

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

This handout photo from the CFA Wandong Fire Brigade, posted on their Facebook page on January 7, 2026, and released on January 8, shows a bushfire burning near the town of Longwood, northern Victoria.
"Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition."
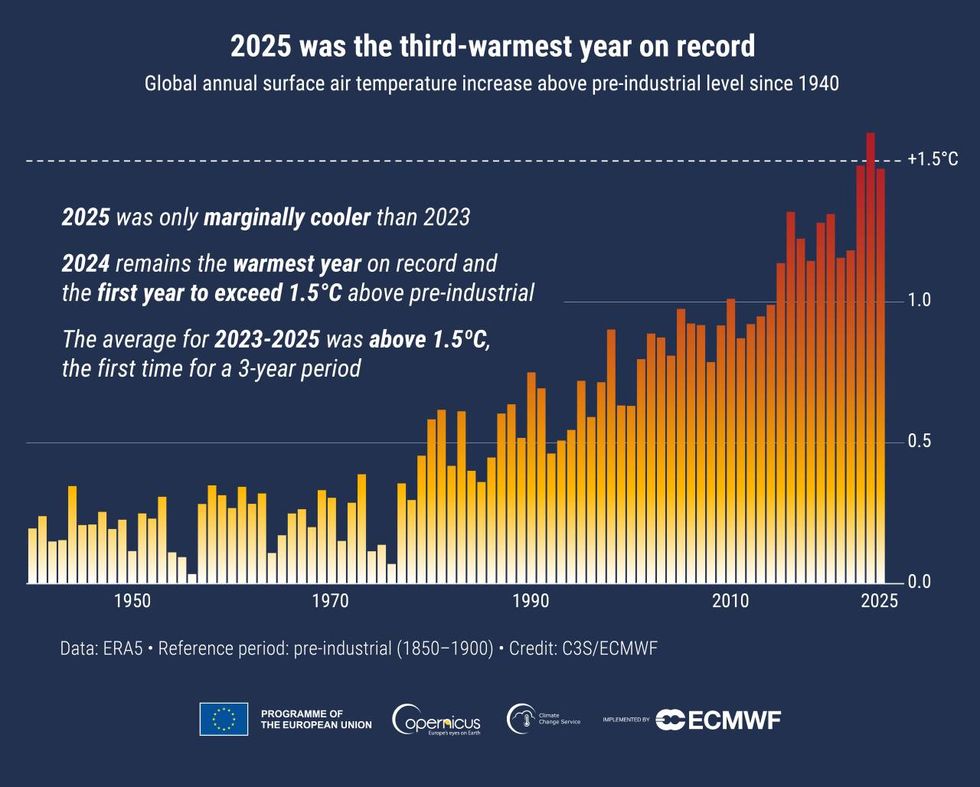
Increasing fossil fuel extraction helped make 2025 the third-hottest year on record and marked the third straight year of “extraordinary global temperatures,” according to a major new report on the climate crisis.
On Wednesday, the European Union's Copernicus climate agency published a report based on data from climate-monitoring organizations, including NASA and the World Meteorological Organization.
Based on billions of weather readings from satellites, ships, aircraft, and weather stations, the report found that, for the first time in recorded history, global temperatures over a three-year period have exceeded the critical threshold of 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
At current rates of heating, the report found, the Earth could surpass the Paris Climate Accord’s target of 1.5°C on a long-term basis by 2030, more than a decade sooner than scientists' projection when nations negotiated the pledge to reduce emissions back in 2015.
“Atmospheric data from 2025 paints a clear picture: Human activity remains the dominant driver of the exceptional temperatures we are observing,” said Laurence Rouil, the director of Copernicus’ Atmosphere Monitoring Service. “Atmospheric greenhouse gases have steadily increased over the last 10 years.”
As with previous years, 2025 was marked by a series of disasters fueled by rising temperatures: From a historic heatwaves that killed an estimated 24,000 people in Europe, to typhoons across Asia that displaced millions, to the wildfires that ravaged the Los Angeles area roughly a year ago and were one of a record 23 disasters in the US that exceeded more than a billion dollars in damage.
The Copernicus report was released as Australia suffered what DW News called possibly its "first megafire of the climate change age" in Victoria, which had charred over 350,000 hectares (more than 864,000 acres) of land as of Sunday and forced thousands to flee their homes.
(Video: Sky News Australia)
"Extreme weather isn’t rare anymore—it’s driving up food prices, insurance premiums, water shortages, and upending daily life across the globe," said Savio Carvalho, the managing director for campaigns and networks for the climate activist group 350. "Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition. We don’t have the luxury of wasting time or taking side paths—we are running out of time."
The past year was marked by yet more disappointment for those hoping to see collective global action to reduce carbon emissions.
The most glaring setbacks occurred in the United States—the globe's largest historic polluter—where President Donald Trump has virtually halted renewable energy expansion, pushed to crank up fossil fuel extraction, and sought to end the "endangerment finding" that allows carbon emissions to be regulated on the basis of their harm to the climate.
But even in the absence of Trump, the past year's global climate summit in Brazil, COP30, once again fell well short of a cohesive international action plan, ending with no global agreement to wind down the use of oil, gas, and coal. Eighty nations failed to submit global emissions pledges, and many of those that did failed to make commitments that would likely bend the global temperature curve in a favorable direction.
Where scientists once urged nations to take swift action in the hope of passing the 1.5°C tipping point, Carlo Buontempo, the director of Copernicus, said following Wednesday's report that "we are bound to pass it."
He said, "The choice we now have is how to best manage the inevitable overshoot and its consequences on societies and natural systems."
But an overshoot is intolerable to many on the front lines of the crisis.
"In the Pacific, climate disasters are costing us billions of dollars in recovery and rebuilding," said Fenton Lutunatabua, 350's program manager for the Pacific and Caribbean. "A world beyond 1.5°C would devastate our resources even more."
"Entire villages in Fiji are being uprooted and relocated, losing connection to traditional lands and fishing grounds," he added. "Atoll nations like Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands are grappling with both adaptation and addressing the reality of potential forced migration. To give up on 1.5°C is to say that any of these realities is acceptable."
In Indonesia, where unprecedented flash floods in November killed 1,100 people, Suriadi Darmoko, an activist in Bali who is suing his government following an International Court of Justice ruling allowing states to be held legally accountable over climate harms, agreed that complacency is not an option.
“Entire communities are still buried in mud. Thousands of families are still grieving and struggling to have their basic needs met. We refuse to be treated as mere climate disaster victims," he said. "Our leaders have kept the world hooked on fossil fuels even as they knew decades ago it would lead to such tragedies."
Carvalho, too, rejected the notion that extreme warming is something the Earth must accept. Despite setbacks to collective action, 2025 also saw certain actors on the global stage make great strides toward a renewable future.
In large part due to massive investments by China, renewable sources generated more power worldwide than coal for the first time, and solar energy generation grew by 31% in the first half of the year, outpacing demand growth.
"We need to do what’s right now: a global phase out of fossil fuels is urgent," said Carvalho. "We already have the renewable energy solutions we need—what’s missing is the political will. We can prevent the worst if we act now."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
Increasing fossil fuel extraction helped make 2025 the third-hottest year on record and marked the third straight year of “extraordinary global temperatures,” according to a major new report on the climate crisis.
On Wednesday, the European Union's Copernicus climate agency published a report based on data from climate-monitoring organizations, including NASA and the World Meteorological Organization.
Based on billions of weather readings from satellites, ships, aircraft, and weather stations, the report found that, for the first time in recorded history, global temperatures over a three-year period have exceeded the critical threshold of 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
At current rates of heating, the report found, the Earth could surpass the Paris Climate Accord’s target of 1.5°C on a long-term basis by 2030, more than a decade sooner than scientists' projection when nations negotiated the pledge to reduce emissions back in 2015.
“Atmospheric data from 2025 paints a clear picture: Human activity remains the dominant driver of the exceptional temperatures we are observing,” said Laurence Rouil, the director of Copernicus’ Atmosphere Monitoring Service. “Atmospheric greenhouse gases have steadily increased over the last 10 years.”

As with previous years, 2025 was marked by a series of disasters fueled by rising temperatures: From a historic heatwaves that killed an estimated 24,000 people in Europe, to typhoons across Asia that displaced millions, to the wildfires that ravaged the Los Angeles area roughly a year ago and were one of a record 23 disasters in the US that exceeded more than a billion dollars in damage.
The Copernicus report was released as Australia suffered what DW News called possibly its "first megafire of the climate change age" in Victoria, which had charred over 350,000 hectares (more than 864,000 acres) of land as of Sunday and forced thousands to flee their homes.
(Video: Sky News Australia)
"Extreme weather isn’t rare anymore—it’s driving up food prices, insurance premiums, water shortages, and upending daily life across the globe," said Savio Carvalho, the managing director for campaigns and networks for the climate activist group 350. "Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition. We don’t have the luxury of wasting time or taking side paths—we are running out of time."
The past year was marked by yet more disappointment for those hoping to see collective global action to reduce carbon emissions.
The most glaring setbacks occurred in the United States—the globe's largest historic polluter—where President Donald Trump has virtually halted renewable energy expansion, pushed to crank up fossil fuel extraction, and sought to end the "endangerment finding" that allows carbon emissions to be regulated on the basis of their harm to the climate.
But even in the absence of Trump, the past year's global climate summit in Brazil, COP30, once again fell well short of a cohesive international action plan, ending with no global agreement to wind down the use of oil, gas, and coal. Eighty nations failed to submit global emissions pledges, and many of those that did failed to make commitments that would likely bend the global temperature curve in a favorable direction.
Where scientists once urged nations to take swift action in the hope of passing the 1.5°C tipping point, Carlo Buontempo, the director of Copernicus, said following Wednesday's report that "we are bound to pass it."
He said, "The choice we now have is how to best manage the inevitable overshoot and its consequences on societies and natural systems."
But an overshoot is intolerable to many on the front lines of the crisis.
"In the Pacific, climate disasters are costing us billions of dollars in recovery and rebuilding," said Fenton Lutunatabua, 350's program manager for the Pacific and Caribbean. "A world beyond 1.5°C would devastate our resources even more."
"Entire villages in Fiji are being uprooted and relocated, losing connection to traditional lands and fishing grounds," he added. "Atoll nations like Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands are grappling with both adaptation and addressing the reality of potential forced migration. To give up on 1.5°C is to say that any of these realities is acceptable."
In Indonesia, where unprecedented flash floods in November killed 1,100 people, Suriadi Darmoko, an activist in Bali who is suing his government following an International Court of Justice ruling allowing states to be held legally accountable over climate harms, agreed that complacency is not an option.
“Entire communities are still buried in mud. Thousands of families are still grieving and struggling to have their basic needs met. We refuse to be treated as mere climate disaster victims," he said. "Our leaders have kept the world hooked on fossil fuels even as they knew decades ago it would lead to such tragedies."
Carvalho, too, rejected the notion that extreme warming is something the Earth must accept. Despite setbacks to collective action, 2025 also saw certain actors on the global stage make great strides toward a renewable future.
In large part due to massive investments by China, renewable sources generated more power worldwide than coal for the first time, and solar energy generation grew by 31% in the first half of the year, outpacing demand growth.
"We need to do what’s right now: a global phase out of fossil fuels is urgent," said Carvalho. "We already have the renewable energy solutions we need—what’s missing is the political will. We can prevent the worst if we act now."
Increasing fossil fuel extraction helped make 2025 the third-hottest year on record and marked the third straight year of “extraordinary global temperatures,” according to a major new report on the climate crisis.
On Wednesday, the European Union's Copernicus climate agency published a report based on data from climate-monitoring organizations, including NASA and the World Meteorological Organization.
Based on billions of weather readings from satellites, ships, aircraft, and weather stations, the report found that, for the first time in recorded history, global temperatures over a three-year period have exceeded the critical threshold of 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
At current rates of heating, the report found, the Earth could surpass the Paris Climate Accord’s target of 1.5°C on a long-term basis by 2030, more than a decade sooner than scientists' projection when nations negotiated the pledge to reduce emissions back in 2015.
“Atmospheric data from 2025 paints a clear picture: Human activity remains the dominant driver of the exceptional temperatures we are observing,” said Laurence Rouil, the director of Copernicus’ Atmosphere Monitoring Service. “Atmospheric greenhouse gases have steadily increased over the last 10 years.”

As with previous years, 2025 was marked by a series of disasters fueled by rising temperatures: From a historic heatwaves that killed an estimated 24,000 people in Europe, to typhoons across Asia that displaced millions, to the wildfires that ravaged the Los Angeles area roughly a year ago and were one of a record 23 disasters in the US that exceeded more than a billion dollars in damage.
The Copernicus report was released as Australia suffered what DW News called possibly its "first megafire of the climate change age" in Victoria, which had charred over 350,000 hectares (more than 864,000 acres) of land as of Sunday and forced thousands to flee their homes.
(Video: Sky News Australia)
"Extreme weather isn’t rare anymore—it’s driving up food prices, insurance premiums, water shortages, and upending daily life across the globe," said Savio Carvalho, the managing director for campaigns and networks for the climate activist group 350. "Governments know fossil fuels are the cause of climate breakdown, yet they keep stalling on the transition. We don’t have the luxury of wasting time or taking side paths—we are running out of time."
The past year was marked by yet more disappointment for those hoping to see collective global action to reduce carbon emissions.
The most glaring setbacks occurred in the United States—the globe's largest historic polluter—where President Donald Trump has virtually halted renewable energy expansion, pushed to crank up fossil fuel extraction, and sought to end the "endangerment finding" that allows carbon emissions to be regulated on the basis of their harm to the climate.
But even in the absence of Trump, the past year's global climate summit in Brazil, COP30, once again fell well short of a cohesive international action plan, ending with no global agreement to wind down the use of oil, gas, and coal. Eighty nations failed to submit global emissions pledges, and many of those that did failed to make commitments that would likely bend the global temperature curve in a favorable direction.
Where scientists once urged nations to take swift action in the hope of passing the 1.5°C tipping point, Carlo Buontempo, the director of Copernicus, said following Wednesday's report that "we are bound to pass it."
He said, "The choice we now have is how to best manage the inevitable overshoot and its consequences on societies and natural systems."
But an overshoot is intolerable to many on the front lines of the crisis.
"In the Pacific, climate disasters are costing us billions of dollars in recovery and rebuilding," said Fenton Lutunatabua, 350's program manager for the Pacific and Caribbean. "A world beyond 1.5°C would devastate our resources even more."
"Entire villages in Fiji are being uprooted and relocated, losing connection to traditional lands and fishing grounds," he added. "Atoll nations like Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands are grappling with both adaptation and addressing the reality of potential forced migration. To give up on 1.5°C is to say that any of these realities is acceptable."
In Indonesia, where unprecedented flash floods in November killed 1,100 people, Suriadi Darmoko, an activist in Bali who is suing his government following an International Court of Justice ruling allowing states to be held legally accountable over climate harms, agreed that complacency is not an option.
“Entire communities are still buried in mud. Thousands of families are still grieving and struggling to have their basic needs met. We refuse to be treated as mere climate disaster victims," he said. "Our leaders have kept the world hooked on fossil fuels even as they knew decades ago it would lead to such tragedies."
Carvalho, too, rejected the notion that extreme warming is something the Earth must accept. Despite setbacks to collective action, 2025 also saw certain actors on the global stage make great strides toward a renewable future.
In large part due to massive investments by China, renewable sources generated more power worldwide than coal for the first time, and solar energy generation grew by 31% in the first half of the year, outpacing demand growth.
"We need to do what’s right now: a global phase out of fossil fuels is urgent," said Carvalho. "We already have the renewable energy solutions we need—what’s missing is the political will. We can prevent the worst if we act now."