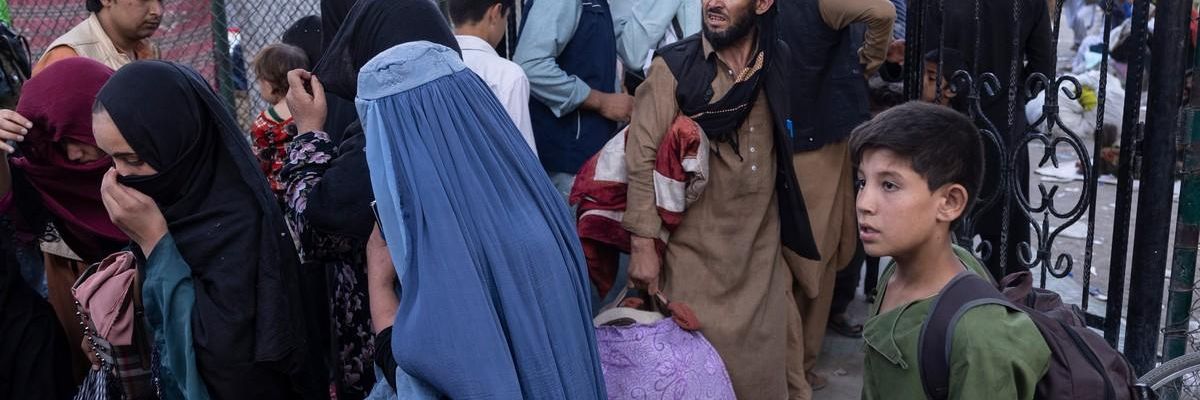
For twenty years, two dominant narratives have shaped our view of the illegal US invasion and occupation of Afghanistan, and neither one of these narratives would readily accept the use of such terms as 'illegal', 'invasion' and 'occupation.'
The framing of the US 'military intervention' in Afghanistan, starting on October 7, 2001, as the official start of what was dubbed as a global 'war on terror' was left almost entirely to US government strategists. Former President, George W. Bush, his Vice President, Dick Cheney, his Secretary of Defense, Donald Rumsfeld and an army of spokespersons, neoconservative 'intellectuals', journalists and so on, championed the military option as a way to rid Afghanistan of its terrorists, make the world a safe place and, as a bonus, bring democracy to Afghanistan and free its oppressed women.
The US-Western propaganda, which has afflicted our collective understanding of Afghanistan for twenty years and counting, has been so overpowering to the point that we are left without the slightest understanding of the dynamics that led to the Taliban's swift takeover of the country.
For that crowd, the US war in an already war-torn and extremely impoverished country was a just cause, maybe violent at times, but ultimately humanistic.
Another narrative, also a western one, challenged the gung-ho approach used by the Bush administration, argued that democracy cannot be imposed by force, reminded Washington of Bill Clinton's multilateral approach to international politics, warned against the 'cut and run' style of foreign policymaking, whether in Afghanistan, Iraq or elsewhere.
Although both narratives may have seemed at odds, at times, in actuality they accepted the basic premise that the United States is capable of being a moral force in Afghanistan and elsewhere. Whether those who may refer to themselves as 'antiwar' realize this or not, they, too, subscribe to the same notion of American exceptionalism and 'Manifest Destiny' that Washington continues to assign to itself.
The main difference between both of these narratives is that of methodology and approach and not whether the US has the right to 'intervene' in the affairs of another country, whether to 'eradicate terrorism' or to supposedly help a victim population, incapable of helping themselves and desperate for a western savior.
However, the humiliating defeat suffered by the US in Afghanistan should inspire a whole new way of thinking, one that challenges all Western narratives, without exception, in Afghanistan and throughout the world.
Obviously, the US has failed in Afghanistan, not only militarily and politically--let alone in terms of 'state-building' and every other way--the US-Western narratives on Afghanistan were, themselves, a failure. Mainstream media, which for two decades have reported on the country with a palpable sense of moral urgency, now seem befuddled. US 'experts' are as confused as ordinary people regarding the hasty retreat from Kabul, the bloody mayhem at the airport or why the US was in Afghanistan in the first place.
Meanwhile, the 'humanistic interventionists' are more concerned with Washington's 'betrayal' of the Afghan people, 'leaving them to their fate', as if the Afghans are irrational beings with no agency of their own, or as if the Afghan people have called on the Americans to invade their country or have 'elected' American generals as their democratic representatives.
The US-Western propaganda, which has afflicted our collective understanding of Afghanistan for twenty years and counting, has been so overpowering to the point that we are left without the slightest understanding of the dynamics that led to the Taliban's swift takeover of the country. The latter group is presented in the media as if entirely alien to the socio-economic fabric of Afghanistan. This is why the Taliban's ultimate victory seemed, not only shocking but extremely confusing as well.
For twenty years, the very little we knew about the Taliban has been communicated to us through Western media analyses and military intelligence assessments. With the Taliban's viewpoint completely removed from any political discourse pertaining to Afghanistan, an alternative Afghan national narrative was carefully constructed by the US and its NATO partners. These were the 'good Afghans', we were told, ones who dress up in Western-style clothes, speak English, attend international conferences and, supposedly, respect women. These were also the Afghans who welcomed the US occupation of their country, as they benefited greatly from Washington's generosity.
If those 'good Afghans' truly represented Afghan society, why did their army of 300,000 men drop their weapons and flee the country, along with their President, without a serious fight? And if the 75,000 poorly-armed and, at times, malnourished Taliban seemed to merely represent themselves, why then did they manage to defeat formidable enemies in a matter of days?
There can be no argument that an inferior military power, like that of the Taliban, could have possibly persisted, and ultimately won, such a brutal war over the course of many years, without substantial grassroots support pouring in from the Afghan people in large swathes of the country. The majority of the Taliban recruits who have entered Kabul on August 15 were either children, or were not even born, when the US invaded their country, all those years ago. What compelled them to carry arms? To fight a seemingly unwinnable war? To kill and be killed? And why did they not join the more lucrative business of working for the Americans, like many others have?
We are just beginning to understand the Taliban narrative, as their spokespersons are slowly communicating a political discourse that is almost entirely unfamiliar to most of us. A discourse that we were not allowed to hear, interact with or understand.
Now that the US and its NATO allies are leaving Afghanistan, unable to justify or even explain why their supposed humanitarian mission led to such an embarrassing defeat, the Afghan people are left with the challenge of weaving their own national narrative, one that must transcend the Taliban and their enemies to include all Afghans, regardless of their politics or ideology.
Afghanistan is now in urgent need of a government that truly represents the people of that country. It must grant rights to education, to minorities and to political dissidents, not to acquire a Western nod of approval, but because the Afghan people deserve to be respected, cared for and treated as equals. This is the true national narrative of Afghanistan that must be nurtured outside the confines of the self-serving Western mischaracterization of Afghanistan and her people.