August, 29 2013, 10:17am EDT
Development Aid Falls Short, While Other Financial Flows Show Rising Volatility
New Worldwatch Institute trend examines international aid flows
WASHINGTON
As the world approaches its 2015 deadline for achieving the Millennium Development Goals outlined in 2000, development aid by the 26 members of the Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development declined in 2012 for the second year. Preliminary data indicate that official development assistance (ODA) totaled $128.4 billion (in 2011 dollars) that year, down 4 percent from 2011's $133.7 billion. The 2012 figure marks a 6 percent decline from 2010, when global ODA peaked at $136.7 billion, write Worldwatch staff in the latest Vital Signs Online trend (www.worldwatch.org).
The United States provided the largest amount of ODA, with a total of $29.9 billion in 2012, which was 23.3 percent of the DAC total. Trailing the United States are the United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Japan. When tracking ODA as a percentage of gross national income (GNI), however, a different picture emerges. Since 1970 the United Nations has set 0.7 percent of GNI as the target for ODA: in 2012, only Luxembourg, Sweden, Norway, and Denmark exceeded this target. In comparison, the U.S. figure was only 0.19 percent. Not surprisingly, given the severity of the Eurozone crisis, the 15 European Union members of DAC decreased their assistance by a total of 7.4 percent, with the most severe cuts coming from Spain, Italy, Greece, and Portugal.
It should be noted that DAC governments are not the only ones that provide development assistance: according to a 2012 UN report, non-DAC countries donated a total of $7.2 billion in development aid in 2010, with Saudi Arabia providing almost half of the total. Furthermore, assistance from private sources was estimated at $56 billion that same year, but reporting on such flows is much weaker than for government funds.
Humanitarian assistance, or short-term aid provided in response to disasters and humanitarian crises, is a numerically small but highly visible portion of ODA. Preliminary data indicate that in 2012 assistance provided by governments for such purposes fell 6.5 percent from the previous year, from $13.8 billion to $12.9 billion. (When including non-governmental sources, humanitarian aid fell by 7.7 percent.) This decline is not totally unexpected, as many of the world's leading economies are still recovering from the financial crisis. Also, in 2012 the United Nations categorized 76 million people as in need of humanitarian assistance, fewer than the 93 million in 2011.
"ODA is far from the only mechanism of international capital flows to or from developing countries and emerging markets," said Cameron Scherer, report co-author and program associate at Internews. "A multitude of vehicles----private and public, bilateral and multilateral----fill the global finance landscape. And against this broader canvas, ODA involves relatively small amounts of money."
Among public funds, outflows have actually exceeded inflows into developing countries and emerging markets for most of the past decade. According to the International Monetary Fund, net outflows of more than $180 billion in 2006 turned into net inflows of close to $140 billion in 2009, but by 2012 there was once again a net outflow of close to $42 billion.
Among private flows, the largest amounts are accounted for by foreign direct investment (FDI). Net FDI rose from under $100 billion per year in the 1980s and early 1990s to a peak of $480 billion in 2008. The financial crisis then caused a dip to $335 billion in 2009, but 2011 saw a recovery to $473 billion. The bulk of FDI flowing to developing countries is going to Asia and Latin America. In East Asia and South Asia, almost 90 percent of FDI goes to China and India; in Latin America and the Caribbean, about half goes to Brazil. Only 10 percent of global FDI is destined for Africa.
"In general, FDI is more stable than other forms of private investments, especially where "greenfield" investments in new productive capacity are concerned, FDI is usually undertaken with a longer time horizon in mind, and happens mostly where macroeconomic conditions are stable," said Michael Renner, trend co-author and Worldwatch Senior Researcher. "In contrast, portfolio investment and cross-border interbank lending are often driven by short-term considerations such as changes in interest rates."
However, the United Nations points to evidence that a growing portion of FDI in recent years is going to investments in financial companies or to intra-company debt. Also, a considerable portion of FDI relates to mergers and acquisitions----and thus represents a transfer of ownership rather than fresh investment. These shifts imply that capital can be moved more easily among countries, and indeed the share of short-term and more volatile financial FDI flows has increased.
Further highlights from the report:
The United States tops the list of assistance in absolute amounts, with $3.8 billion in 2012, or 29.4 percent of all humanitarian aid (a number that was $483 million below the figure in 2011). Luxembourg (at 0.16 percent of GNI) and Sweden (at 0.14 percent) top the relative standings.
In 2011, the most recent year for which data are available, Pakistan, Somalia, and the West Bank and Gaza Strip were the three areas to receive the greatest amount of humanitarian assistance, together taking in over a quarter of global assistance.
In 2002, FDI to Africa stood at just $15 billion; in 2012, it totaled $50 billion, having peaked at $59 billion in 2008. China is behind much of this FDI, providing at least $14.7 billion in 2011.
The Worldwatch Institute was a globally focused environmental research organization based in Washington, D.C., founded by Lester R. Brown. Worldwatch was named as one of the top ten sustainable development research organizations by Globescan Survey of Sustainability Experts. Brown left to found the Earth Policy Institute in 2000. The Institute was wound up in 2017, after publication of its last State of the World Report. Worldwatch.org was unreachable from mid-2019.
LATEST NEWS
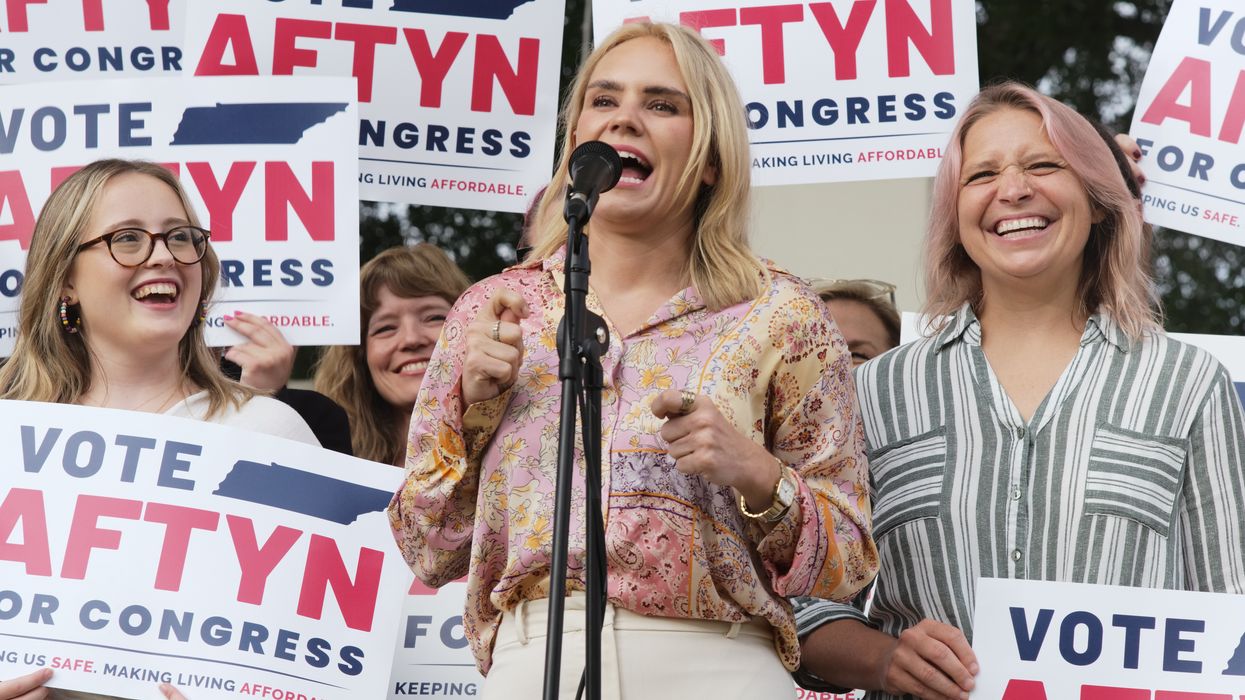
AOC Rallies for Progressive Aftyn Behn in Surprisingly Close Race in Tennessee's Trump Country
Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez said the tight race shows that "people are increasingly recognizing that our fights are not left and right, but they are top and bottom. They are about all of us as working Americans."
Dec 02, 2025
Just over a year after President Donald Trump carried Tennessee's 7th District by more than 20 points, US Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez said Monday night that the final polls in the district's special election race between a Trump ally and a progressive state lawmaker are "a testament to how the American people are feeling in this moment."
Ocasio-Cortez (D-NY) was speaking at a virtual get-out-the-vote rally for state Rep. Aftyn Behn (D-51), who is facing GOP candidate Matt Van Epps in the district in Tuesday's special election. GOP Rep. Mark Green stepped down earlier this year for a private sector job after winning by 21 percentage points last year.
The electoral history of the district would suggest that Republicans could expect to easily win Tuesday's election, but with Van Epps ahead by just one or two percentage points in recent polling, Trump, House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-La.), and other Republicans are signaling fears that Behn could pull off an upset.
The president attacked Behn in a social media post Monday, warning that only Van Epps "cherishes Christianity and Country Music."
Like other progressive candidates in this year's elections, Behn has focused heavily on the need to make life more affordable for residents in the district, which was gerrymandered by state Republicans in 2022. The GOP eliminated a Democratic district in Nashville and its voters were added to three Republican districts, but Behn has worked to mobilize voters in predominantly Black areas that were added to the 7th District and told canvassers Monday evening that the redistricting scheme "backfired" on the Republicans.
AFTYN: “Clearly I’m living rent-free in President Trump’s mind.”
JUST NOW IN FRANKLIN — Rep. @aftynfortn Behn gave a pep talk to a group of fired up canvassers on the eve of an unexpectedly tight #TN7 special election.
(And a group hug) pic.twitter.com/1e0sNmNHEd
— The Tennessee Holler (@TheTNHoller) December 1, 2025
Behn has focused on high prices during the campaign, attacking Trump's tariff policies and decrying the One Big Beautiful Bill Act's cuts to Medicaid and nutrition assistance—calling the law the "Big Bullshit Bill."
"This is a wake-up call," she said after the law passed in July. "If we don't bring change to Congress, the billionaires and bought-out politicians will continue to rig the system against us."
As a state lawmaker, Behn proposed the Homes, Not Hedge Funds bill to stop private equity firms from buying up neighborhoods and advocated "for fair funding for rural communities" with her Rural Prosperity Act.
She's also spoken out and organized on the ground against Trump's mass deportation operation, which she's called a "flagrant abuse of power and state-sanctioned violence."
At the virtual rally on Monday night, Ocasio-Cortez said Behn's decision to take on a Trump-backed opponent in a heavily Republican district "takes a special kind of guts."
"That kind of guts is what we need more of in this country," she said. "A kind of person that says, 'We're not gonna do something because it's easy, we're gonna do it because it's the right thing to do.' And she is leading by putting herself on the line and raising her hand up first to say, 'I am going to fight for my neighbors no matter the odds.'"
🔥 WATCH — @AOC: “Tennessee is ready to elect @aftynfortn Behn. Miracles can happen… to run in an R+22 seat takes a very special kind of person with a very special kind of guts. That the race is so tight is a testament to how the 🇺🇸 people are feeling in this moment.” #TN7 pic.twitter.com/2QKr6EQUMI
— The Tennessee Holler (@TheTNHoller) December 2, 2025
Ocasio-Cortez added that the close race shows "people are increasingly recognizing that our fights are not left and right, but they are top and bottom. They are about all of us as working Americans and working-class people that are standing up against the injustices and the greed of our healthcare system, of our low wages."
Van Epps has sought to attack Behn for speaking out for the rights of immigrants, telling voters at a rally with the president, "The only way to stop crazy is to vote against crazy."
John Geer, a political scientist at Vanderbilt University, told the Washington Post that the fact that a Democratic candidate is being targeted so heavily by her Republican opponent in the 7th District and attracting the attention of the president shows the GOP is "worried."
“It’s interesting that Van Epps isn’t in a strong enough position just to ignore her,” said Geer.
Behn suggested that even if Van Epps ekes out a win in the close race, the competitive election has offered the latest proof of deep dissatisfaction with Trump's agenda.
“If we get close,” she told the Post, it will be due to the “affordability crisis that we are experiencing in Tennessee and the fact that the federal administration has not delivered an economic agenda to address the needs of working people in the state.”
Keep ReadingShow Less
'Sounds Like Another Way' to Cut Benefits as Trump Social Security Chief Aims to Slash Office Visits
The Social Security Administration's plan, warned one Senate Democrat, will likely lead to "worse service and more challenges."
Dec 02, 2025
The Trump administration is reportedly looking to dramatically reduce the number of people who visit Social Security field offices across the United States, a plan that Democratic lawmakers warned is yet another scheme to disrupt and ultimately cut benefits.
Nextgov/FCW viewed internal Social Security Administration (SSA) planning documents showing that the agency is aiming for "no more than 15 million total" in-person visits to field offices in fiscal year 2026—half the level of the prior fiscal year.
"Under Social Security Commissioner Frank Bisignano, the agency is aiming to push people to interact with Social Security online instead of going to a field office or calling the agency, although Bisignano told lawmakers in June that, even with his focus on technology, the agency is not 'getting rid of field offices,' despite reports of planned closures," Nextgov/FCW reported Monday.
One anonymous SSA staffer told the outlet that agency leadership wants "fewer people in the front door and they want all work that doesn't require direct customer interactions to be centralized."
"They appear to be quietly killing field offices," the staffer said.
The plan comes after the Trump administration carried out the largest staffing cut in SSA history, cutting the agency's workforce by around 7,000. The cut left one SSA worker for every 1,480 beneficiaries, resulting in understaffed field offices and overwhelmed phone operations.
Beneficiaries have also repeatedly faced issues this year attempting to access the Social Security website, problems that SSA's plan to curb field office visits could exacerbate.
Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.), one of the lawmakers spearheading a probe into Bisignano's questionable tenure at the fintech company Fiserv, said in response to the new reporting that "this sure sounds like another way to make it even harder for Americans to get the benefits they've earned."
In a social media post on Monday, Warren highlighted testimony from seniors who have faced long wait times and other difficulties while seeking assistance from SSA under Bisignano's leadership:
Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.), the top Democrat on the Senate Finance Committee, told Nextgov/FCW that "between staffing reductions, more restrictive documentation requirements for Americans to get assistance on the phones, and rapid reorganization of offices around the country, it’s difficult to see how" SSA's goal of slashing visits to field offices "will lead to anything other than worse service and more challenges at Social Security."
Keep ReadingShow Less
'Fighting for Our Lives': Youth Sue to Block Utah Fossil Fuel Permits
"Some days I can't even go outside because the air is so polluted," said one plaintiff. "I get headaches, feel dizzy when it’s too hot, and sometimes I can't even see down my own street because of smoke from wildfires."
Dec 01, 2025
Following the Utah Supreme Court's dismissal of a youth-led constitutional climate lawsuit earlier this year, 10 young Utahns on Monday launched a new case intended to block state permits for coal, gas, and oil development.
Backed by Our Children's Trust—a legal group behind various youth climate suits, including Juliana v. United States and Held v. State of Montana—the plaintiffs are suing the Utah Board of Oil, Gas, and Mining; the Division of Oil, Gas, and Mining; and the director of the latter, Mick Thomas, in state court.
"Plaintiffs bring this action to protect their fundamental rights to life, health, and safety that defendants are violating by permitting fossil fuel development, when doing so is harmful, unnecessary, and more expensive than clean, renewable forms of energy," says the complaint.
"Due to localized air and climate pollution caused by defendants' permitting activities, plaintiffs live in some of the worst air quality of any state in the nation and face climate disruptions, including elevated temperatures and deadly heatwaves, frequent and severe wildfires and smoke, exceptional drought, exacerbated medical conditions, and increased health risks," the filing continues.
"Defendants' fossil fuel permitting challenged here is unconstitutional because it harms the health and safety of plaintiffs, interferes with their healthy development, and takes years off of their lives," the document adds.
When the Utah Supreme Court upheld the dismissal of the earlier lawsuit in March, Our Children's Trust called it a "partial win" because, as lead attorney Andrew Welle explained at the time, "the decision opens a clear path forward for continuing our challenge to the state's actions in promoting fossil fuel development."
🚨Ten Utah youth filed a constitutional climate lawsuit against their state for issuing fossil fuel permits that endanger their health, lives, and safety. Learn more: bit.ly/49LVqA0
[image or embed]
— Our Children’s Trust (@youthvgov.bsky.social) December 1, 2025 at 4:07 PM
The lead plaintiff for both cases is Natalie Roberts, an 18-year-old who lives in Salt Lake City. In April, the American Lung Association's annual State of the Air report gave the state capital's metro area an "F" grade for both ground-level ozone (smog) and particle (soot) pollution.
"Both ozone and particle pollution can cause premature death and other serious health effects such as asthma attacks, heart attacks and strokes, preterm births, and impaired cognitive functioning later in life. Particle pollution can also cause lung cancer," said Nick Torres, advocacy director for the American Lung Association, in a statement when the report was released.
"Unfortunately, too many people in the Salt Lake City metro area are living with unhealthy levels of ozone and particle pollution," Torres continued. "This air pollution is causing kids to have asthma attacks, making people who work outdoors sick and unable to work, and leading to low birth weight in babies. We urge Utah policymakers to take action to improve our air quality, and we are calling on everyone to support the incredibly important work of the US Environmental Protection Agency."
Roberts, in a Monday statement, shared her experiences with her city's polluted air and increasingly hot temperatures.
"Some days I can't even go outside because the air is so polluted," the teenager said. "I get headaches, feel dizzy when it's too hot, and sometimes I can't even see down my own street because of smoke from wildfires. I worry every day about my health, my future, and what kind of world I'll live in if the state keeps approving these fossil fuel permits. We're fighting for our lives and asking the court to protect us before it's too late."
The complaint details similar experiences by other plaintiffs. When 21-year-old Park City resident Sedona Murdock "is exposed to dangerous air quality, she experiences pain in her chest and lungs, difficulty breathing, and coughing, and it can trigger life-threatening asthma attacks," it says. "Sedona experiences stress and anxiety because of the harms to her health that she has already suffered."
Otis W. and Lev W., brothers from Salt Lake City who are respectively 16 and 13, "experience painful headaches from bad air quality and have often had days where their schools have not allowed them or their peers to go outside," according to the filing. "Increasingly intense rain events have resulted in flooding and water intrusion in Otis and Lev's home, threatening their shelter and presenting a risk of dangerous mold growth."
"Decreased snowfall, snowpack, precipitation, and warming temperatures are diminishing water sources that provide water for Otis and Lev's family and community, threatening their water security," the complaint says. "Several trees in Otis and Lev's yard that provided shade for their home have already died from increased heat and drought conditions, making their home hotter and increasing the dangers to them of rising temperatures and heatwaves."
The document also points out how the pair and other youth plaintiffs have had to alter or abandon beloved outdoor activities, from team sports such as soccer to camping, hiking, mountain biking, rafting, running, and skiing, because of the fossil fuel-driven climate emergency.
"The state cannot continue issuing fossil fuel permits that put children's lives and health in jeopardy," said Welle, the lead attorney. "This case is about holding Utah accountable to its constitutional obligations to protect youth from serious harm caused by air pollution, climate impacts, and unsafe fossil fuel development. The court now has what it says it needs to hear and decide this case and prevent further harm to these young people and ensure the state governs responsibly."
Keep ReadingShow Less
Most Popular