Global South Decries 'Weak' Progress on Climate Adaptation at COP28
"There are countries here with the capacity to ensure the outcome of this summit is historic for the right reasons," said Mary Robinson, chair of The Elders. "They need to lean in now with ambition and urgency."
With just two days left until the conclusion of the 28th United Nations Climate Change Conference in Dubai, climate justice advocates from the Global South on Sunday expressed alarm over the latest draft of the Global Goal on Adaptation, a document being negotiated at the summit as policymakers finalize an agreement on further progress that must be made to limit planetary heating.
African countries proposed a Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA) a decade ago, and a number of advocates warned Sunday that the document so far appears "vague," with insufficient financial pledges from fossil fuel-producing nations to help the Global South to adapt various sectors—including agriculture, water, and transportation—to the climate emergency.
"Across the world millions of people, most of whom are least responsible for carbon emissions, are attempting to adapt their lives and livelihoods to a distorted climate," wrote Mohamed Adow, founder and director of Power Shift Africa, at Climate Change News. "Although it isn't just about money, funding is important and severely lacking. The goal for 2023 was to raise $300 million for the Adaptation Fund, but at COP28 we've only seen $169 million in pledges, a mere 56% of the intended amount."
On social media, Simon Evans, deputy editor of Carbon Brief, provided an analysis of Sunday's draft, which he said was "very heavily qualitative, not quantitative" and includes only a "vague link to finance."
"Qualitative targets" in the text include "significantly reducing climate induced water scarcity" and "strengthening resilience"—phrases that "could mean almost anything," said Evans.
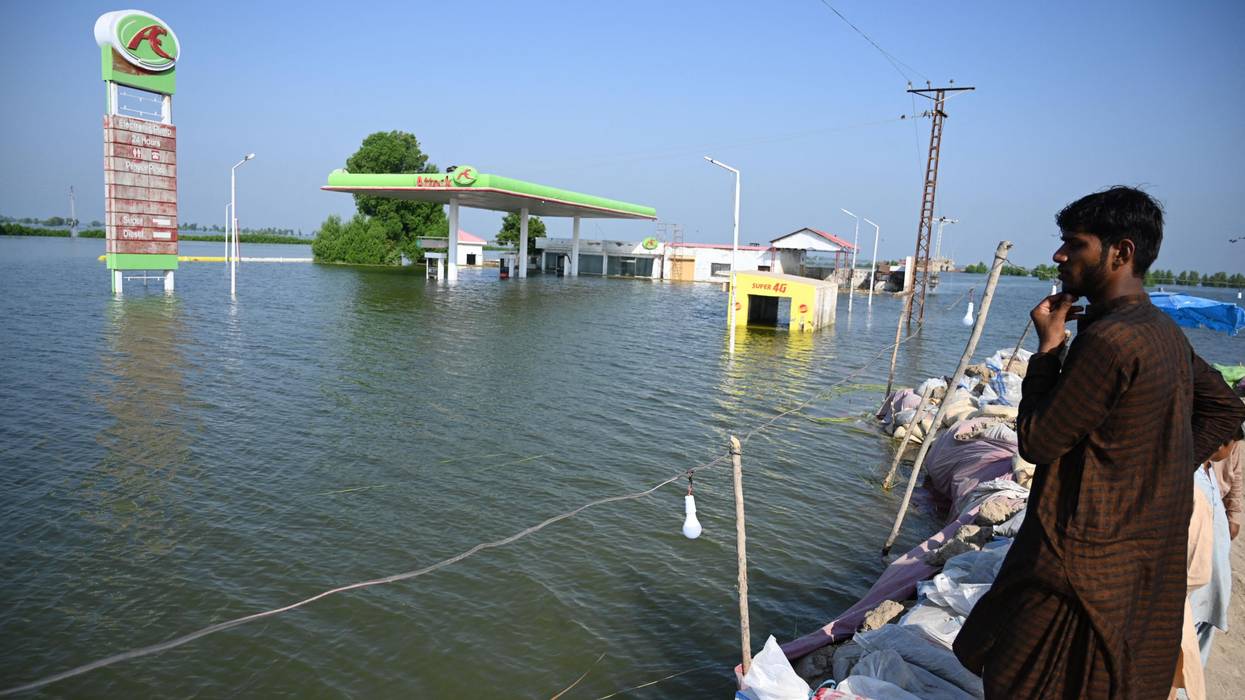
The draft reiterates an earlier call for wealthy nations to double adaptation finance by 2025, but only "urges" and "invites" governments to provide resources for developing countries that are disproportionately affected by climate-linked sea level rise, drought, and flooding—despite the fact that the entire continent of Africa is behind just 4% of planet-heating global greenhouse gas emissions.
The call to "urge" powerful countries to contribute meaningfully to a climate adaptation fund "is code for 'only if you feel like it, but no worries if you don't'," said Teresa Anderson, global climate justice lead for ActionAid.
"Overall, the text is weak and doesn't sufficiently address the aspiration for setting the required adaptation measures and indicators and mobilizing adaptation financing," said Adow.
The U.N. Environment Program said in November that between $215 billion and $387 billion is needed annually to help the Global South adapt their infrastructure to the climate crisis. In 2021, just $21 billion was provided.
While developed countries "have committed to at least double adaptation finance by 2025," said Obed Koringo of CARE Denmark, "a detailed roadmap is the only way to achieve this. This must set out what individual developed countries plan to provide by 2025 and how this adds up to $40 billion annually."
"It is disappointing to see that negotiations on adaptation are hurtling towards a damaging global failure," said Koringo. "We are afraid that it will have catastrophic consequences for communities on the frontlines of the climate crisis, especially in Africa... Failure to invest in adaptation, including early warning systems, flood defenses, and drought-resistant crops, will only increase the costs of loss and damage in the long run."
African policymakers this weekend also continued to sound alarms over the language being negotiated for the Global Stocktake (GST), the document that's expected to direct countries on how to proceed to limit planetary heating. Climate campaigners have joined experts in demanding a phaseout of fossil fuels, but European and American negotiators have pushed for language that would call only for a "phasedown," and fossil fuel-producing countries are demanding that the agreement address only "unabated" emissions—allowing for failed technical fixes like carbon capture instead of moving to reduce emissions altogether.
"Allowing 'abated' fossil fuels will mean developed countries which can afford expensive carbon capture technologies can keep expanding," chief Egyptian negotiator Mohamed Nasr told The Guardian.
Mary Robinson, chair of The Elders, called on governments including Saudi Arabia, the U.S., and the E.U to "abandon their subterfuge" and stop "obstructing a livable future."
"I fear COP28 is falling short of what is required to stay within the 1.5°C warming threshold. The science tells us we are in grave danger of bequeathing our children a completely unlivable world," said Robinson. "There are countries here with the capacity to ensure the outcome of this summit is historic for the right reasons. They need to lean in now with ambition and urgency. COP28 presents an opportunity for leaders to be on the right side of history."
"Governments must not leave this summit without an agreement to phase out all fossil fuels," she said, "and this agreement must not be at the expense of other critical workstreams here."