

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
In the end, the question is not whether a single post is offensive—it is whether we allow cycles of warranted outrage to consume the very attention required for collective survival.
The recent posted image by President Donald Trump depicting the Obamas as primates is unsurprising. This image represents what is believed, what is undoubtedly said behind closed doors. What remains unreal to me is that a sitting president flagrantly posted this. If the Republican Party does not denounce this, they are proclaiming what they truly value. Perhaps that's just as well: The racism has truly not been covert for some time. For so many, this is just another day at the office—another way racist ideology within the Republican Party asserts itself. In posting this, one must question whether the president is unhinged and strategic at the same time. I believe that, surely, he is laughing about just how much he is able to get away with, as befits his temperament and historically documented pattern of behavior.
Already, the White House defends the indefensible: White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt has publicly defended the president’s sharing of the video by framing it as a meme inspired by The Lion King—saying critics should stop what she calls “fake outrage” and focus on more important issues. The White House has repeatedly expressed that the imagery was taken from an internet meme meant to depict the president as “King of the Jungle” and Democrats as animal characters, not intended as racist content.
This disgusting portrayal is distraction while simultaneously challenging the masses to disbelieve what they see with their own eyes. Fascist politics often relies on propaganda and media spectacle to distract the public, undermine shared reality, and redirect attention away from policy consequences toward emotionally charged narratives (Stanley, 2018). This pushes any thinking person to ask, about what are the masses being distracted?
Advancements to curtail Immigration and Customs Enforcement seems the most apt and logical answer. Indeed, politicians must remain steadfast and resolved in their efforts to contain ICE. However, as an education environmental researcher, I am convicted to take a step back to examine the broader landscape and the long-term trends.
If distraction is the strategy, then sustained attention is resistance.
The planetary boundaries framework reminds us that Earth’s stability is shaped by interconnected systems—climate, biodiversity, water, land, and chemical cycles—whose disruption increases the risk of large-scale ecological destabilization. Seen in this light, the severe and lingering cold snaps recently experienced in the US Northeast do not contradict global warming but rather illustrate the volatility of a climate system pushed beyond its historical range of variability. As scientists note, destabilizing the climate system can intensify extremes across seasons, producing not only heatwaves but also disrupted jet streams, polar air incursions, and unusual persistence of cold events. Situating a regional cold spell within this broader planetary context reframes it from an isolated anomaly to a symptom of systemic strain: local weather variability unfolding against a backdrop of transgressed ecological limits. In other words, the discomfort and disruption of a harsh winter can be read as a lived reminder that Earth’s regulatory systems are under pressure, and that climatic instability—whether expressed as heat, cold, drought, or flood—is part of the same planetary story.
Despite overwhelming scientific consensus that climate change is real and accelerating, the current White House under President Trump has repeatedly signaled opposition to aggressive climate mitigation, undercutting efforts to address the crisis while publicly downplaying its urgency. At the United Nations General Assembly in September 2025, Trump referred to climate change as “the greatest con job ever perpetrated on the world,” dismissing expert predictions and climate science in broad terms even as global averages continue to rise and impacts intensify. Domestically, his administration has pursued policies that limit federal engagement in climate leadership—such as rescinding foundational greenhouse gas regulations by challenging the Environmental Protection Agency’s scientific endangerment finding and refusing to send senior officials to the COP30 climate summit—and rolling back environmental protections while promoting expanded fossil fuel extraction.
These actions illustrate a pattern of rhetoric and policymaking that accepts the existence of environmental change but rejects concerted governmental action to confront the climate crisis at the scale scientists say is necessary.
Unchecked climate change is already reshaping Earth’s systems in ways that pose severe risks to human and ecological well-being, often in counterintuitive ways. In the northeastern United States, unseasonably severe cold spells have contributed to fatalities and widespread disruption, reflecting how a destabilized climate system can produce more extreme and erratic weather patterns even as the planet warms overall. Scientific assessments show that critical components of the climate system—such as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a major ocean current system that redistributes heat around the globe—are showing signs of disruption associated with warming and freshwater influx from melting ice, with potential large-scale impacts on regional climates, precipitation patterns, and food security if thresholds are crossed. Researchers warn that such a weakening of ocean currents could intensify weather extremes and disrupt agricultural systems and ecosystems worldwide, compounding other alarming indicators like mass species loss and coral reef die-off under thermal stress.
Reflecting the convergence of climate change, geopolitical tension, and emerging technological risks, the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists has moved the symbolic Doomsday Clock closer to midnight than at any point in its history, signaling growing vulnerability to existential threats driven by human actions and inaction. As of the latest update, the clock stood at a historically high proximity to midnight—indicating an elevated sense of global peril tied in part to the accelerating impacts of climate change alongside nuclear and disruptive technologies—underscoring that societies worldwide have not yet mounted an adequate policy or governance response to the mounting evidence of planetary destabilization.
Far from being speculative or alarmist rhetoric, these warnings are grounded in measurable scientific trends that reveal cascading risks to ecosystems and societies, even as elites prepare for worst-case futures: Reports describe wealthy investors and defense planners expanding private bunkers and survival retreats in anticipation of climatic and geopolitical disruption, while the broader public’s attention is often diverted to the latest political scandal rather than sustained policy engagement with structural risks.
There is circumstantial evidence that the current White House is using distraction as a communication strategy, one consistent with well-studied political diversion tactics, but there is no direct proof that this is an intentionally orchestrated White House policy without formal investigation. Analysts and critics of Project 2025—the extensive conservative policy blueprint authored by the Heritage Foundation and many associates of this administration—have raised alarms about proposals that would restructure media oversight, diminish independent journalism, and alter technology and communications policies in ways that could reduce scrutiny of executive power, a move some see as creating fertile terrain for distraction over accountability.
Political commentators have documented how sensational statements and provocative posts often dominate headlines at the expense of in-depth coverage of systemic risks like climate change or immigration enforcement priorities, consistent with agenda-setting research showing how political actors can shift public attention.
Additionally, scholars studying messaging patterns around scandals suggest that shifts in provocative communications often occur simultaneously with increased media focus on crisis narratives, although establishing intentional coordination by an administration would require formal oversight or committee inquiry, not journalistic inference alone. In short, critics interpret these developments as strategic distraction tactics, but distinguishing intent from effect is a matter for official investigation and evidence beyond public reporting.
In the end, the question is not whether a single post is offensive—it is whether we allow cycles of warranted outrage to consume the very attention required for collective survival. Racism must be named and opposed wherever it appears, especially when amplified by the highest office, but we must also recognize when spectacle functions to fracture public focus. The climate crisis does not pause for political theater, nor do ecological thresholds wait for electoral cycles. If distraction is the strategy, then sustained attention is resistance. The work before us is to hold moral clarity and planetary reality together, refusing to let either be eclipsed by the churn of the news cycle, and insisting that democratic accountability includes safeguarding the conditions for life itself.
For agriculture as with energy, the real climate solutions are being silenced by the corporate cacophony.
I remember being filled with excitement when the Paris agreement to limit global warming to 1.5°C was adopted by nearly 200 countries at COP21. But after the curtains closed on COP29 last month—almost a decade later—my disenchantment with the event reached a new high.
As early as the 2010s, scientists from academia and the United Nations Environment Program warned that the U.S. and Europe must cut meat consumption by 50% to avoid climate disaster. Earlier COPs had mainly focused on fossil fuels, but meat and dairy corporations undoubtedly saw the writing on the wall that they too would soon come under fire.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet.
Animal agriculture accounts for at least 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, over quadruple the amount from global aviation. Global meat and dairy production have increased almost fivefold since the 1960s with the advent of industrialized agriculture. These factory-like systems are characterized by cramming thousands of animals into buildings or feedlots and feeding them unnatural grain diets from crops grown offsite. Even if all fossil fuel use was halted immediately, we would still exceed 1.5°C temperature rise without changing our food system, particularly our production and consumption of animal-sourced foods.
But climate change is just one of the threats we face. We have also breached five other planetary boundaries—biodiversity; land-use change; phosphorus and nitrogen cycling; freshwater use; and pollution from man-made substances such as plastics, antibiotics, and pesticides—all of which are also driven mainly by animal-sourced food production.
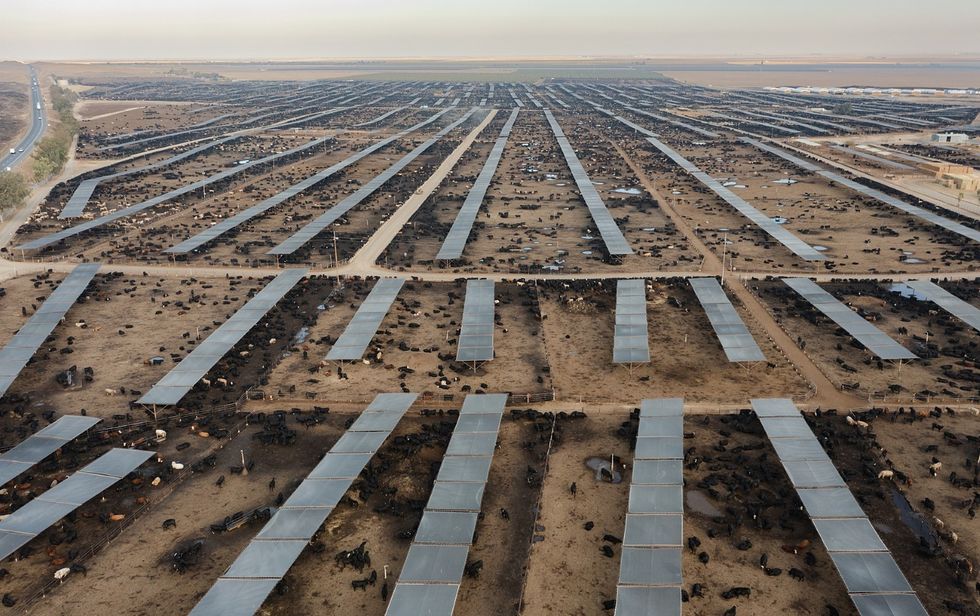
By the time world leaders were ready to consider our food system's impact on climate and the environment, the industrialized meat and dairy sector had already prepared its playbook to maintain the status quo. The Conference of Parties is meant to bring together the world's nations and thought leaders to address climate change. However, the event has become increasingly infiltrated by corporate interests. There were 52 delegates from the meat and dairy sector at COP29, many with country badges that gave them privileged access to diplomatic negotiations.
In this forum and others, the industry has peddled bombastic "solutions" under the guise of technology and innovation. Corporate-backed university research has lauded adding seaweed to cattle feed and turning manure lagoons the size of football fields into energy sources to reduce methane production. In Asia, companies are putting pigs in buildings over 20 stories tall, claiming the skyscrapers cut down on space and disease risks. And more recently, Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos started bankrolling research and development into vaccines that reduce the methane-causing bacteria found naturally in cows' stomachs. The industry hopes that the novelty and allure of new technologies will woo lawmakers and investors, but these "solutions" create more problems than they solve, exacerbating net greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, wildlife loss, and freshwater depletion.
Emissions from animal-sourced foods can be broadly divided into four categories: ruminant fermentation (cow burps); manure; logistics (transport, packaging, processing, etc.); and land-use change, i.e., the conversion of wild spaces into pasture, feedlots, and cropland for feed. In the U.S., ruminant fermentation and manure emit more methane than natural gas and petroleum systems combined.
A new report found that beef consumption must decline by over a quarter globally by 2035 to curb methane emissions from cattle, which the industry's solutions claim to solve without needing to reduce consumption. But the direct emissions from cattle aren't the only problem—beef and dairy production is also the leading driver of deforestation, which must decline by 72% by 2035, and reforestation must rise by 115%. About 35% of habitable land is used to raise animals for food or to grow their feed (mostly corn and soy), about the size of North and South America combined.

Put simply, the inadequate solutions put forth by Big Ag cannot outpace industrialized farming's negative impacts on the planet. While seaweed and methane vaccines may address cow burps, they don't address carbon emissions from deforestation or manure emissions of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas over 270 times more powerful than CO2. They also don't address the nitrate water pollution from manure, which can sicken people and cause massive fish kills and harmful algal blooms; biodiversity decline from habitat loss, which has dropped 73% since the rise of industrialized animal agriculture; freshwater use, drying up rivers and accounting for over a quarter of humanity's water footprint; or pesticide use on corn and soy feed, which kills soil microorganisms that are vital to life on Earth.
Skyscrapers, while solving some land-use change, do not consider the resources and the land used to grow animal feed, which is globally about equivalent to the size of Europe. They also don't address the inherent inefficiencies with feeding grain to animals raised for food. If fed directly to people, those grains could feed almost half the world's population. And while the companies using pig skyscrapers claim they enhance biosecurity by keeping potential viruses locked inside, a system failure could spell disaster, posing a bigger threat to wildlife and even humans.
We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple.
One solution that is gaining traction as an alternative to Big Ag's proposals is regenerative grazing. When done right, regenerative grazing eliminates the need for pesticides and leans into the natural local ecology, putting farm animals onto rotated pastures and facilitating carbon uptake into the soil. Regenerative animal agriculture is arguably the only solution put forward that addresses all six breached planetary boundaries as well as animal welfare and disease risk, and studies suggest it can improve the nutritional quality of animal-sourced foods. While it is imperative to transition from industrialized to regenerative systems, regenerative grazing comes with major caveats. This type of farming is only beneficial in small doses—cutting down centuries-old forests or filling in carbon-rich wetlands to make way for regenerative pastures would do much more climate and ecological harm than good. Soil carbon sequestration takes time and increases with vegetation and undisturbed soil, meaning that any regenerative pastures made today will never be able to capture as much carbon as the original natural landscape, especially in forests, mangroves, wetlands, and tundra. And while regenerative farmlands create better wildlife habitats than feedlots and monocultures, they still don't function like a fully natural ecosystem and food web. Also, cattle emit more methane than their native ruminant counterparts such as bison and deer.
Most notably, however, we simply don't have enough land to produce regeneratively raised animal products at the current consumption rate. Regenerative grazing requires more land than industrialized systems, sometimes two to three times more, and as mentioned the livestock industry already occupies over one-third of the world's habitable land. In all, we have much more to gain from rewilding crop- and rangeland than from turning the world into one big regenerative pasture.

All this brings us to one conclusion—the one that was made by scientists over a decade ago: We need to eat less meat. As Action Aid's Teresa Anderson noted at this year's COP, "The real answers to the climate crisis aren’t being heard over the corporate cacophony."
Scientific climate analyses over the last few years have been grim at best, and apocalyptic at worst. According to one of the latest U.N. reports, limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C (2.7°F) requires cutting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 57% by 2035, relative to 2023 emissions. However, current national policies—none of which currently include diet shifts—will achieve less than a 1% reduction by 2035. If the 54 wealthiest nations adopted sustainable healthy diets with modest amounts of animal products, they could slash their total emissions by 61%. If we also allowed the leftover land to rewild, we could sequester 30% of our global carbon budget in these nations and nearly 100% if adopted globally.
Our food system needs to be sustainable for all—people, animals, and our planet. Quick fixes and bandages will not save our planet from climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. We need both a monumental shift from industrialized agriculture to regenerative systems and a dramatic shift from animal-heavy diets to diets rich in legumes, beans, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, with meat and dairy as a specialty rather than a staple. As nations draft their policies for COP30, due early this year, we need leaders to adopt real food system solutions instead of buying into the corporate cacophony.
"Our updated diagnosis shows that vital organs of the Earth system are weakening, leading to... rising risks of crossing tipping points."
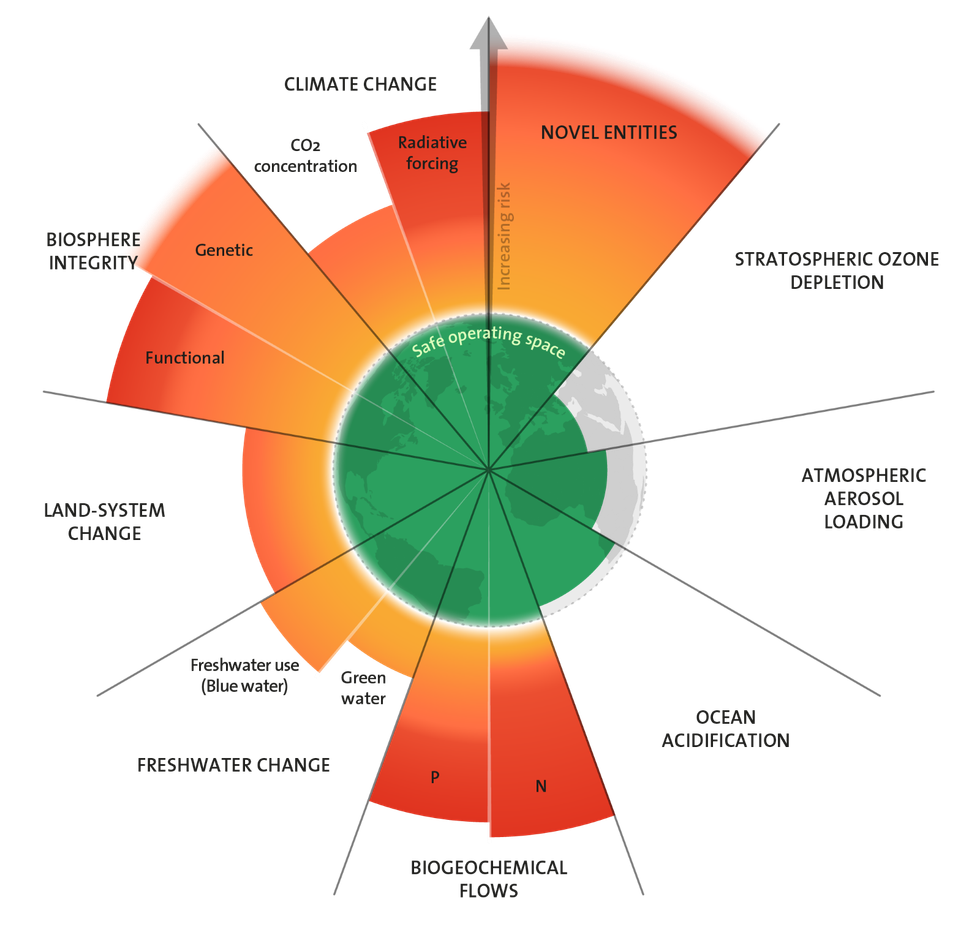
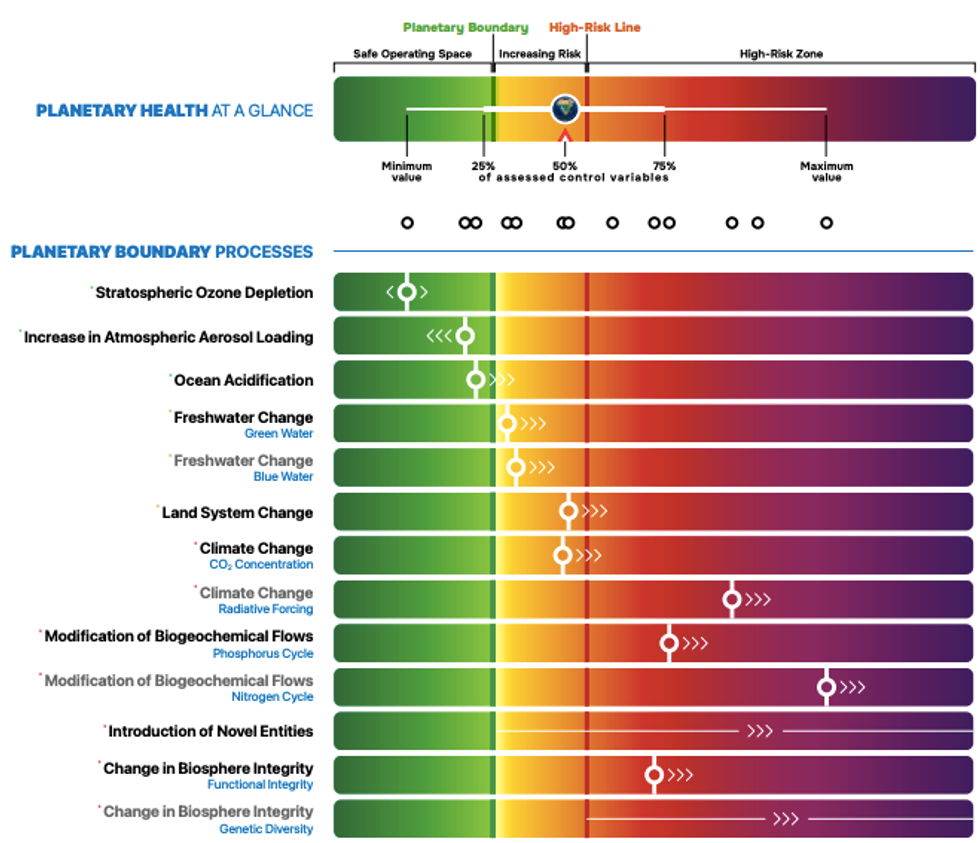
Six of nine planetary boundaries have already been transgressed, and a seventh, for ocean acidification, is on the verge of being breached, according to a major report released Monday.
The 96-page report, produced by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), is the first in a planned series of annual "planetary health checks."
The authors found that safe planetary boundaries had already been crossed for the climate, freshwater, land use, biogeochemical flows, novel entities, and biosphere integrity—in keeping with a study in Science Advances last year. They found a "clear trend towards further transgression"—moving deeper into the danger zone, where irreversible tipping points are more likely to be triggered—in each of the six categories.
"Our updated diagnosis shows that vital organs of the Earth system are weakening, leading to a loss of resilience and rising risks of crossing tipping points," Levke Caesar, a PIK climate physicist lead author of the report, said in a statement that announced a "red alert."
The health check also showed that ocean acidification, a seventh category, has reached a dangerous precipice, putting the foundations of the marine food web at risk. Ocean acidification, which can threaten coral reefs and phytoplankton populations, is caused by the buildup of carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels and other human activities.
Caesar said a "safe operating space" threshold for acidification could be crossed in the next few years.
"Looking at the current evolution, I'd say it’s really, really difficult to prevent that [boundary] crossing," she told Mongabay.
PIK director Johan Rockström, a co-author of the new report, helped develop planetary boundary research in the late 2000s. In a seminal 2009 paper in Nature, he and his co-authors found that three of the nine boundaries had already been crossed. That number has gradually gone up based on a series of studies over the last decade.
The planet boundary framework, which is often connected to the degrowth movement, emphasizes that the categories are interconnected.
"The interconnectedness of [planetary boundary] processes means that addressing one issue, such as limiting global warming to 1.5°C, requires tackling all of them collectively," the new report says.
Boris Sakschewski, a climate scientist who, along with Caesar, is a lead author of the report said that, "We know that all planetary boundary processes act together and each one needs protection to protect the whole system."
The consequences of continued ocean acidification, which is primarily measured by aragonite saturation, would be severe, the report warns.
Ocean acidification is approaching a critical threshold, with significant declines in surface aragonite saturation, particularly in high-latitude regions like the Arctic and Southern Ocean. These areas are vital for the marine carbon pump and global nutrient cycles, which support marine productivity, biodiversity, and global fisheries. The growing acidification poses an increasing threat to marine ecosystems, especially those reliant on calcium carbonate for shell formation.
Some researchers believe that the ocean acidification threshold has already been crossed, especially given regional variability, with cooler polar waters absorbing more carbon dioxide, causing a faster drop in pH levels.
The report was written with a general audience in mind and is not peer-reviewed, though it's based on peer-reviewed studies, the authors said.
The final pages of the report present solutions, especially agricultural. A radical overhaul of the global food system, heavily dependent on fertilizer and other harmful inputs, will be necessary to reverse the disturbing trends documented in the report, the authors wrote.
"Sometimes overlooked compared to the impacts of energy production and consumption—particularly the use of fossil fuels—the food systems we depend on are among the largest drivers of environmental degradation. The global food system is the single largest driver behind the transgression of multiple planetary boundaries," the report says.