The Roberts Court Will Be Remembered for Surrendering to Trump
Instead of healing divisions on the bench, Roberts and his Republican confederates old and new have issued a blistering succession of polarizing and reactionary majority opinions.
John Roberts came to the U.S. Supreme Court professing the best of intentions. In his 2005 Senate confirmation hearing, he promised to serve as chief justice in the fashion of a baseball umpire, calling only “balls and strikes, and not to pitch or bat.” Two years later, in an interview with law professor Jeffrey Rosen, he mused that the court’s many acrimonious 5-to-4 decisions could lead to “a steady wasting away of the notion of the rule of law” and ultimately undermine the court’s perceived legitimacy as a nonpartisan institution.
Roberts said that as the court’s leader, he would stress a “team dynamic,” encouraging his colleagues to join narrow, unanimous decisions rather than sweeping split rulings. “You do have to put [the Justices] in a situation where they will appreciate, from their own point of view, having the court acquire more legitimacy, credibility, that they will benefit from the shared commitment to unanimity in a way that they wouldn’t otherwise,” he reasoned.
Today, that reasoning is on the cutting-room floor. Although the court’s conservatives today outnumber its liberals by a 6-to-3 margin, the tribunal remains fractured and is widely regarded as just another political branch of government. According to a Reuters/Ipsos poll released in mid-June, neither Republicans nor Democrats see the nation’s top judicial body as neutral. Just 20% of respondents to the poll agreed that the Supreme Court is unbiased while 58% disagreed.
Instead of healing divisions on the bench, Roberts and his Republican confederates old and new, including three Justices nominated by Donald Trump, have issued a blistering succession of polarizing and reactionary majority opinions on voting rights, gerrymandering, union organizing, the death penalty, environmental protection, gun control, abortion, affirmative action, campaign finance, the use of dark money in politics, equality for LGBTQ+ people, and perhaps most disastrous of all, presidential immunity.
The challenges placed Roberts and his conservative benchmates in the uncomfortable but entirely predictable position of balancing the judiciary’s independence as a co-equal branch of government with their fundamental ideological support of Trump’s policy agenda.
The court’s reputation has also been tainted by a series of ethics scandals involving its two most right-wing members, Justices Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito, over the receipt of unreported gifts from Republican megadonors. Alito came under added fire for flying an American flag upside down (sometimes used as a symbol of distress at mostly left-wing protests) outside his Virginia home just a few months after the insurrection on January 6, 2021.
The court’s lurch to the far-right accelerated in the recently concluded 2024-2025 term, driven in large part by the immunity ruling—Trump v. United States, penned by Roberts himself—and the authoritarian power grab that it has unleashed. The decision effectively killed special counsel Jack Smith’s election-subversion case against Trump. It also altered the landscape of constitutional law and the separation of powers, endowing presidents with absolute immunity from prosecution for actions taken pursuant to their enumerated constitutional powers, such as pardoning federal offenses and removing executive officers from their departments; and presumptive immunity for all other “official acts” undertaken within the “outer perimeter” of their official duties.
Seemingly emboldened by the ruling, Trump has made good on his boast to be a “dictator on day one” of his second stint in the White House, releasing a torrent of executive orders and proclamations aimed at dismantling federal diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs; eviscerating environmental regulations; imposing sanctions on liberal law firms and elite universities; creating the so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE); authorizing mass deportations; and ending birthright citizenship under the Fourteenth Amendment, among dozens of other edicts.
Trump’s executive orders have generated a myriad of legal challenges, some of which reached the Supreme Court this past term as emergency, or “shadow docket,” appeals. The challenges placed Roberts and his conservative benchmates in the uncomfortable but entirely predictable position of balancing the judiciary’s independence as a co-equal branch of government with their fundamental ideological support of Trump’s policy agenda. By the term’s end, it was clear that ideology had won the day.
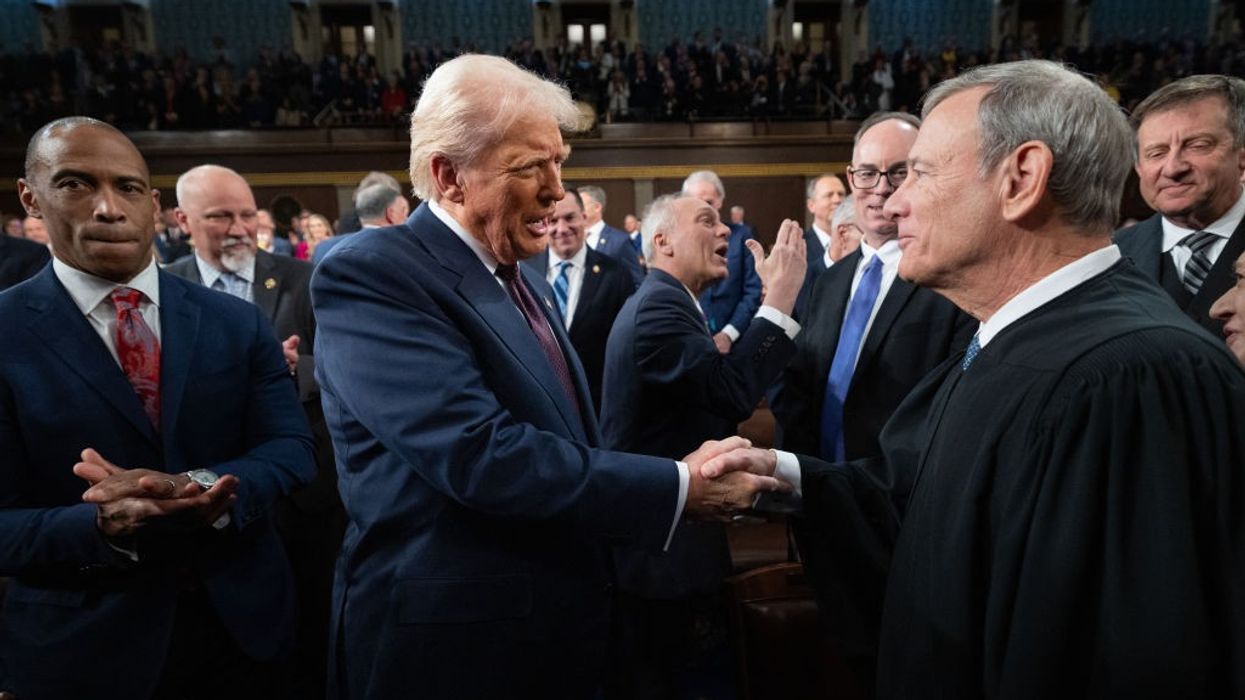
One of the first signs that Trump 2.0 would cause renewed headaches for the court occurred at the outset of the president’s March 4, 2025, address to a joint session of Congress. As he made his way to the podium, Trump shook hands with retired Justice Anthony Kennedy and with Justices Brett Kavanaugh, Amy Coney Barrett, and Elena Kagan. Nothing appeared out of the ordinary until he approached Chief Justice Roberts, whose hand he took, and with a pat on the shoulder could be heard saying, “Thank you again. Thank you again. Won’t forget.”
Whether Trump was thanking Roberts for his immunity ruling was ambiguous, but on March 18, Roberts was compelled to issue a rare public rebuke of the president after Trump called for the impeachment of U.S. District Judge James Boasberg for issuing two temporary restraining orders (TROs) that halted the deportation of alleged Venezuelan gang members under the Alien Enemies Act of 1798. “For more than two centuries, it has been established that impeachment is not an appropriate response to disagreement concerning a judicial decision. The normal appellate review process exists for that purpose,” Roberts said in a statement released by the court.
The rebuke, however, came too late to stop the removal of two planeloads of Venezuelans to El Salvador in apparent defiance of Boasberg’s TROs, sparking concerns that Trump might ultimately defy the high court as well, and trigger a full-scale constitutional crisis.
The deportation controversy, along with several others, quickly came before the Supreme Court. On April 7, by a 5-to-4 vote with Justice Barrett in dissent, the majority granted the administration’s request to lift Boasberg’s TROs and remove the cases for further proceedings to the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals, which covers Texas, where the named plaintiffs and other potential class members in the litigation (who had not yet been deported) were being detained under the Alien Enemies Act (AEA). The court’s four-page per curiam order (Trump v. J.G.G.) was unsigned, and, in a small defeat for the administration, also instructed that the detainees had the right to receive advance “notice and an opportunity to challenge their removal” by means of habeas corpus petitions.
In a related unsigned eight-page ruling (A.A.R.P. v. Trump) issued on May 16, this time by a 7-to-2 vote with Justices Thomas and Alito in dissent, the court blocked the administration from deporting alleged Venezuelan gang members held in northern Texas under the AEA, but also held that the detainees could be deported “under other lawful authorities.”
In another unsigned immigration decision released on April 10 (Noem v. Abrego Garcia), the court ordered the Trump administration to “facilitate” the return of Kilmar Armando Ábrego García, a resident of Maryland married to a U.S. citizen who had been sent to his native El Salvador because of an “administrative error.” Ábrego García was brought back to the United States in early June, and was indicted on charges of smuggling migrants and conspiracy.
The court waited until June 23 to release its most draconian immigration decision of the term (DHS v. D.V.D.), holding 6 to 3 that noncitizens under final orders of removal can be deported to third-party countries, even ones with records of severe human-rights violations. And on June 27, in a highly technical but very important procedural ruling (Trump v. CASA) on Trump’s birthright citizenship order, the court held 6 to 3 that district court judges generally lack the power to issue nationwide injunctions. Although the decision did not address the constitutionality of the executive order or the substantive scope of the 14th Amendment’s provision extending citizenship to virtually all persons born in the country, it sent three legal challenges to the order back to three district court judges who had blocked the order from taking effect. The litigation continues.
The immigration cases were decided on the court’s “shadow docket,” a term of art coined by University of Chicago professor William Baude in a 2015 law review article. It describes emergency appeals that come before the court outside of its standard “merits” docket that are typically resolved rapidly, without complete briefing, detailed opinions, or, except in the CASA case, oral arguments.
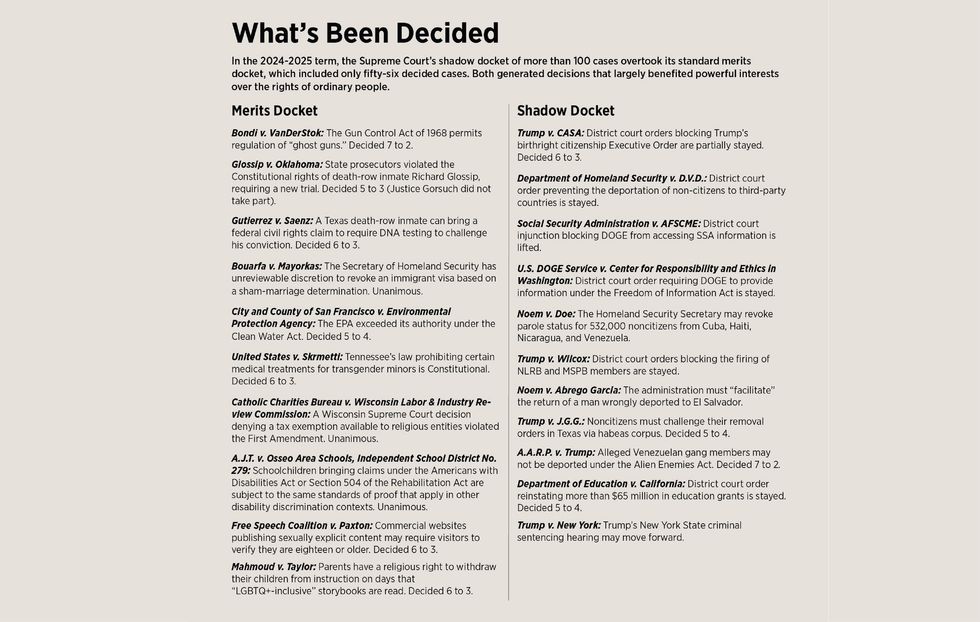
The Supreme Court has a long history of entertaining emergency appeals—such as last-minute requests for stays of execution in death penalty cases—but emergency requests in high-profile cases proliferated during Trump’s first presidency. According to Georgetown University law professor and shadow-docket scholar Steve Vladeck, the first Trump Administration sought emergency relief 41 times, with the Supreme Court granting relief in 28 of those cases. By comparison, the George W. Bush and Obama administrations filed a combined total of eight emergency relief requests over a16-year period while the Biden administration filed 19 applications across four years.
Fueled by Trump’s authoritarian overreach, the court’s shadow docket exploded to more than 100 cases in 2024-2025 while the merits docket shrank to 56. Not surprisingly, the upsurge has generated significant pushback, with a variety of critics contending the shadow docket diminishes the court’s already limited transparency, and yields hastily written and poorly reasoned decisions that are often used by the conservative wing of the bench to expand presidential power, essentially adopting the “unitary executive” theory as a basic principle of constitutional law. Popularized in the 1980s, the unitary theory posits that all executive power is concentrated in the person of the president, and that the president should be free to act with minimal congressional and judicial oversight.
Although shadow-docket rulings are preliminary in nature, they sometimes have the same practical effect as final decisions on the merits. For example, on May 22, in an unsigned two-page decision (Trump v. Wilcox), the Supreme Court stayed two separate judgments issued by two different U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia judges that had blocked the Trump administration from firing members of the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) and the Merit Systems Protection Board (MSPB) without cause. The decision remanded the cases back to the D.C. Circuit and the district courts, but even as the board members continue to litigate their unlawful discharge claims, they remain out of work.
Back on the merits docket, with Roberts at the helm and with Barrett and the conservatives united, the court has continued to tack mostly to the right, giving Trump nearly everything he wants.
Shadow-docket rulings also have an impact on Supreme Court precedents, often foreshadowing how the court will ultimately rule on the merits of important issues. The Wilcox decision called into question the precedential effect of Humphrey’s Executor v. United States, decided in 1935, which held that Congress has the constitutional power to enact laws limiting a president’s authority to fire executive officers of independent agencies like the NLRB, which oversees private-sector collective bargaining, and the MSPB, which adjudicates federal employee adverse-action claims.
The three appointed to the court by Democrats dissented. Writing for herself and Justices Sonia Sotomayor and Ketanji Brown Jackson, Justice Kagan accused the Republican-appointed majority of political bias and acting in bad faith. “For 90 years,” she charged, “Humphrey’s Executor v. United States... has stood as a precedent of this court. And not just any precedent. Humphrey’s undergirds a significant feature of American governance: bipartisan administrative bodies carrying out expertise-based functions with a measure of independence from presidential control.”
Quoting Alexander Hamilton, she added, “To avoid an arbitrary discretion in the courts, it is indispensable that they should be bound down by strict rules and precedents.” She castigated the majority for recklessly rushing to judgment, writing, “Our emergency docket, while fit for some things, should not be used to overrule or revise existing law.”
The court also issued other pro-Trump emergency shadow-docket rulings in the 2024-2025 term, permitting the administration to bar transgender people from serving in the military and to withhold $65 million in teacher training grants to states that include DEI initiatives in their operations and curriculums. The court similarly used shadow-docket rulings to endorse DOGE’s access to Social Security Administration records and to insulate DOGE from a Freedom of Information Act lawsuit brought by the watchdog group Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics in Washington (CREW).
Yet despite the court’s deference, Trump complained about his treatment at critical junctures throughout the term. After the shadow-docket ruling blocking deportations under the Alien Enemies Act in May, he took to Truth Social, his social media platform, writing in all caps, “THE SUPREME COURT WON’T ALLOW US TO GET CRIMINALS OUT OF OUR COUNTRY!” It also has been widely reported that Trump has raged in private against his own appointees—especially Justice Barrett—for not being sufficiently supportive of his executive orders and initiatives, and his personal interests.
Meanwhile, back on the merits docket, with Roberts at the helm and with Barrett and the conservatives united, the court has continued to tack mostly to the right, giving Trump nearly everything he wants. On June 18, Roberts delivered a resounding victory to the Make America Great Again movement with a 6-to-3 opinion (United States v. Skrmetti) that upheld Tennessee’s ban on gender transition medical care for minors. The decision will have wide-ranging implications for 26 other states that have enacted similar bans. Echoing the sentiments of many liberal legal commentators, Slate writer Mark Joseph Stern described the ruling as “an incoherent mess of contradiction and casuistry, a travesty of legal writing that injects immense, gratuitous confusion into the law of equal protection.”
In other high-stakes merits cases, the court, by a vote of 6 to 3, approved South Carolina’s plan to remove Planned Parenthood from its Medicaid program because of the group’s status as an abortion provider; and held 6 to 3 that parents have a religious right to withdraw their children from instruction on days that “LGBTQ+-inclusive” storybooks are read.
Progressives searching for a thin ray of hope for the future might take some solace in the spirited performance of Justice Jackson, the panel’s most junior member, who has become a dominant force in oral arguments, and a consistent voice in support of social justice. Dissenting from a 7-to-2 decision (Diamond Alternative Energy LLC v. Environmental Protection Agency) that weakened the Clean Air Act, she ripped the majority for giving “fodder to the unfortunate perception that moneyed interests enjoy an easier road to relief in this court than ordinary citizens.”
Eras of Supreme Court history are generally defined by the accomplishments of the court’s chief justices. The court of John Marshall, the longest-serving chief justice who held office from 1801 to 1835, is remembered for establishing the principle of judicial review in Marbury v. Madison. The Court of Earl Warren, whose tenure stretched from 1953 to 1969, is remembered for expanding constitutional rights and the landmark Brown v. Board of Education decision.
The Roberts Court will be remembered for reversing many of the Warren era’s advances. But unless it suddenly changes course, it will also be remembered as the court that surrendered its independence and neutrality to an authoritarian president.


