic Party primary politics, the party this year elected some candidates in the New Jersey General Assembly that lacked backing from state Democratic Party bigwigs.
"This is really the first time that there’s been Working Families candidates that ran outside of the Democratic Party structure, and so we’re building what that future looks like and what it means," Katie Brennan, a New Jersey assemblywoman-elect endorsed by the WFP who won without official Democratic Party backing, told the Guardian. “They've grown and have been making progress year in and year out, and this next year will be big for us. Now we’re in the statehouse, and what does that mean? I think it’ll continue to bring attention to the Working Families party."
One issue that the WFP hopes will propel its candidates to victory in 2026 is the nationwide backlash to artificial intelligence data centers.
In an announcement made earlier this month, the WFP said it is recruiting candidates to run against building AI data centers, which have been blamed for spiking utility bills and draining water resources, in their local communities.
“Billionaires are getting richer from data centers, while working people see their electricity and water bills go through the roof,” said Ravi Mangla, national press secretary for the WFP. "Fortunately, regular people are joining with their neighbors to push back against these big tech takeovers. We’re inviting local leaders who are fighting back to consider running for the seats where decisions about data centers are being made.”
Another reason the party may sense an opportunity is that the Trump-led GOP appears headed for brutal elections in 2026.
Polling expert G. Elliot Morris published an analysis on Monday showing that Trump's current net approval rating of -16 percentage points will likely translate into a "landslide electoral defeat" for Republicans next year.
Morris added that Trump's approval on the issue of inflation was "downright catastrophic," and noted that the president has been bleeding support even in states that voted for him by decisive margins last year.
"Trump’s approval rating is not just underwater because of Democratic resistance," he observed. "Lots of independents and Republicans disapprove of how he’s running the country, too. In fact, the decline from Trump’s vote margin in 2024 is steeper in redder parts of the country."
Keep ReadingShow Less
Nearly Half of Americans Say Their Financial Security Is Getting Worse Under Trump
In a recent focus group, one voter who supported the president in 2024 said Trump's recent claims that the economy is strong were "delusional."
Dec 29, 2025
New polling from The Guardian on Monday bolstered recent analyses that have shown low consumer confidence and job creation numbers and higher household costs and unemployment: Americans are struggling under President Donald Trump's economic policies, and they increasingly believe the White House—for all Trump's claims that the economy is strong—is to blame.
The poll, conducted by Harris for the news outlet between December 11 and 13, found that respondents were twice as likely to say their financial security is getting worse as they were to report an improvement.
Nearly half of those surveyed said their financial situation is worsening, and 57% said they perceived that the US is in a recession—although that would be defined by two quarters of negative growth in the US economy, which the country has not experienced at this point.
Despite that, the poll—along with recent focus groups including members of Trump's 2024 base, held by Syracuse University and reported on Monday by NBC News—illustrated how Trump's focus on imposing tariffs on countries around the world and his promotion of policies that have raised household bills for millions of people have left Americans feeling pessimistic about their own financial health and that of the country.
Democratic voters were far more likely than Republicans to tell Harris that their financial security is getting worse, with 52% of the latter saying so compared with 27% of the former.
But 54% of independent voters agreed that they are struggling more financially, despite Trump's recent claim that he would give the economy a grade of "A-plus-plus-plus-plus-plus.”
"We have seen a shift among these voters collectively, cracks in their faith, more questioning, oscillating, or outright change of heart about Trump."
Respondents from across the political spectrum were more likely than ever before to blame the White House for their financial struggles, Harris said.
More than three-quarters of Democrats blamed Trump's policies and "government management of the economy," along with 72% of independents and more than half of Republicans—55%.
Analyses this year have shown Trump's tariffs, which he claimed soon after taking office would "liberate" Americans from the national debt, are raising costs for small businesses and making it harder for them to stay afloat, and are passing on higher prices to consumers—resulting in ballooning grocery bills for millions of Americans.
Trump made lowering grocery prices a central promise of his campaign last year, along with repeatedly pledging that he was "going to get your energy prices down by 50%.”
But the president's embrace of artificial intelligence and the expansion of data centers—something he and congressional Republicans have aggressively pushed states to allow despite public disapproval—is unlikely to result in lower utility prices for households. Those costs have risen by 13% since Trump took office, with the president's cancellation of renewable energy projects to blame as well as energy-sucking data centers.
The focus groups held by Syracuse recently found that voters who supported the president last year have rapidly grown discouraged by his economic policies, including his tariffs, which one participant called "a tax on the American people."
"That’s who pays for it, so I don’t support it,” David S. of New Jersey told NBC. “The people who are buying those imports are paying the tax.”
With less than a year until voters are set to decide if Republicans should keep their majorities in the US House and Senate, fewer than half of the people surveyed in four focus groups said they believed Trump has made it a priority to fight inflation and reduce their costs. Robert L. of Virginia told Syracuse researchers that the president's recent comments painting a sunny picture of the economy were "delusional."
Another Virginia voter, Justin K., said the president has been focused on "prosecuting his political enemies" and "pardoning people" and has not "tried at all" to tackle the rising cost of living.
A number of those surveyed said they had decided to back Democratic candidates Abigail Spanberger and Mikie Sherrill in this year's gubernatorial elections in Virginia and New Jersey just a year after supporting Trump.
"Many of these voters gave President Trump a long runway well into the summer because they believed that he understands how business works better than they do and that his own fortune would eventually translate to enriching the country and their own finances," Margaret Talev, director of Syracuse University’s Institute for Democracy, Journalism, and Citizenship, told NBC on Monday.
"But as the year wore on, we have seen a shift among these voters collectively, cracks in their faith, more questioning, oscillating, or outright change of heart about Trump," Talev said. "What we almost never see is a wish for a do-over vote or a rush toward Democrats for the answer."
Keep ReadingShow Less
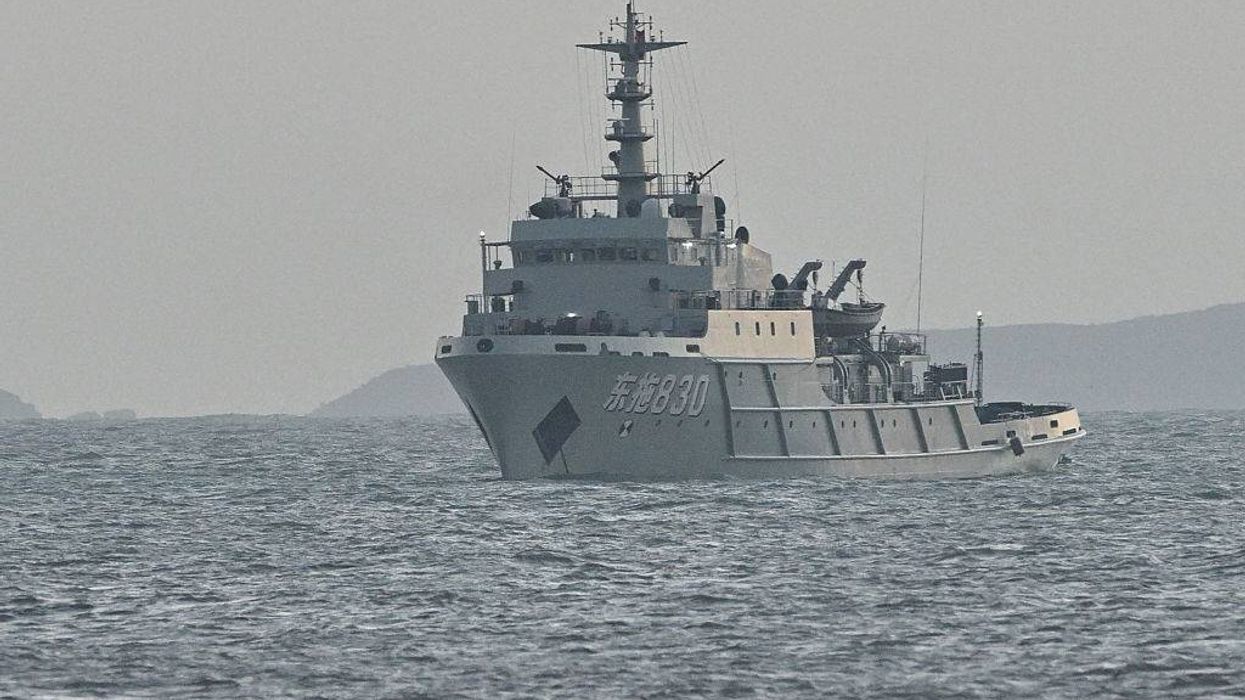
China Announces 'Major Military Drills' Around Taiwan in Wake of Massive US Arms Sale
The Chinese military drills appear to be "an effort to gain air and maritime superiority and cut off external military support" for Taiwan, said one expert.
Dec 29, 2025
The Chinese military on Monday announced it was conducting "major military drills" around Taiwan weeks after the US announced an $11 billion arms deal with the island nation.
As reported by CNN, China is mobilizing its army, navy, and air force units around Taiwan in a move that it says should serve as a "serious warning" to any "external" forces interfering with the island, which China has long claimed as its territory.
Taiwan's government, meanwhile, responded by accusing China of conducting a campaign of "military intimidation," while vowing to "take concrete action to defend the values of democracy and freedom."
Su Tzu-yun, a research fellow at the Institute for National Defense and Security Research in Taipei, told German broadcaster Deutsche Welle that China's military drills appear to be "an effort to gain air and maritime superiority and cut off external military support."
William Yang, a senior Northeast Asia analyst at the International Crisis Group think tank, told DW that while Chinese military exercises around Taiwan are now regular occurrences, the speed with which China ramped up its latest exercises "shows that the Chinese People's Liberation Army is becoming increasingly capable of rapidly deploying forces to combat-ready positions."
Although China did not mention the US directly when denouncing "external" powers, CNN noted that the decision to launch military drills came weeks after the US reached an $11 billion arms deal with Taiwan that included HIMARS rocket systems, anti-tank and anti-armor missiles, drones, howitzers, and military software.
China responded to this arms sale directly last week by announcing sanctions against US defense firms including Boeing, Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation, and L3Harris Maritime Services, according to the Guardian.
In announcing the sanctions against US firms, a Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson emphasized that "the Taiwan issue is the core of China's core interests and the first red line that cannot be crossed in China-US relations," while warning that "any provocative actions that cross the line on the Taiwan issue will be met with a strong response from China."
Keep ReadingShow Less
Most Popular