
A new study from United Way found 43 percent of U.S. households struggle to afford basic expenses. (Photo: Len Tsou/Flickr/cc)
Sanders Slams US Inequality as Report Finds Nearly Half of Americans Can't Afford Basic Necessities
"The three wealthiest people in America own more wealth than the bottom 50 percent — over 160 million people," says Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.).
"Is that really the kind of society we want to be living in?"
That's how Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) responded to a new study from United Way's ALICE Project, which found that 43 percent of U.S. households--nearly 51 million families--cannot afford "a bare-bones household budget of housing, child care, food, transportation, and healthcare."
Sanders has long advocated for policies to serve these households. The senator is working on a plan that would establish a federal jobs guarantee, and during the current session of Congress, he has introduced legislation that would strengthen trade unions and ensure healthcare for all Americans through a "Medicare for All" model.
ALICE--which stands for Asset Limited, Income Constrained, Employed--is a term United Way developed to describe the population that is above the federal poverty level but still struggling to pay for basic expenses. In addition to the 16.1 million American families living below the poverty line, 34.7 million U.S. households fit the group's ALICE classification.
"People are struggling to make their ends meet. Not hard to see why problematic substance use and suicide are at crisis levels," tweeted Leo Beletsky, a professor of law and public health at Northeastern University.
"Many of these folks are the nation's child care workers, home health aides, office assistants, and store clerks, who work low-paying jobs and have little savings," CNN reported. "California, New Mexico, and Hawaii have the largest share of struggling families, at 49 percent each."
Project director Stephanie Hoopes told CNN that "despite seemingly positive economic signs, the ALICE data shows that financial hardship is still a pervasive problem."
The study, Axios noted, "suggests that the economically forgotten are a far bigger group than many studies assume," and according to Hoopes, that group seems to be growing.
"It's a magnitude of financial hardship that we haven't been able to capture until now," she said.
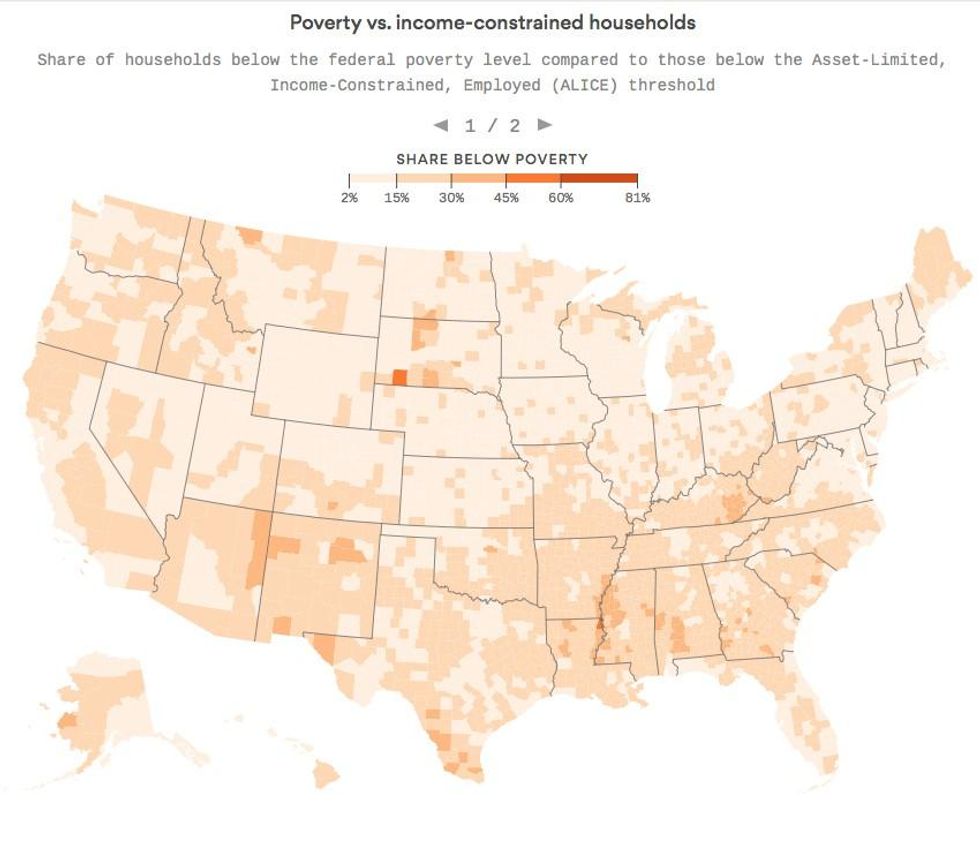
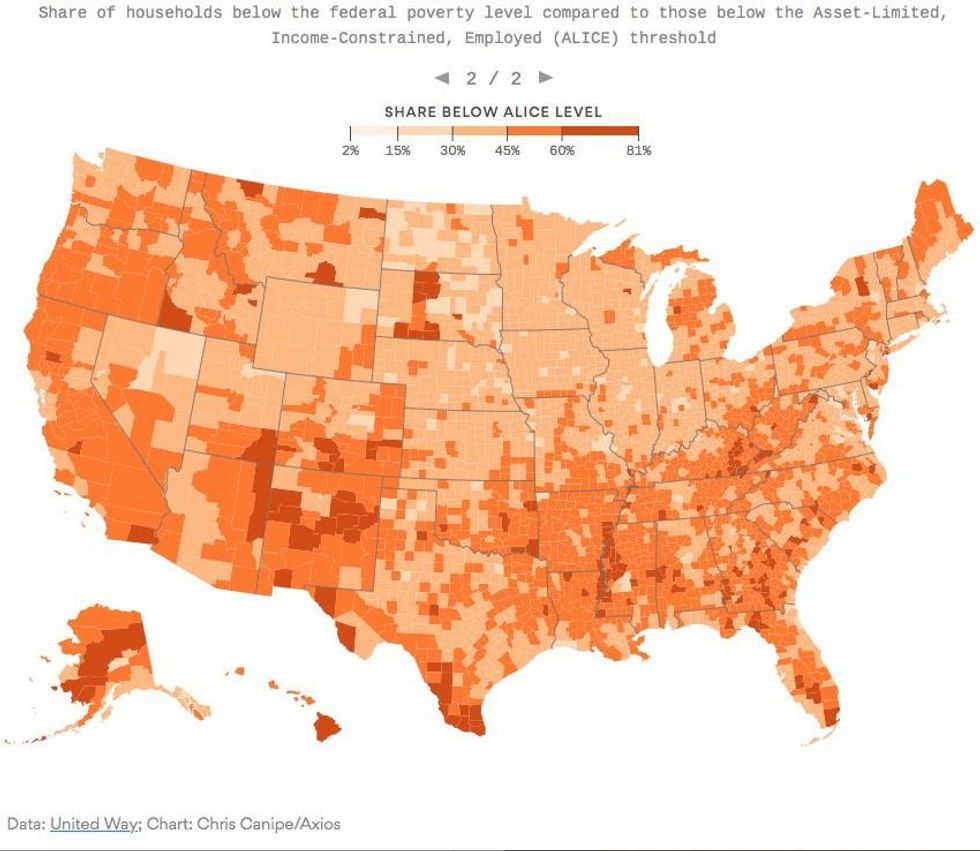
In a pair of graphics, Axios showed how the official federal poverty level fails to accurately measure the number of U.S. families that cannot afford basic costs of living.
An Urgent Message From Our Co-Founder
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
"Is that really the kind of society we want to be living in?"
That's how Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) responded to a new study from United Way's ALICE Project, which found that 43 percent of U.S. households--nearly 51 million families--cannot afford "a bare-bones household budget of housing, child care, food, transportation, and healthcare."
Sanders has long advocated for policies to serve these households. The senator is working on a plan that would establish a federal jobs guarantee, and during the current session of Congress, he has introduced legislation that would strengthen trade unions and ensure healthcare for all Americans through a "Medicare for All" model.
ALICE--which stands for Asset Limited, Income Constrained, Employed--is a term United Way developed to describe the population that is above the federal poverty level but still struggling to pay for basic expenses. In addition to the 16.1 million American families living below the poverty line, 34.7 million U.S. households fit the group's ALICE classification.
"People are struggling to make their ends meet. Not hard to see why problematic substance use and suicide are at crisis levels," tweeted Leo Beletsky, a professor of law and public health at Northeastern University.
"Many of these folks are the nation's child care workers, home health aides, office assistants, and store clerks, who work low-paying jobs and have little savings," CNN reported. "California, New Mexico, and Hawaii have the largest share of struggling families, at 49 percent each."
Project director Stephanie Hoopes told CNN that "despite seemingly positive economic signs, the ALICE data shows that financial hardship is still a pervasive problem."
The study, Axios noted, "suggests that the economically forgotten are a far bigger group than many studies assume," and according to Hoopes, that group seems to be growing.
"It's a magnitude of financial hardship that we haven't been able to capture until now," she said.
In a pair of graphics, Axios showed how the official federal poverty level fails to accurately measure the number of U.S. families that cannot afford basic costs of living.


"Is that really the kind of society we want to be living in?"
That's how Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) responded to a new study from United Way's ALICE Project, which found that 43 percent of U.S. households--nearly 51 million families--cannot afford "a bare-bones household budget of housing, child care, food, transportation, and healthcare."
Sanders has long advocated for policies to serve these households. The senator is working on a plan that would establish a federal jobs guarantee, and during the current session of Congress, he has introduced legislation that would strengthen trade unions and ensure healthcare for all Americans through a "Medicare for All" model.
ALICE--which stands for Asset Limited, Income Constrained, Employed--is a term United Way developed to describe the population that is above the federal poverty level but still struggling to pay for basic expenses. In addition to the 16.1 million American families living below the poverty line, 34.7 million U.S. households fit the group's ALICE classification.
"People are struggling to make their ends meet. Not hard to see why problematic substance use and suicide are at crisis levels," tweeted Leo Beletsky, a professor of law and public health at Northeastern University.
"Many of these folks are the nation's child care workers, home health aides, office assistants, and store clerks, who work low-paying jobs and have little savings," CNN reported. "California, New Mexico, and Hawaii have the largest share of struggling families, at 49 percent each."
Project director Stephanie Hoopes told CNN that "despite seemingly positive economic signs, the ALICE data shows that financial hardship is still a pervasive problem."
The study, Axios noted, "suggests that the economically forgotten are a far bigger group than many studies assume," and according to Hoopes, that group seems to be growing.
"It's a magnitude of financial hardship that we haven't been able to capture until now," she said.
In a pair of graphics, Axios showed how the official federal poverty level fails to accurately measure the number of U.S. families that cannot afford basic costs of living.



