

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
We are now within two months of what may be humankind's most dangerous moment since the Cuban Missile Crisis.
There is no excuse for not acting. All the resources our species can muster must be focused on the fuel pool at Fukushima Unit 4.
We are now within two months of what may be humankind's most dangerous moment since the Cuban Missile Crisis.
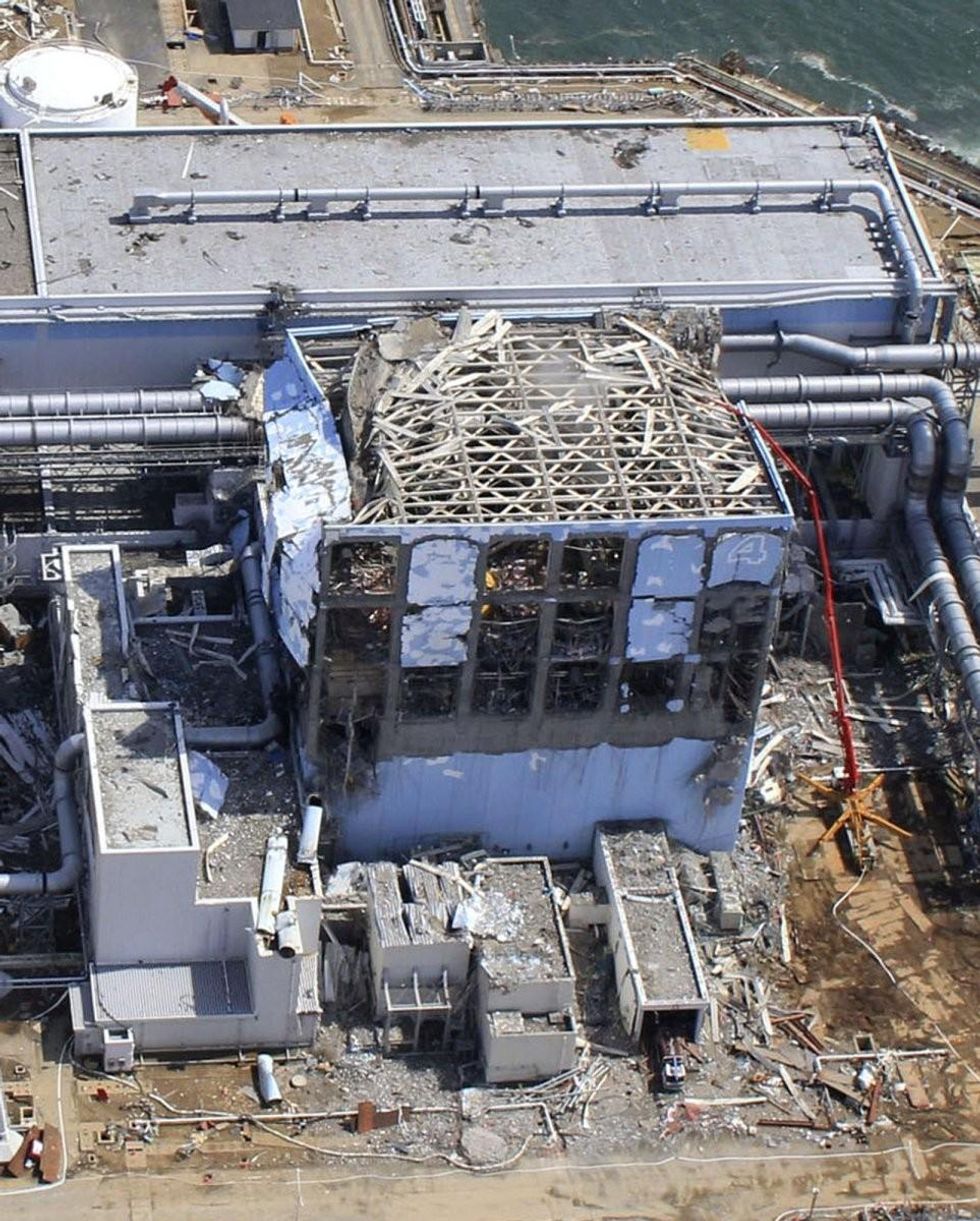
There is no excuse for not acting. All the resources our species can muster must be focused on the fuel pool at Fukushima Unit 4.
Fukushima's owner, Tokyo Electric (Tepco), says that within as few as 60 days it may begin trying to remove more than 1300 spent fuel rods from a badly damaged pool perched 100 feet in the air. The pool rests on a badly damaged building that is tilting, sinking and could easily come down in the next earthquake, if not on its own.
Some 400 tons of fuel in that pool could spew out more than 15,000 times as much radiation as was released at Hiroshima.
The one thing certain about this crisis is that Tepco does not have the scientific, engineering or financial resources to handle it. Nor does the Japanese government. The situation demands a coordinated worldwide effort of the best scientists and engineers our species can muster.
Why is this so serious?
We already know that thousands of tons of heavily contaminated water are pouring through the Fukushima site, carrying a devil's brew of long-lived poisonous isotopes into the Pacific. Tuna irradiated with fallout traceable to Fukushima have already been caught off the coast of California. We can expect far worse.
Tepco continues to pour more water onto the proximate site of three melted reactor cores it must somehow keep cool. Steam plumes indicate fission may still be going on somewhere underground. But nobody knows exactly where those cores actually are.
Much of that irradiated water now sits in roughly a thousand huge but fragile tanks that have been quickly assembled and strewn around the site. Many are already leaking. All could shatter in the next earthquake, releasing thousands of tons of permanent poisons into the Pacific. (Note: A relatively small earthquake struck Fukushima prefecture on Thursday, an indication of the inevitable occurrence of larger future ones in the area.)
The water flowing through the site is also undermining the remnant structures at Fukushima, including the one supporting the fuel pool at Unit Four.
More than 6,000 fuel assemblies now sit in a common pool just 50 meters from Unit Four. Some contain plutonium. The pool has no containment over it. It's vulnerable to loss of coolant, the collapse of a nearby building, another earthquake, another tsunami and more.
Overall, more than 11,000 fuel assemblies are scattered around the Fukushima site. According to long-time expert and former Department of Energy official Robert Alvarez, there is more than 85 times as much lethal cesium on site as was released at Chernobyl.
Radioactive hot spots continue to be found around Japan. There are indications of heightened rates of thyroid damage among local children.
The immediate bottom line is that those fuel rods must somehow come safely out of the Unit Four fuel pool as soon as possible.
Just prior to the 2011 earthquake and tsunami that shattered the Fukushima site, the core of Unit Four was removed for routine maintenance and refueling. Like some two dozen reactors in the US and too many more around the world, the General Electric-designed pool into which that core now sits is 100 feet in the air.
Spent fuel must somehow be kept under water. It's clad in zirconium alloy which will spontaneously ignite when exposed to air. Long used in flash bulbs for cameras, zirconium burns with an extremely bright hot flame.
Each uncovered rod emits enough radiation to kill someone standing nearby in a matter of minutes. A conflagration could force all personnel to flee the site and render electronic machinery unworkable.
According to Arnie Gundersen, a nuclear engineer with forty years in an industry for which he once manufactured fuel rods, the ones in the Unit 4 core are bent, damaged and embrittled to the point of crumbling. Cameras have shown troubling quantities of debris in the fuel pool, which itself is damaged.
The engineering and scientific barriers to emptying the Unit Four fuel pool are unique and daunting, says Gundersen. But it must be done to 100% perfection.
Should the attempt fail, the rods could be exposed to air and catch fire, releasing horrific quantities of radiation into the atmosphere. The pool could come crashing to the ground, dumping the rods together into a pile that could fission and possibly explode. The resulting radioactive cloud would threaten the health and safety of all us.
Chernobyl's first 1986 fallout reached California within ten days. Fukushima's in 2011 arrived in less than a week. A new fuel fire at Unit 4 would pour out a continuous stream of lethal radioactive poisons for centuries.
Former Ambassador Mitsuhei Murata says full-scale releases from Fukushima "would destroy the world environment and our civilization. This is not rocket science, nor does it connect to the pugilistic debate over nuclear power plants. This is an issue of human survival."
Neither Tokyo Electric nor the government of Japan can go this alone. There is no excuse for deploying anything less than a coordinated team of the planet's best scientists and engineers.
We have two months or less to act.
For now, we are petitioning the United Nations and President Obama to mobilize the global scientific and engineering community to take charge at Fukushima and the job of moving these fuel rods to safety.
If you have a better idea, please follow it. But do something and do it now.
The clock is ticking. The hand of global nuclear disaster is painfully close to midnight.
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
We are now within two months of what may be humankind's most dangerous moment since the Cuban Missile Crisis.

There is no excuse for not acting. All the resources our species can muster must be focused on the fuel pool at Fukushima Unit 4.
Fukushima's owner, Tokyo Electric (Tepco), says that within as few as 60 days it may begin trying to remove more than 1300 spent fuel rods from a badly damaged pool perched 100 feet in the air. The pool rests on a badly damaged building that is tilting, sinking and could easily come down in the next earthquake, if not on its own.
Some 400 tons of fuel in that pool could spew out more than 15,000 times as much radiation as was released at Hiroshima.
The one thing certain about this crisis is that Tepco does not have the scientific, engineering or financial resources to handle it. Nor does the Japanese government. The situation demands a coordinated worldwide effort of the best scientists and engineers our species can muster.
Why is this so serious?
We already know that thousands of tons of heavily contaminated water are pouring through the Fukushima site, carrying a devil's brew of long-lived poisonous isotopes into the Pacific. Tuna irradiated with fallout traceable to Fukushima have already been caught off the coast of California. We can expect far worse.
Tepco continues to pour more water onto the proximate site of three melted reactor cores it must somehow keep cool. Steam plumes indicate fission may still be going on somewhere underground. But nobody knows exactly where those cores actually are.
Much of that irradiated water now sits in roughly a thousand huge but fragile tanks that have been quickly assembled and strewn around the site. Many are already leaking. All could shatter in the next earthquake, releasing thousands of tons of permanent poisons into the Pacific. (Note: A relatively small earthquake struck Fukushima prefecture on Thursday, an indication of the inevitable occurrence of larger future ones in the area.)
The water flowing through the site is also undermining the remnant structures at Fukushima, including the one supporting the fuel pool at Unit Four.
More than 6,000 fuel assemblies now sit in a common pool just 50 meters from Unit Four. Some contain plutonium. The pool has no containment over it. It's vulnerable to loss of coolant, the collapse of a nearby building, another earthquake, another tsunami and more.
Overall, more than 11,000 fuel assemblies are scattered around the Fukushima site. According to long-time expert and former Department of Energy official Robert Alvarez, there is more than 85 times as much lethal cesium on site as was released at Chernobyl.
Radioactive hot spots continue to be found around Japan. There are indications of heightened rates of thyroid damage among local children.
The immediate bottom line is that those fuel rods must somehow come safely out of the Unit Four fuel pool as soon as possible.
Just prior to the 2011 earthquake and tsunami that shattered the Fukushima site, the core of Unit Four was removed for routine maintenance and refueling. Like some two dozen reactors in the US and too many more around the world, the General Electric-designed pool into which that core now sits is 100 feet in the air.
Spent fuel must somehow be kept under water. It's clad in zirconium alloy which will spontaneously ignite when exposed to air. Long used in flash bulbs for cameras, zirconium burns with an extremely bright hot flame.
Each uncovered rod emits enough radiation to kill someone standing nearby in a matter of minutes. A conflagration could force all personnel to flee the site and render electronic machinery unworkable.
According to Arnie Gundersen, a nuclear engineer with forty years in an industry for which he once manufactured fuel rods, the ones in the Unit 4 core are bent, damaged and embrittled to the point of crumbling. Cameras have shown troubling quantities of debris in the fuel pool, which itself is damaged.
The engineering and scientific barriers to emptying the Unit Four fuel pool are unique and daunting, says Gundersen. But it must be done to 100% perfection.
Should the attempt fail, the rods could be exposed to air and catch fire, releasing horrific quantities of radiation into the atmosphere. The pool could come crashing to the ground, dumping the rods together into a pile that could fission and possibly explode. The resulting radioactive cloud would threaten the health and safety of all us.
Chernobyl's first 1986 fallout reached California within ten days. Fukushima's in 2011 arrived in less than a week. A new fuel fire at Unit 4 would pour out a continuous stream of lethal radioactive poisons for centuries.
Former Ambassador Mitsuhei Murata says full-scale releases from Fukushima "would destroy the world environment and our civilization. This is not rocket science, nor does it connect to the pugilistic debate over nuclear power plants. This is an issue of human survival."
Neither Tokyo Electric nor the government of Japan can go this alone. There is no excuse for deploying anything less than a coordinated team of the planet's best scientists and engineers.
We have two months or less to act.
For now, we are petitioning the United Nations and President Obama to mobilize the global scientific and engineering community to take charge at Fukushima and the job of moving these fuel rods to safety.
If you have a better idea, please follow it. But do something and do it now.
The clock is ticking. The hand of global nuclear disaster is painfully close to midnight.
We are now within two months of what may be humankind's most dangerous moment since the Cuban Missile Crisis.

There is no excuse for not acting. All the resources our species can muster must be focused on the fuel pool at Fukushima Unit 4.
Fukushima's owner, Tokyo Electric (Tepco), says that within as few as 60 days it may begin trying to remove more than 1300 spent fuel rods from a badly damaged pool perched 100 feet in the air. The pool rests on a badly damaged building that is tilting, sinking and could easily come down in the next earthquake, if not on its own.
Some 400 tons of fuel in that pool could spew out more than 15,000 times as much radiation as was released at Hiroshima.
The one thing certain about this crisis is that Tepco does not have the scientific, engineering or financial resources to handle it. Nor does the Japanese government. The situation demands a coordinated worldwide effort of the best scientists and engineers our species can muster.
Why is this so serious?
We already know that thousands of tons of heavily contaminated water are pouring through the Fukushima site, carrying a devil's brew of long-lived poisonous isotopes into the Pacific. Tuna irradiated with fallout traceable to Fukushima have already been caught off the coast of California. We can expect far worse.
Tepco continues to pour more water onto the proximate site of three melted reactor cores it must somehow keep cool. Steam plumes indicate fission may still be going on somewhere underground. But nobody knows exactly where those cores actually are.
Much of that irradiated water now sits in roughly a thousand huge but fragile tanks that have been quickly assembled and strewn around the site. Many are already leaking. All could shatter in the next earthquake, releasing thousands of tons of permanent poisons into the Pacific. (Note: A relatively small earthquake struck Fukushima prefecture on Thursday, an indication of the inevitable occurrence of larger future ones in the area.)
The water flowing through the site is also undermining the remnant structures at Fukushima, including the one supporting the fuel pool at Unit Four.
More than 6,000 fuel assemblies now sit in a common pool just 50 meters from Unit Four. Some contain plutonium. The pool has no containment over it. It's vulnerable to loss of coolant, the collapse of a nearby building, another earthquake, another tsunami and more.
Overall, more than 11,000 fuel assemblies are scattered around the Fukushima site. According to long-time expert and former Department of Energy official Robert Alvarez, there is more than 85 times as much lethal cesium on site as was released at Chernobyl.
Radioactive hot spots continue to be found around Japan. There are indications of heightened rates of thyroid damage among local children.
The immediate bottom line is that those fuel rods must somehow come safely out of the Unit Four fuel pool as soon as possible.
Just prior to the 2011 earthquake and tsunami that shattered the Fukushima site, the core of Unit Four was removed for routine maintenance and refueling. Like some two dozen reactors in the US and too many more around the world, the General Electric-designed pool into which that core now sits is 100 feet in the air.
Spent fuel must somehow be kept under water. It's clad in zirconium alloy which will spontaneously ignite when exposed to air. Long used in flash bulbs for cameras, zirconium burns with an extremely bright hot flame.
Each uncovered rod emits enough radiation to kill someone standing nearby in a matter of minutes. A conflagration could force all personnel to flee the site and render electronic machinery unworkable.
According to Arnie Gundersen, a nuclear engineer with forty years in an industry for which he once manufactured fuel rods, the ones in the Unit 4 core are bent, damaged and embrittled to the point of crumbling. Cameras have shown troubling quantities of debris in the fuel pool, which itself is damaged.
The engineering and scientific barriers to emptying the Unit Four fuel pool are unique and daunting, says Gundersen. But it must be done to 100% perfection.
Should the attempt fail, the rods could be exposed to air and catch fire, releasing horrific quantities of radiation into the atmosphere. The pool could come crashing to the ground, dumping the rods together into a pile that could fission and possibly explode. The resulting radioactive cloud would threaten the health and safety of all us.
Chernobyl's first 1986 fallout reached California within ten days. Fukushima's in 2011 arrived in less than a week. A new fuel fire at Unit 4 would pour out a continuous stream of lethal radioactive poisons for centuries.
Former Ambassador Mitsuhei Murata says full-scale releases from Fukushima "would destroy the world environment and our civilization. This is not rocket science, nor does it connect to the pugilistic debate over nuclear power plants. This is an issue of human survival."
Neither Tokyo Electric nor the government of Japan can go this alone. There is no excuse for deploying anything less than a coordinated team of the planet's best scientists and engineers.
We have two months or less to act.
For now, we are petitioning the United Nations and President Obama to mobilize the global scientific and engineering community to take charge at Fukushima and the job of moving these fuel rods to safety.
If you have a better idea, please follow it. But do something and do it now.
The clock is ticking. The hand of global nuclear disaster is painfully close to midnight.