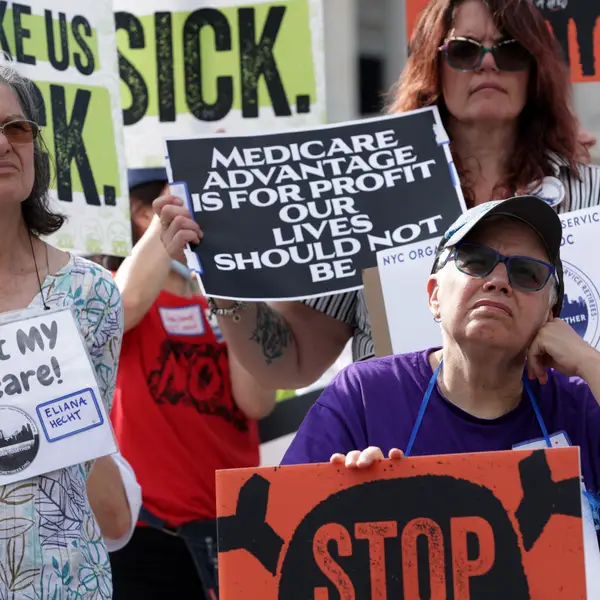Insurance giants are exploiting Medicare Advantage--a corporate-managed program that threatens to result in the complete privatization of traditional Medicare--to capture billions of dollars in extra profits, Saturday reporting by The New York Times confirmed.
" Medicare Advantage shouldn't exist."
The newspaper's analysis of dozens of lawsuits, inspector general reports, and watchdog investigations found that overbilling by Medicare Advantage (MA) providers is so pervasive it exceeds the budgets of entire federal agencies, prompting journalist Ryan Cooper to call the program "a straight up fraud scheme."
Nearly half of Medicare's 60 million beneficiaries are now enrolled in MA plans managed by for-profit insurance companies, and it is expected that most of the nation's seniors will be ensnared in the private-sector alternative to traditional Medicare by next year. Six weeks ago, Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) launched an inquiry into "potentially deceptive" marketing tactics used by MA providers to "take advantage" of vulnerable individuals.
As the table below shows, almost every major player in the industry has been accused of fraud by a whistleblower or the U.S. government. In addition, the vast majority are engaged in rampant upcoding, or exaggerating patients' illnesses in order to reap more money from taxpayers--something they do while refusing to provide necessary care for tens of thousands each year.
Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), which has no connection with Kaiser Permanente, wrote on social media that "the move to privatize Medicare" has "been very profitable, in part because insurers are good at making their patients seem sicker."
Journalist Natalie Shure concurred, tweeting: "Privatized Medicare plans cherry-pick healthier enrollees, fudge medical records to make them look as sick as possible, coax doctors into tacking on extra sham diagnoses to bill for, and pay themselves a profit on top of it. Medicare Advantage shouldn't exist."
"For all its faults, Medicare is a (nearly) universal program for 65+, with overhead hovering around 2%--far lower than its private counterparts," Shure added. "What inefficiencies did anyone think MA would be solving exactly[?]" she asked.
According to the Times, MA was created by congressional Republicans "two decades ago to encourage health insurers to find innovative ways to provide better care at lower cost."
Matt Bruenig, founder of the People's Policy Project, a left-wing think tank, argued that the notion that private insurers would "provide more benefit for less money" than traditional Medicare "while taking a profit" is insane on its face.
"They innovate on other margins, namely by bending and breaking rules that determine how much money Medicare gives them, as such things are hard to detect," said Bruenig, "and we are now stuck in an endless cat and mouse enforcement game with them."
As the Times reported:
The government pays Medicare Advantage insurers a set amount for each person who enrolls, with higher rates for sicker patients. And the insurers, among the largest and most prosperous American companies, have developed elaborate systems to make their patients appear as sick as possible, often without providing additional treatment, according to the lawsuits.
As a result, a program devised to help lower health care spending has instead become substantially more costly than the traditional government program it was meant to improve.
[...]
The government now spends nearly as much on Medicare Advantage's 29 million beneficiaries as on the Army and Navy combined. It's enough money that even a small increase in the average patient's bill adds up: The additional diagnoses led to $12 billion in overpayments in 2020, according to an estimate from the group that advises Medicare on payment policies--enough to cover hearing and vision care for every American over 65.
Another estimate, from a former top government health official, suggested the overpayments in 2020 were double that, more than $25 billion.
Citing a KFF study which found that companies typically rake in twice as much gross profit from MA plans as from other types of insurance, the Times pointed out that the growing privatization of Medicare is "strikingly lucrative."
MA plans "can limit patients' choice of doctors, and sometimes require jumping through more hoops before getting certain types of expensive care," the newspaper noted. "But they often have lower premiums or perks like dental benefits--extras that draw beneficiaries to the programs. The more the plans are overpaid by Medicare, the more generous to customers they can afford to be."
"By exploiting and overbilling Medicare, these companies profit off the public. Think of how this money could have been better spent."
The MA program has grown in popularity, including in Democratic strongholds, over the course of four presidential administrations. Meanwhile, regulatory and legislative efforts to rein in abuses have failed to gain traction.
Officials at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), some of whom move between the agency and industry, have not been aggressive "even as the overpayments have been described in inspector general investigations, academic research, Government Accountability Office studies, MedPAC reports, and numerous news articles," the Times reported. "Congress gave the agency the power to reduce the insurers' rates in response to evidence of systematic overbilling, but CMS has never chosen to do so."
Ted Doolittle, who served as a senior official for CMS' Center for Program Integrity from 2011 to 2014, said that "it was clear that there was some resistance coming from inside" the agency. "There was foot-dragging."
Almost 80% percent of U.S. House members, many of whom are bankrolled by the insurance industry, signed a letter earlier this year indicating their readiness "to protect the program from policies that would undermine" its stability.
David Moore, co-founder of Sludge, an independent news outlet focused on the corrupting influence of corporate cash on politics, observed on social media that "members of the health subcommittee of the House Ways and Means Committee could speak publicly on whether they think oversight of the insurance industry has been adequate."
However, Moore pointed out, committee Chair Richard Neal (D-Mass.) "has received $3.1 million from the insurance industry, the most in the House."
As the Times noted, "Some critics say the lack of oversight has encouraged the industry to compete over who can most effectively game the system rather than who can provide the best care."
"Medicare Advantage overpayments are a political third rail," Richard Gilfillan, a former hospital and insurance executive and a former top regulator at Medicare, told the newspaper. "The big healthcare plans know it's wrong, and they know how to fix it, but they're making too much money to stop."
"There's a risk" that the increased scrutiny of MA providers "blows over because the program's beneficiaries continue to have access to doctors and hospitals," Joseph Ross, a primary care physician and health policy researcher at the Yale School of Medicine, wrote on Twitter. "But by exploiting and overbilling Medicare, these companies profit off the public."
"Think of how this money could have been better spent," said Ross. "The overbilling alone could have provided hearing and vision care to ALL Medicare beneficiaries, or been used to fund any of these agency's budgets."
"The overbilling alone could have provided hearing and vision care to ALL Medicare beneficiaries."
Despite mounting evidence of widespread fraud in MA plans, the Biden administration announced in April that MA insurers will receive one of the largest payment increases in the program's history in 2023, eliciting pushback from several congressional Democrats led by Rep. Katie Porter of California.
Progressives argue that MA is part of a broader effort to privatize Medicare and must be resisted.
Another major culprit is ACO REACH, a pilot program that critics have described as "Medicare Advantage on steroids."
The pilot--an updated version of Direct Contracting launched by the Trump administration and continued by the Biden administration--invites MA insurers and Wall Street firms to "manage" care for Medicare beneficiaries and allows the profit-maximizing middlemen to pocket as much as 40% of what they don't spend on patients, all but ensuring deadly cost-cutting.
Physicians and healthcare advocates have warned that failing to stop ACO REACH could result in the total privatization of traditional Medicare in a matter of years.
"Even though Medicare is relied on by millions of seniors across the country, and precisely because it is so necessary and cost-effective, it is under threat today from the constant efforts of private insurance companies and for-profit investors who want to privatize it and turn it into yet another shameful opportunity to make money off of peoples' health problems," Rep. Pramila Jayapal (D-Wash.) said in May.
Jayapal, chair of the Congressional Progressive Caucus, has called on the Biden administration to "fully end" ACO REACH and other privatization schemes and urged lawmakers to enact the Medicare for All Act, of which she is the lead sponsor in the House.
Numerous studies have found that implementing a single-payer health insurance program would guarantee the provision of lifesaving care for every person in the country while reducing overall spending by as much as $650 billion per year.