We're on the Verge of Exceeding 1.5°C of Warming, But It's Not Too Late for Action
With the mounting economic and human toll of climate disasters and the benefits of affordable, renewable energy so clear and urgent, there is still space for genuine progress and alignment at COP30—and world leaders must seize it!
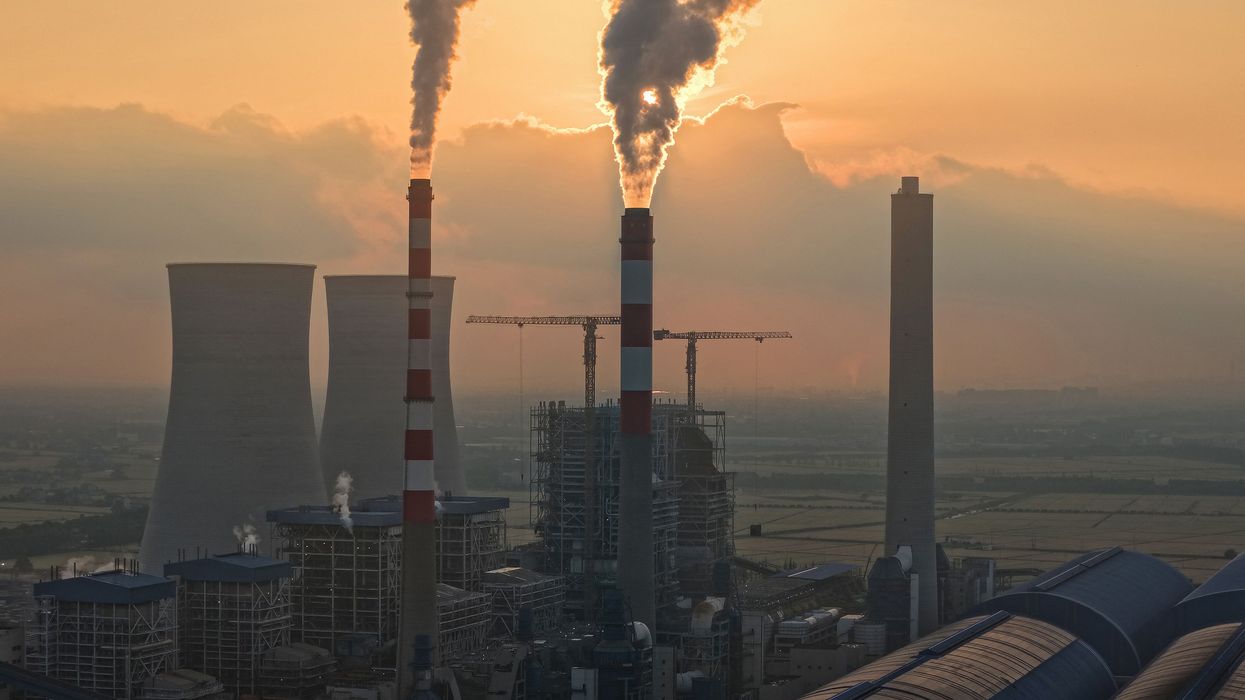
Nations will soon be gathering in Belém, Brazil for the annual United Nations climate “conference of the parties”—COP30—against a backdrop of incredibly challenging geopolitical and climate realities. Grossly insufficient action from world leaders has already resulted in worsening climate extreme events and has put the crucial, science-informed goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C above preindustrial levels out of reach. As I write this, Jamaica, Cuba, the Bahamas, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic are bracing for the monster Hurricane Melissa—the most recent example of the deadly and costly damages from the fossil-fueled climate crisis.
Political headwinds—including the Trump administration’s attacks on climate science and clean energy policies in the United States—and the fossil fuel industry’s continued deception and obstruction are conspiring to make this a very fraught moment for climate action. Yet, with the mounting economic and human toll of climate disasters and the benefits of affordable, renewable energy so clear and urgent, there is still space for genuine progress and alignment at COP30—and world leaders must seize it!
The Significance of a Brazilian COP
The significance of this COP taking place in Brazil, a COP that should forefront the rights of Indigenous communities and the protection of the Amazon forest, cannot be overstated. Across the world, frontline communities bearing a disproportionate toll of climate impacts need solutions that prioritize their needs—not the profits of big polluters and billionaires seeking to evade their responsibility for driving the climate crisis. Unfortunately, the complicated logistics and high accommodation costs for this COP are already creating concerns about inclusivity, especially for those with fewer resources.
The COP Presidency’s Global Mutirão is a bracing call to action. COP30 President André Corrêa do Lago and CEO Ana Toni have laid out a strong vision for a focus on implementation of actions to address climate change, not just a list of future aspirations. They have been engaged in diplomacy all year, bilaterally and multilaterally, to try to lay the groundwork for consensus at COP30 even in the face of geopolitical tensions.
My colleagues and I will be on the ground in Belém, shining a light on the latest science and what it means for decision-makers, people, and the planet as we fight for climate justice alongside civil society representatives from Brazil and across the world. You can follow along with our blog series on COP30.
Breaching 1.5°C of Global Warming Is Alarming, Enraging, and Heartbreaking
UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres’ stark remarks on the 1.5°C climate goal, made at the 75th anniversary of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) last week, hit hard: “…one thing is already clear: we will not be able to contain the global warming below 1.5°C in the next few years. The overshooting is now inevitable, which means that we are going to have a period, bigger or smaller, with higher or lower intensity, above 1.5°C in the years to come.”
Unfortunately, Secretary General Guterres has simply confirmed what several Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change scientists, Union of Concerned Scientists scientists, and many others have been sounding the alarm about since the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report was released.
Ten years after securing the Paris Agreement, the fact that the world is now on the verge of exceeding 1.5°C of warming on a long-term basis—after already surpassing it temporarily for a full year in 2024—was not inevitable. It is an absolutely enraging, shameful, and heartbreaking consequence of continued delays and obstruction of ambitious action. The fault lies entirely with gutless, self-interested political leaders—especially those from richer, high-emitting nations—and the fossil fuel industry, which has continued to brazenly and shamelessly prioritize its profits over the planet.
No country—not even the United States—can stop global climate action AND it will take a lot of countries acting together to tackle this problem at the scale and with the urgency required.
Breaching 1.5°C will undoubtedly unleash further damaging and irreversible climate harms on the world, but it is not a cliff edge. Climate impacts unfold and accelerate on a continuum, and even now, at about 1.3°C of global warming, we are—and have been—seeing profound harms to people and the planet.
Our response now—because humans still have agency over this dire problem we have caused—will make a crucial difference in the extent of the harms to come and what we can do to prepare for them. How much past 1.5°C temperatures overshoot, and how long that overshoot lasts, will depend crucially on our emissions choices. Those factors will make a tremendous difference for the magnitude of impacts like climate-driven extreme heat in the future. We must also ramp up our investments in resilience to help prepare people for graver threats as temperatures increase.
But some planetary boundaries, once crossed, can set off feedback loops in Earth systems that we will not be able to control. For example, some impacts, like the further irreversible loss of land-based ice, can set off additional multi-century accelerating sea-level rise beyond what is currently locked in, and that cannot be turned back once it gets going even if we manage to bring temperatures back down after overshooting 1.5°C.
The choices our political leaders make now—including at COP30—will determine the future we leave to our children and grandchildren. Those choices include prioritizing actions to:
- Sharply curtail heat-trapping emissions, phase out fossil fuels, and drive toward net negative heat-trapping emissions;
- Invest in climate resilience;
- Share the burdens and opportunities of climate action equitably;
- Secure justice for people on the frontlines of the climate crisis; and
- Demand accountability for fossil fuel companies and others who have contributed the most to the climate crisis.
Latest Science and Data Show Climate Action Is Far Offtrack
Despite all the loud alarm bells, most indicators continue to show a world far offtrack. Data from a recent report from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) show that global carbon dioxide emissions were at an all-time high in 2024, with the biggest increase from 2023 to 2024 since modern measurements began. In addition to emissions from burning fossil fuels, a strikingly anomalous factor in 2024 was the high levels of emissions from wildfires in North and South America, including in Bolivia, Brazil, and Canada. Meanwhile, the Production Gap Report shows that nations’ fossil fuel production plans are on track to be twice as much in 2030 as would be consistent with a 1.5°C pathway. And countries’ current emission reduction commitments (aka Nationally Determined Contributions or NDCs) are collectively well short of Paris Agreement-aligned goals.
The 2025 NDC Synthesis report and the forthcoming 2025 UN Environment Programme Emissions Gap report further underscore these realities and highlight the very real risk that without immediate action the world could be on track for a global average temperature increase of more than 2.5°C, even approaching 3°C above preindustrial levels. A 3°C world would be catastrophic—with unrelenting extreme heatwaves, major coastal cities inundated by rising seas, food and water shortages, loss of coral reefs and die-back of tropical forests, harms to human health and other disastrous impacts. Meanwhile, the forthcoming 2025 Adaptation Gap report, themed "Running on Empty," will highlight the huge shortfall in investments in resilience to help frontline communities cope with climate impacts already locked in due to heat-trapping emissions primarily from richer nations.
Together, these reports form a dismal assessment of political leaders who are still not acting in line with what science or equity shows is necessary, despite years of high-minded promises and even as people are enduring crushing climate impacts.
Seven Things to Watch at COP30
While the context for COP30 is daunting, and the process of negotiations ahead is likely to be frustrating, global cooperation is absolutely essential to solve this challenge. There are no shortcuts around that. Every country must have a role, a responsibility, and a voice—no matter how big or small, or how powerful or not they are. That said, richer nations and major emitters of heat-trapping emissions have unique responsibilities to act boldly.
Here are seven things I’ll be watching for:
- Will nations remain steadfast in their commitment to the Paris Agreement? At the UN climate summit in September in New York it was clear that nearly every nation recognizes the utmost importance of the Paris Agreement goals for their self-interest and the global collective interest to limit dangerous climate change. The Trump administration, which has shamefully announced its intention to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement for the second time, is an isolated rogue actor, acting against the interests of the American people. At COP30, will the BRICS nations, the European Union countries, and others step up to fill the leadership vacuum and drive forward ambitious climate action? Many US states, subnational governments, and businesses also remain committed and will be in Brazil to show the other face of the US.
- How will countries’ emissions reduction commitments (aka NDCs) stack up collectively? So far, the NDC announcements have been a real mixed bag and collectively the announcements have fallen well short of what’s needed. The UN’s NDC Synthesis Report underscores the huge gap in ambition, with most major emitting countries still far off course in terms of their emissions trajectories, putting the world at risk of over 2.5°C of warming. Many countries have yet to even announce their updated NDCs. Closing that ambition gap will require rapid implementation, transparent progress tracking, and stronger accountability mechanisms before 2030.
- How much progress will be made on transitioning away from fossil fuels, tripling renewables, and doubling energy efficiency by 2030? Renewable energy progress—especially propelled by China and India, among others—is cause of optimism. Renewable energy is not just ramping up but actually displacing fossil fuels, and now that momentum must be accelerated. However, coal, oil, and gas are simply not being phased out fast enough, despite countries’ commitments to transition away from fossil fuels made at COP28.
- Will there be any breakthroughs on climate finance? Last year’s COP in Baku, billed as the climate finance COP, ended in deep disappointment and a breakdown of trust between richer nations and lower income nations because of the paltry finance pledges offered. This year, it will be critical to rebuild that trust, including sending a strong signal about a plan for provision of finance for both cutting emissions and for adaptation—the latter of which has long left behind and is an urgent priority for developing nations.
- Will there be an ambitious, fair agreement on safeguarding tropical forest ecosystems? Fittingly, this Brazilian COP taking place in the Amazon must prioritize a strong agreement to help protect tropical forests, a crucial aspect of climate action, centering the needs and perspectives of the people and other species who live in and depend on them. Negotiations on the Tropical Forest Forever Facility will be keenly watched as a barometer of success at COP30.
- Will COP outcomes be protected from interference from fossil fuel interests? Petrostates and increasingly large numbers of fossil fuel company lobbyists have worked behind the scenes and publicly to co-opt the UN COP space and water down global climate agreements that they see as a threat to their profits. Their lies and disinformation about climate science and renewable energy are a significant obstacle to progress and must be called out and resisted.
- Will civil society voices, especially the voices of Indigenous Peoples, get a fair hearing? While civil society representatives do not have a seat at the negotiating table, our voices as observer groups in the broader COP space are crucial to remind political leaders of who they are supposed to be serving (not fossil fuel executives and billionaires!) and that they must prioritize fairness and science in their deliberations. Through engagement with country negotiators, side events, press conferences, and public demonstrations, we will work to register our views loudly and clearly.
What Will It Take for COP30 to Be Successful?
The 10 years since the world secured the historic Paris Agreement have been a time of both incredible progress in renewable energy and worsening climate impacts, illuminating who the real climate champions are and who are the obstacles. COP30’s success depends on whether countries can rise above narrow self-interest and recommit to ambitious action. It depends on whether a shifting world order can unlock progress and leadership from new quarters. It depends on isolating the Trump administration and resisting its anti-science rhetoric and actions, as well as its efforts to upend multilateral diplomacy to solve global challenges.
I am going to Brazil in sober mind frame, deeply worried about the increasingly authoritarian Trump administration. But much as the US is an outsize actor on the global stage, this international climate meeting with 190+ countries is also a reminder of the wider world and each country’s vital place in it. The 1.5°C goal is enshrined in the Paris Agreement because of the bravery of small island nations that carried the refrain of "1.5 to stay alive" at COP21 in 2015. Vanuatu and a group of small island nations led a heroic effort to secure a landmark advisory opinion from the International Court of Justice this year, affirming states’ legal obligations to address climate change. Meanwhile, renewable energy is taking off around the world because it is now the cheapest form of electricity in most places. No country—not even the United States—can stop global climate action AND it will take a lot of countries acting together to tackle this problem at the scale and with the urgency required.
In Belém, I know I will find inspiration and courage from the global climate justice movement, from Indigenous Peoples who have stood firm to defend their lands and communities in the face of brutal attacks, and from passionate young people who are the planet’s future. I know I will come back reenergized for the right and necessary fight here at home
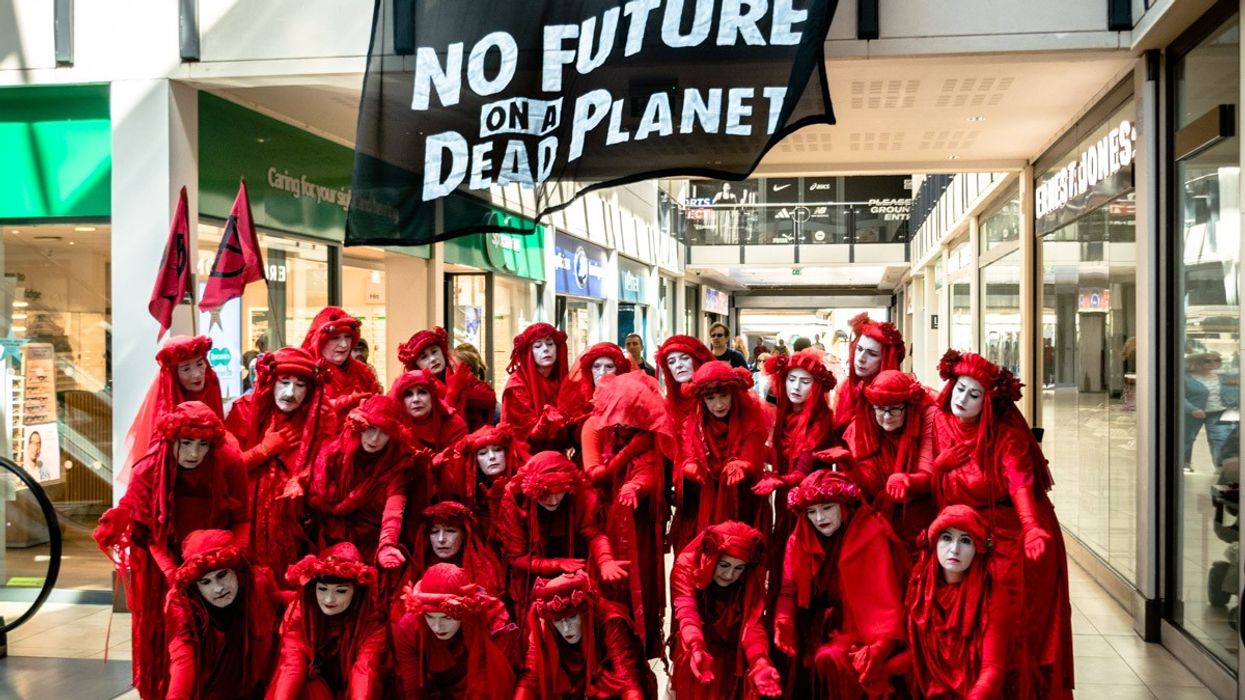
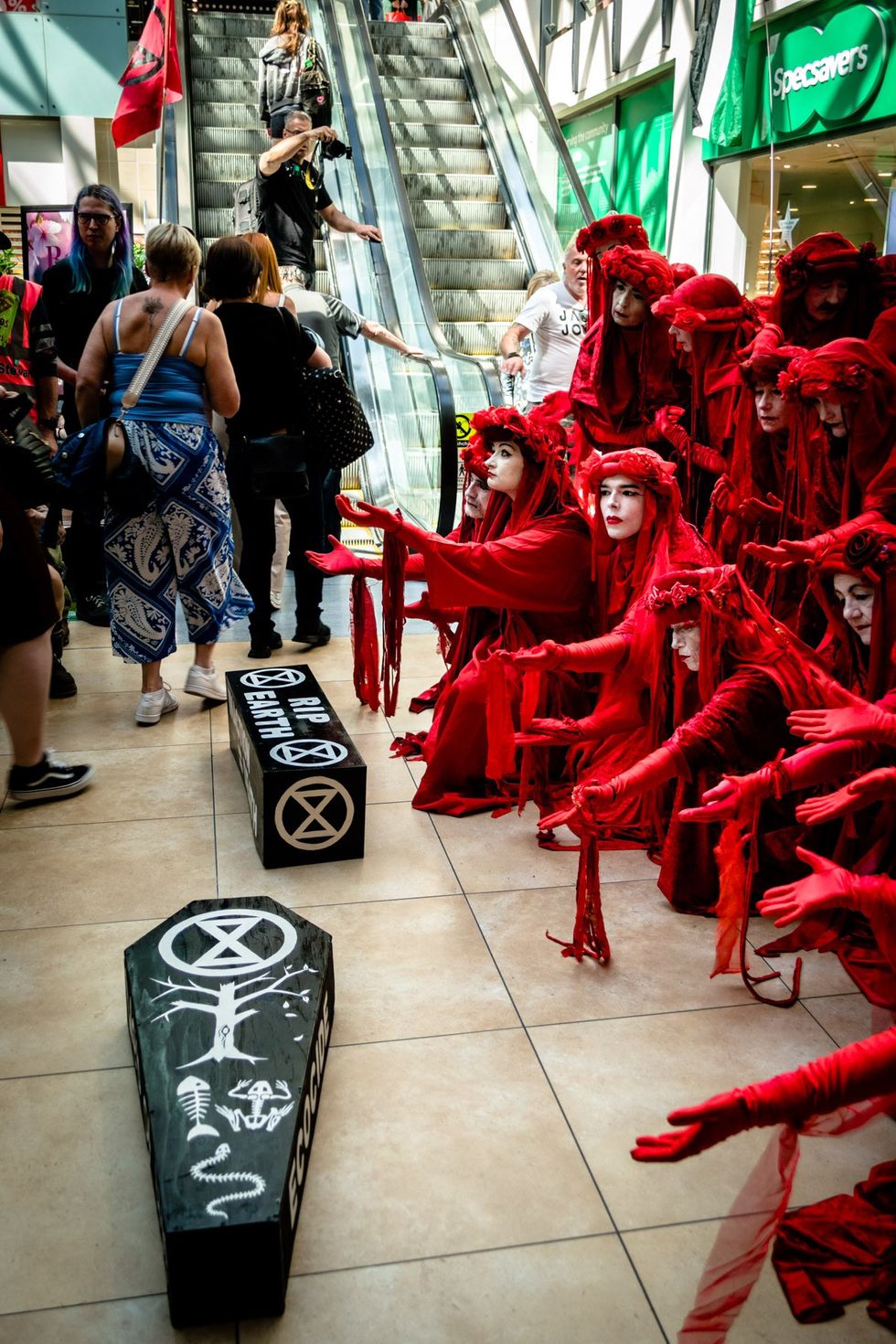


 Members of the "Red Rebel Brigade" led a procession around Cambridge, England as part of a funeral for the Paris agreement's 1.5°C temperature target on May 10, 2025. (Photo: Derek Langley)
Members of the "Red Rebel Brigade" led a procession around Cambridge, England as part of a funeral for the Paris agreement's 1.5°C temperature target on May 10, 2025. (Photo: Derek Langley)