

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

Governments must be held accountable for the deaths of health and essential workers who they have failed to protect from COVID-19, Amnesty International said today, as it released a new report documenting the experiences of health workers around the world.
The organization's analysis of available data has revealed that more than 3000 health workers are known to have died from COVID-19 worldwide - a figure which is likely to be a significant underestimate.
Governments must be held accountable for the deaths of health and essential workers who they have failed to protect from COVID-19, Amnesty International said today, as it released a new report documenting the experiences of health workers around the world.
The organization's analysis of available data has revealed that more than 3000 health workers are known to have died from COVID-19 worldwide - a figure which is likely to be a significant underestimate.
Alarmingly, Amnesty International documented cases where health workers who raise safety concerns in the context of the COVID-19 response have faced retaliation, ranging from arrest and detention to threats and dismissal.
"With the COVID-19 pandemic still accelerating around the world, we are urging governments to start taking health and essential workers' lives seriously. Countries yet to see the worst of the pandemic must not repeat the mistakes of governments whose failure to protect workers' rights has had devastating consequences," said Sanhita Ambast, Amnesty International's Researcher and Advisor on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
"It is especially disturbing to see that some governments are punishing workers who voice their concerns about working conditions that may threaten their lives. Health workers on the frontline are the first to know if government policy is not working, and authorities who silence them cannot seriously claim to be prioritising public health."
Thousands have lost their lives
There is currently no systematic global tracking of how many health and essential workers have died after contracting COVID-19.
However, Amnesty International has collated and analysed a wide range of available data that shows that over 3000 health workers are known to have died after contracting COVID-19 in 79 countries around the world.
According to Amnesty International's monitoring, the countries with the highest numbers of health worker deaths thus far include the USA (507), Russia (545), UK (540, including 262 social care workers), Brazil (351), Mexico (248), Italy (188), Egypt (111), Iran (91), Ecuador (82) and Spain (63).
The overall figure is likely to be a significant underestimate due to under-reporting, while accurate comparisons across countries are difficult due to differences in counting. For example, France has collected data from just some of its hospitals and health centres, while figures of deceased health workers provided by health associations in Egypt and Russia have been contested by their governments.
Shortages of life saving protective equipment
Health workers reported serious shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE) in nearly all of the 63 countries and territories surveyed by Amnesty International.
This includes countries which may yet see the worst of the pandemic, such as India and Brazil and several countries across Africa. A doctor working in Mexico City told Amnesty International that doctors were spending about 12% of their monthly salaries buying their own PPE.
In addition to a global shortage of supply, trade restrictions may have aggravated this problem. In June 2020, 56 countries and two trade blocs (the European Union and the Eurasian Economic Union) had put in place measures to either ban or restrict the export of some, or all, forms of PPE or its components.
"While states must ensure there is sufficient PPE for workers within their territories, trade restrictions risk exacerbating shortages in countries that are dependent on imports," said Sanhita Ambast.
"The COVID-19 pandemic is a global problem that requires global cooperation."
Reprisals
In at least 31 of the countries surveyed by Amnesty International, researchers recorded reports of strikes, threatened strikes, or protests, by health and essential workers as a result of unsafe working conditions. In many countries, such actions were met with reprisals from authorities.
In Egypt, for example, Amnesty documented the cases of nine health care workers who were arbitrarily detained between March and June on vague and overly broad charges of "spreading false news" and "terrorism". All those detained had expressed safety concerns or criticized the government's handling of the pandemic.
Another Egyptian doctor told Amnesty International that doctors who speak out are subjected to threats, interrogations by the National Security Agency (NSA), administrative questioning, and penalties. He said:
"Many [doctors] are preferring to pay for their own personal equipment to avoid this exhausting back and forth. [The authorities] are forcing doctors to choose between death and jail."
In some cases, strike action and protests have been met with heavy-handed responses.
In Malaysia for example, police dispersed a peaceful picket against a hospital cleaning services company. The picketers' complaints centred around what they said was the unfair treatment of union members by the company as well as a lack of sufficient protection for hospital cleaners. Police arrested, detained and charged five health care workers for "unauthorized gathering" in violation of their rights to freedom of association and assembly.
"Health and essential workers have a right to raise their voices against unfair treatment," said Sanhita Ambast.
"Health workers can help governments improve their response to the pandemic and keep everyone safe - but they can't do this if they are in prison, and they can't do it if they are afraid to speak up."
There have also been reports in several countries of health and essential workers being fired or facing disciplinary action for speaking out about their concerns.
In the USA for example, certified nursing assistant Tainika Somerville was fired after posting a video on Facebook where she read out a petition calling for more PPE. Tainika says staff at the nursing home in Illinois where she works were not informed that they were working with COVID-19 patients and found out through the media. The nursing home had reported 34 infections and 15 COVID-19 related deaths as of May 29.
In Russia, Amnesty International highlighted the cases of two doctors, Yulia Volkova and Tatyana Reva, who are facing retaliation after complaining about a lack of PPE. Yulia Volkova has been charged under Russia's fake news laws and faces a fine of up to RUB 100,000 (USD 1,443), while Tatyana Reva is facing disciplinary proceedings that may result in her dismissal.
Unfair pay and lack of benefits
In addition to unsafe working conditions, Amnesty International has documented how some health and essential workers are being unfairly paid or in some cases not paid at all.
In South Sudan for example, doctors on the government's payroll have not received their salaries since February and do not receive welfare packages or medical cover. In Guatemala, at least 46 facilities staff were not paid for the two-and-a-half months they spent working at a COVID-19 hospital.
In some countries, there are no additional benefits for health and essential workers in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic, and in other countries benefits exclude certain categories of workers.
Amnesty International is calling on states to consider COVID-19 an occupational illness.
As part of this they must ensure that health and essential workers have access to compensation and other support in case they contract the infection. They must also be included in priority groups for COVID-19 testing.
Stigma and Violence
Amnesty International documented several cases where health and essential workers experienced stigma and violence because of their jobs. For example, a nurse in Mexico was reportedly drenched with chlorine while walking on the street, and in the Philippines, attackers poured bleach in the face of a hospital utility worker.
These incidents point to a climate of misinformation and stigma and underscore the importance of governments providing accurate and accessible information on the spread of COVID-19.
In Pakistan, Amnesty International has recorded several instances of violence against health workers since April. Hospitals have been vandalized, doctors have been attacked, and one was even shot by a member of the Counter Terrorism Force.
There have been several statements from ministers in Pakistan claiming that hospitals have the necessary resources, despite reports that hospitals have been forced to turn away even critical patients, due to the shortage of beds, ventilators and other life-saving equipment. This puts health workers in danger as people don't believe them when they say they do not have room for more patients.
Recommendations
"We call on all states affected by COVID-19 to carry out independent public reviews into their preparedness for and responses to the pandemic, with a view to better protecting human rights and lives in the event of a future mass disease outbreak," said Sanhita Ambast.
This should include a review into whether the rights of health and essential workers - including the right to just and favourable conditions of work, and the right to freedom of expression - were adequately protected.
States must ensure adequate compensation for all health and essential workers who have contracted COVID-19 as a result of work-related activities. They must also investigate cases where workers have faced reprisals for raising health and safety concerns, and provide effective remedy to those who have been unjustly treated including by reinstating workers who have lost their jobs for speaking out.
Background
For the purpose of this briefing, "health workers" refers to everyone involved in the delivery of health and social care in any capacity, including but not limited to doctors, nurses, social care workers, cleaners, ambulance drivers and facilities staff. While the briefing largely focuses on health workers, given available information, the same issues apply to a broader range of 'essential workers' who have been exposed to COVID-19 in a range of frontline jobs during the pandemic.
*Figures were correct as of 6 July 2020.
Amnesty International is a worldwide movement of people who campaign for internationally recognized human rights for all. Our supporters are outraged by human rights abuses but inspired by hope for a better world - so we work to improve human rights through campaigning and international solidarity. We have more than 2.2 million members and subscribers in more than 150 countries and regions and we coordinate this support to act for justice on a wide range of issues.
In some cases, the administration has kept immigrants locked up even after a judge has ordered their release, according to an investigation by Reuters.
Judges across the country have ruled more than 4,400 times since the start of October that US Immigration and Customs Enforcement has illegally detained immigrants, according to a Reuters investigation published Saturday.
As President Donald Trump carries out his unprecedented "mass deportation" crusade, the number of people in ICE custody ballooned to 68,000 this month, up 75% from when he took office.
Midway through 2025, the administration had begun pushing for a daily quota of 3,000 arrests per day, with the goal of reaching 1 million per year. This has led to the targeting of mostly people with no criminal records rather than the "worst of the worst," as the administration often claims.
Reuters' reporting suggests chasing this number has also resulted in a staggering number of arrests that judges have later found to be illegal.
Since the beginning of Trump's term, immigrants have filed more than 20,200 habeas corpus petitions, claiming they were held indefinitely without trial in violation of the Constitution.
In at least 4,421 cases, more than 400 federal judges have ruled that their detentions were illegal.
Last month, more than 6,000 habeas petitions were filed. Prior to the second Trump administration, no other month dating back to 2010 had seen even 500.
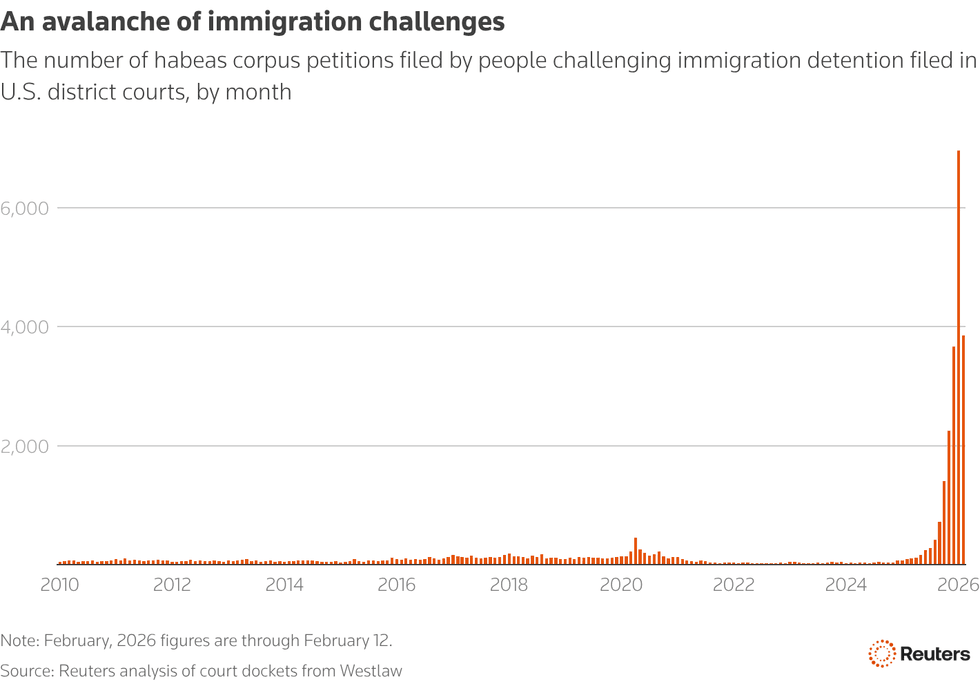
In part due to the sheer volume of legal challenges, the Trump administration has often failed to comply with court rulings, leaving people locked up even after judges ordered them to be released.
Reuters' new report is the most comprehensive examination to date of the administration's routine violation of the law with respect to immigration enforcement. But the extent to which federal immigration agencies have violated the law under Trump is hardly new information.
In a ruling last month, Chief Judge Patrick J. Schiltz of the US District Court in Minnesota—a conservative jurist appointed by former President George W. Bush—provided a list of nearly 100 court orders ICE had violated just that month while deployed as part of Trump's Operation Metro Surge.
The report of ICE's systemic violation of the law comes as the agency faces heightened scrutiny on Capitol Hill, with leaders of the agency called to testify and Democrats attempting to hold up funding in order to force reforms to ICE's conduct, which resulted in a partial shutdown beginning Saturday.
Following the release of Reuters' report, Rep. Ted Lieu (D-Calif.) directed a pointed question over social media to Kristi Noem, the secretary of the Department of Homeland Security, which oversees ICE.
"Why do your out-of-control agents keep violating federal law?" he said. "I look forward to seeing you testify under oath at the House Judiciary Committee in early March."
"Aggies do what is necessary for our rights, for our survival, and for our people,” said one student organizer at North Carolina A&T State University, the largest historically Black college in the nation.
As early voting began for the state primaries, North Carolina college students found themselves walking more than a mile to cast their ballots after the Republican-controlled State Board of Elections closed polling places on their campuses.
The board, which shifted to a 3-2 GOP majority, voted last month to close a polling site at Western Carolina University and to reject the creation of polling sites at two other colleges—the University of North Carolina at Greensboro (UNC Greensboro), and the North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University (NC A&T), the largest historically Black college in the nation. Each of these schools had polling places available on campus during the 2024 election.
The decision, which came just weeks before early voting was scheduled to begin, left many of the 40,000 students who attend these schools more than a mile away from the nearest polling place.
It was the latest of many efforts by North Carolina Republicans to restrict voting ahead of the 2026 midterms: They also cut polling place hours in dozens of counties and eliminated early voting on Sundays in some, which dealt a blow to "Souls to the Polls" efforts led by Black churches.
A lawsuit filed late last month by a group of students at the three schools said, “as a result, students who do not have access to private transportation must now walk that distance—which includes walking along a highway that lacks any pedestrian infrastructure—to exercise their right to vote.
The students argued that this violates their access to the ballot and to same-day registration, which is only available during the early voting period.
Last week, a federal judge rejected their demand to open the three polling centers. Jay Pavey, a Republican member of the Jackson County elections board, who voted to close the WCU polling site, dismissed fears that it would limit voting.
“If you really want to vote, you'll find a way to go one mile,” Pavey said.
Despite the hurdles, hundreds of students in the critical battleground state remained determined to cast a ballot as early voting opened.
On Friday, a video posted by the Smoky Mountain News showed dozens of students marching in a line from WCU "to their new polling place," at the Jackson County Recreation Center, "1.7 miles down a busy highway with no sidewalks."
The university and on-campus groups also organized shuttles to and from the polling place.
A similar scene was documented at NC A&T, where about 60 students marched to their nearest polling place at a courthouse more than 1.3 miles away.
The students described their march as a protest against the state's decision, which they viewed as an attempt to limit their power at the ballot box.
The campus is no stranger to standing up against injustice. February 1 marked the 66th anniversary of when four Black NC A&T students launched one of the most pivotal protests of the civil rights movement, sitting down at a segregated Woolworth's lunch counter in downtown Greensboro—an act that sparked a wave of nonviolent civil disobedience across the South.
"Aggies do what is necessary for our rights, for our survival, and for our people,” Jae'lah Monet, one of the student organizers of the march, told Spectrum News 1.
Monet said she and other students will do what is necessary to get students to the polls safely and to demonstrate to the state board the importance of having a polling place on campus. She said several similar events will take place throughout the early voting period.
"We will be there all day, and we will all get a chance to vote," Monet said.
"We need massive reforms in DHS with real accountability before we send another dime their way," said Rep. Pramila Jayapal.
The US Department of Homeland Security partially shut down on Saturday at midnight after Congress failed to reach an agreement to reform its immigration agencies, which have faced mounting scrutiny after the killings of multiple US citizens and rampant civil rights violations.
A shutdown was virtually assured when lawmakers left town for a recess on Thursday without a deal that included Democrats' key demands to rein in Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
Sixty votes are needed to pass any deal through the Senate, meaning seven Democrats would need to join every Republican to break the stalemate.
Democrats have demanded that agents around the nation wear body cameras, carry identification, and stop hiding their identities with masks. They said agents must adhere to the Constitution by obtaining judicial warrants before entering private property and ending the use of racial profiling.
Senate Republicans on Thursday attempted to pass another short-term funding measure that would keep the agency running while negotiations play out. But without adopting any of the Democrats' reforms, Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY) said his party would "not support a blank check for chaos."
The bill was voted down 47-52, with only one Democrat, the ICE-defending Sen. John Fetterman (D-Pa.) voting in support.
The lapse in funding comes amid a whirlwind of scandals surrounding DHS, most notably the fatal shootings in Minneapolis of two US citizens, Alex Pretti and Renee Good, last month. DHS officials, including Secretary Kristi Noem, immediately leapt to justify the killings in contradiction to video evidence, which smeared the victims as "domestic terrorists" before any investigation took place.
Earlier this week, unsealed body camera footage showed definitively that the agency also lied about the shooting of 30-year-old US citizen Marimar Martinez in Chicago in October.
On Friday, it was reported that two ICE agents are under investigation for making false statements about the events leading up to yet another shooting of a Venezuelan national, Julio Cesar Sosa-Celis, in Minnesota last month.
In a rare acknowledgement of wrongdoing by his agency, ICE's acting director, Todd Lyons, said on Friday that the agents appear “to have made untruthful statements” about what led to his shooting.
An explosive Wall Street Journal report also recently put Noem further under the microscope, revealing an alleged romantic relationship with top Trump adviser Corey Lewandowski, who insiders said has been put in charge of the agency's contracting despite being only a temporary "special government employee" and has reportedly doled out contracts in an "opaque and arbitrary manner."
The DHS shutdown will not affect funding for immigration agencies, since both ICE and CBP received more than $70 billion from Congress last summer as part of the GOP's massive tax and spending bill.
Their activities are expected to continue normally during the shutdown. But other functions of the agency may see delays and funding lapses.
While most Transportation Security Administration (TSA) employees are considered essential and expected to stay on the job, more may begin to stay home if the shutdown drags on and they miss paychecks. Some Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) funding for states' disaster recovery may also be delayed as a result of the shutdown, and employees may be furloughed, slowing the process.
Congress is expected to reconvene on February 23 after a weeklong recess, but may return earlier if a deal is reached during the break.
Democrats have appeared largely united on holding out unless significant reforms are achieved, though party leaders—Schumer and House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries (D-NY) have faced a crisis of confidence within their own caucus, as they've appeared willing to taper back some demands—including masking requirements—in order to find a compromise.
As the clock inched toward midnight on Friday, Rep. Pramila Jayapal (D-Wash.), the chair emerita of the Congressional Progressive Caucus, emphasized the existential stakes of the fight ahead.
"If the government shuts down, it will be because Republicans refuse to hold DHS and their deplorable actions accountable," she said. "The reality is if we start to erode the rights of some, we start to erode the rights of all—and I will not stand for it. We need massive reforms in DHS with real accountability before we send another dime their way."