Powell "has a dual mandate," said Warren. "Yes, he is responsible for dealing with inflation, but he is also responsible for employment. And what Chair Powell is trying to do, and he has said fairly explicitly, is that they are trying to, in effect, slow down the economy so that, this is by the Fed's own estimate, two million people will lose their jobs. And I believe that is not what the chair of the Federal Reserve should be doing."
Since the Covid-19 pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine disrupted international supply chains—rendered fragile by decades of neoliberal globalization—powerful corporations in highly consolidated industries have taken advantage of these and other crises such as the bird flu outbreak to justify profit-boosting price hikes that far outpace the increased costs of doing business.
"Raising interest rates doesn't do anything to solve" a cost-of-living crisis driven primarily by "price gouging, supply chain kinks, [and] the war in Ukraine," Warren said Sunday. "All it does is put millions of people out of work."
"Jay Powell... has had two jobs. One is to deal with monetary policy, one is to deal with regulation. He has failed at both."
Powell, an ex-investment banker, was first appointed by then-President Donald Trump in 2018 and reappointed by Biden in 2021. Warren noted that she opposed Powell's nomination in both cases "because of his views on regulation and what he was already doing to weaken regulation."
"But I think he's failing in both jobs, both as the oversight and manager of these big banks, which is his job, and also what he's doing with inflation," said Warren.
Asked by Todd if Biden should fire Powell, Warren said: "My views on Jay Powell are well-known at this point. He has had two jobs. One is to deal with monetary policy, one is to deal with regulation. He has failed at both."
"Would you advise President Biden to replace him?" Todd inquired.
"I don't think he should be Chairman of the Federal Reserve," the Massachusetts Democrat responded. "I have said it as publicly as I know how to say it. I've said it to everyone."
Meanwhile, in a Saturday letter, Warren asked Richard Delmar, Tyler Smith, and Mark Bialek—respectively the deputy inspector general of the Treasury Department, acting inspector general of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and inspector general of the Fed's board of governors—to "immediately open a thorough, independent investigation of the causes of the bank management and regulatory and supervisory problems that resulted in this month's failure of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and Signature Bank (Signature) and deliver preliminary results within 30 days."
Until the Treasury Department, the Fed, and the FDIC "intervened to guarantee billions of dollars of deposits," the second- and third-biggest bank failures in U.S. history "threatened economic contagion and severe damage to the banking and financial systems," Warren noted. "The bank's executives, who took unnecessary risks or failed to hedge against entirely foreseeable threats, must be held accountable for these failures."
"But this mismanagement was allowed to occur because of a series of failures by lawmakers and regulators," Warren continued.
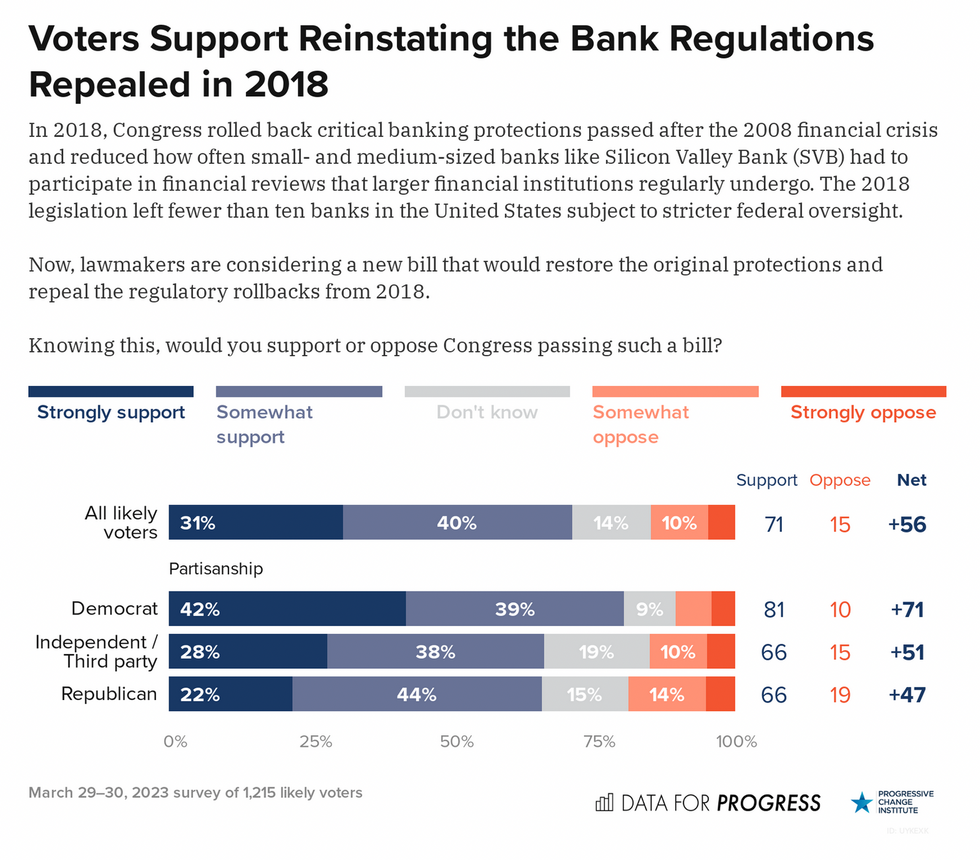
In 2018, several Democrats joined Republicans in approving Sen. Mike Crapo's (R-Idaho) Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act, which weakened the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act passed in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis. Crapo's deregulatory measure, signed into law by Trump, loosened federal oversight of banks with between $50 billion and $250 billion in assets—a category that includes SVB and Signature.
"As officials sought to develop a plan responding to SVB's failure, Chair Powell muzzled regulators from any public mention of the regulatory failures that occurred under his watch."
Moreover, the Fed under Powell's leadership "initiated key regulatory rollbacks," Warren wrote Saturday, echoing criticisms that she and financial industry watchdogs voiced earlier in the week. "And the banks' supervisors—particularly the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, which oversaw SVB—missed or ignored key signals about their impending failure."
It is "critical that your investigation be completely independent and free of influence from the bank executives or regulators that were responsible for action that led to these bank failures," Warren stressed. "I am particularly concerned that you avoid any interference from Fed Chair Jerome Powell, who bears direct responsibility for—and has a long record of failure involving—regulatory and supervisory matters involving these two banks."
"I have already asked Chair Powell to recuse himself from the Fed's internal investigation of this matter, but he has not yet responded to this request," wrote Warren. The progressive lawmaker said "this silence is troubling" in light of recent reporting that "as officials sought to develop a plan responding to SVB's failure, Chair Powell muzzled regulators from any public mention of the regulatory failures that occurred under his watch."
"Bank regulators and Congress must move quickly to close the gaps that allowed these bank failures to happen, and your investigation will provide us important insight as we take steps to do so," added Warren, who has introduced legislation to repeal a vital provision of the Trump-era bank deregulation law enacted five years ago with bipartisan support.
In appearances on three Sunday morning talk shows, Warren doubled down on her demands for an independent investigation into recent bank failures, stronger financial regulations, and punishing those responsible.
After lawmakers from both parties helped Trump fulfill his campaign promise to weaken federal oversight of the banking system, Powell "took a flamethrower to the regulations, saying, 'I'm doing this because Congress let me do it,'" Warren told ABC's "This Week" co-anchor Jonathan Karl. "And what happened was exactly what we should have predicted, and that is the banks, these big, multi-billion-dollar banks, loaded up on risk; they boosted their short-term profits; they gave themselves huge bonuses and big salaries; and they exploded their banks."
"When you explode a bank, you ought to be banned from banking forever."
"When you explode a bank, you ought to be banned from banking forever," said Warren, who acknowledged that criminal charges could be coming. "The Department of Justice has opened an investigation. I think that's appropriate for them to do. We'll see where the facts take them. But we've got to take a close look at this."
Not only did former SVB chief executive officer Greg Becker, who lobbied aggressively for the 2018 bank deregulation law, sell millions of dollars of shares as recently as late last month, but until federal regulators took control of the failed bank on March 10, he was on the board of directors at the San Francisco Fed—the institution responsible for overseeing SVB.
On Saturday, Independent Sen. Bernie Sanders of Vermont announced that he plans to introduce legislation "to end this conflict of interest by banning big bank CEOs from serving on Fed boards."
"We've got to say overall that we can't keep repeating this approach of weakening the regulation over the banks, then stepping in when these giant banks get into trouble," Warren said Sunday, arguing for stronger federal oversight to prevent the need for bailouts.