

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
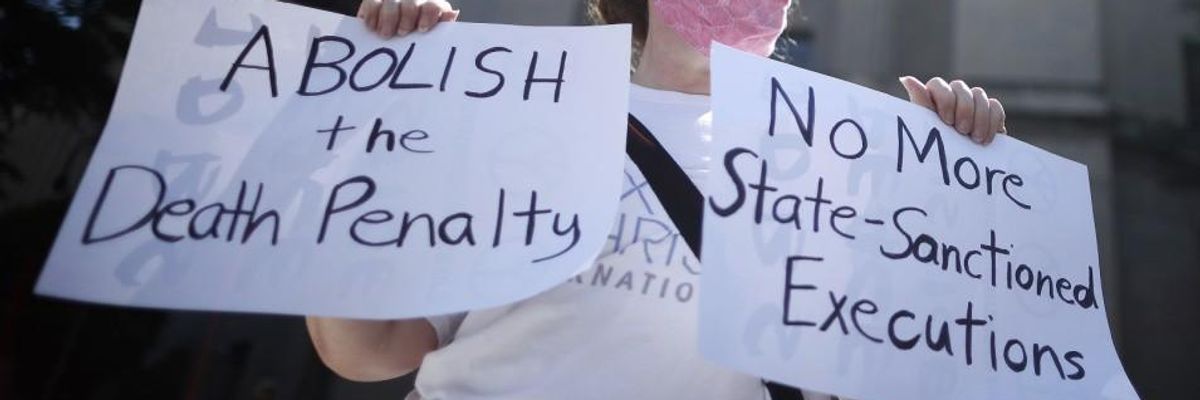
Anti-death penalty activist Judy Coode of Pax Christi International demonstrates in front of the U.S. Justice Department's Robert F. Kennedy Building July 13, 2020 in Washington, D.C.
"The death penalty is the ultimate cruel, inhuman, and degrading punishment, and we urge Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey to use her clemency power to stop the execution of Kenneth Smith before it's too late," said one group.
The U.S. Supreme Court on Wednesday denied an application to stop the execution of a man on Alabama's death row who is set to become the first person in the country to be killed with nitrogen gas in a method rejected by veterinarians for euthanizing animals and condemned by United Nations human rights experts as possible torture.
The justices rejected assertions by lawyers representing 58-year-old Kenneth Smith—who was convicted and sentenced to death for the 1988 murder of Elizabeth Sennett—that execution by the untested method of suffocation with nitrogen gas violates the U.S. Constitution's prohibition of "cruel and unusual punishment."
The attorneys' argument was based largely on the fact that Smith survived a botched attempt to execute him by lethal injection in November 2022.
Smith's petition for a writ of certiorari asked: "Does a second attempt to execute a condemned person following a single, cruelly willful attempt to execute that same person violate the prohibition against cruel and unusual punishments under the Eighth and 14th amendments to the United States Constitution?"
A separate challenge by Smith to the use of nitrogen gas in his execution is pending before the 11th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals.
Two other states, Mississippi and Oklahoma, have approved the use of nitrogen gas for executions. States have scrambled to find alternative means of killing condemned inmates after the European Union banned the sale and export of lethal injection drugs in 2011.
Earlier this month, Ravina Shamdasani, a spokesperson for the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, warned that the U.S. may be violating the Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment by allowing Smith's execution by nitrogen asphyxia.
Shamdasani noted that the American Veterinary Medical Association recommends sedating animals before euthanizing them with nitrogen—a step that is not included in Alabama's protocol.
In addition to concerns over the method of Smith's impending execution, advocates have also pointed to flaws in his sentencing process. The jury that convicted him in 1996 voted 11-1 to recommend a sentence of life imprisonment without the possibility of parole, but a judge invoked a since-outlawed rule to override the jurors.
Rights groups urged Alabama's Republican governor to halt Smith's execution—a move she declined in 2022.
"The death penalty is the ultimate cruel, inhuman, and degrading punishment, and we urge Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey to use her clemency power to stop the execution of Kenneth Smith before it's too late," Amnesty International implored Wednesday.
Abraham Bonowitz, co-founder of the abolitionist group Death Penalty Action, called Wednesday "a shameful day for our country."
"The discussion that is missing in all of this hubbub around nitrogen hypoxia is the mental torture of a second execution attempt," he added. "That, and the fact that if Kenny Smith were on trial today, he could not be sentenced to death at all because his jury was not unanimous regarding his sentence. Jury overrides were outlawed in Alabama in 2017. Alabama's capital punishment system as a whole is broken and cannot be trusted to get it right."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
The U.S. Supreme Court on Wednesday denied an application to stop the execution of a man on Alabama's death row who is set to become the first person in the country to be killed with nitrogen gas in a method rejected by veterinarians for euthanizing animals and condemned by United Nations human rights experts as possible torture.
The justices rejected assertions by lawyers representing 58-year-old Kenneth Smith—who was convicted and sentenced to death for the 1988 murder of Elizabeth Sennett—that execution by the untested method of suffocation with nitrogen gas violates the U.S. Constitution's prohibition of "cruel and unusual punishment."
The attorneys' argument was based largely on the fact that Smith survived a botched attempt to execute him by lethal injection in November 2022.
Smith's petition for a writ of certiorari asked: "Does a second attempt to execute a condemned person following a single, cruelly willful attempt to execute that same person violate the prohibition against cruel and unusual punishments under the Eighth and 14th amendments to the United States Constitution?"
A separate challenge by Smith to the use of nitrogen gas in his execution is pending before the 11th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals.
Two other states, Mississippi and Oklahoma, have approved the use of nitrogen gas for executions. States have scrambled to find alternative means of killing condemned inmates after the European Union banned the sale and export of lethal injection drugs in 2011.
Earlier this month, Ravina Shamdasani, a spokesperson for the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, warned that the U.S. may be violating the Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment by allowing Smith's execution by nitrogen asphyxia.
Shamdasani noted that the American Veterinary Medical Association recommends sedating animals before euthanizing them with nitrogen—a step that is not included in Alabama's protocol.
In addition to concerns over the method of Smith's impending execution, advocates have also pointed to flaws in his sentencing process. The jury that convicted him in 1996 voted 11-1 to recommend a sentence of life imprisonment without the possibility of parole, but a judge invoked a since-outlawed rule to override the jurors.
Rights groups urged Alabama's Republican governor to halt Smith's execution—a move she declined in 2022.
"The death penalty is the ultimate cruel, inhuman, and degrading punishment, and we urge Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey to use her clemency power to stop the execution of Kenneth Smith before it's too late," Amnesty International implored Wednesday.
Abraham Bonowitz, co-founder of the abolitionist group Death Penalty Action, called Wednesday "a shameful day for our country."
"The discussion that is missing in all of this hubbub around nitrogen hypoxia is the mental torture of a second execution attempt," he added. "That, and the fact that if Kenny Smith were on trial today, he could not be sentenced to death at all because his jury was not unanimous regarding his sentence. Jury overrides were outlawed in Alabama in 2017. Alabama's capital punishment system as a whole is broken and cannot be trusted to get it right."
The U.S. Supreme Court on Wednesday denied an application to stop the execution of a man on Alabama's death row who is set to become the first person in the country to be killed with nitrogen gas in a method rejected by veterinarians for euthanizing animals and condemned by United Nations human rights experts as possible torture.
The justices rejected assertions by lawyers representing 58-year-old Kenneth Smith—who was convicted and sentenced to death for the 1988 murder of Elizabeth Sennett—that execution by the untested method of suffocation with nitrogen gas violates the U.S. Constitution's prohibition of "cruel and unusual punishment."
The attorneys' argument was based largely on the fact that Smith survived a botched attempt to execute him by lethal injection in November 2022.
Smith's petition for a writ of certiorari asked: "Does a second attempt to execute a condemned person following a single, cruelly willful attempt to execute that same person violate the prohibition against cruel and unusual punishments under the Eighth and 14th amendments to the United States Constitution?"
A separate challenge by Smith to the use of nitrogen gas in his execution is pending before the 11th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals.
Two other states, Mississippi and Oklahoma, have approved the use of nitrogen gas for executions. States have scrambled to find alternative means of killing condemned inmates after the European Union banned the sale and export of lethal injection drugs in 2011.
Earlier this month, Ravina Shamdasani, a spokesperson for the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, warned that the U.S. may be violating the Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment by allowing Smith's execution by nitrogen asphyxia.
Shamdasani noted that the American Veterinary Medical Association recommends sedating animals before euthanizing them with nitrogen—a step that is not included in Alabama's protocol.
In addition to concerns over the method of Smith's impending execution, advocates have also pointed to flaws in his sentencing process. The jury that convicted him in 1996 voted 11-1 to recommend a sentence of life imprisonment without the possibility of parole, but a judge invoked a since-outlawed rule to override the jurors.
Rights groups urged Alabama's Republican governor to halt Smith's execution—a move she declined in 2022.
"The death penalty is the ultimate cruel, inhuman, and degrading punishment, and we urge Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey to use her clemency power to stop the execution of Kenneth Smith before it's too late," Amnesty International implored Wednesday.
Abraham Bonowitz, co-founder of the abolitionist group Death Penalty Action, called Wednesday "a shameful day for our country."
"The discussion that is missing in all of this hubbub around nitrogen hypoxia is the mental torture of a second execution attempt," he added. "That, and the fact that if Kenny Smith were on trial today, he could not be sentenced to death at all because his jury was not unanimous regarding his sentence. Jury overrides were outlawed in Alabama in 2017. Alabama's capital punishment system as a whole is broken and cannot be trusted to get it right."