

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

Jeff Miller, Center for Biological Diversity, (510) 499-9185
New surveys show a 27-percent drop in the number of breeding burrowing owls in California's Imperial Valley and provide some of the most striking evidence yet that the species is badly in need of state protections. Recent surveys of the state's largest burrowing owl population have been conducted by the Imperial Irrigation District. The Imperial owl population has declined from an estimated 5,600 pairs in the early 1990s to 4,879 pairs in 2007, then dropped sharply to 3,557 pairs in 2008.
"It's alarming to see such a rapid, single-year drop in owl numbers in an area that is supposed to be a stronghold. Breeding owls been eliminated from a quarter of their former range in California over the past two decades as their habitat has been destroyed and they've been shoved aside for urban development," said Jeff Miller, conservation advocate at the Center for Biological Diversity, which led several groups in petitioning for state Endangered Species Act protection for the owl in 2003. "A state threatened listing is clearly needed for burrowing owls, which are likely to disappear from major portions of the state. It is now uncertain whether owls will persist in areas they were thought to be secure, including the Imperial Valley."
Burrowing owls in the Imperial Valley nest almost entirely in ground-squirrel burrows along earthen irrigation canals and drains. They represent nearly half the state's breeding pairs. Once common in California, burrowing owls have been driven out of much of the state, with large populations primarily in areas of intensive agriculture, including parts of the Central Valley, along the lower Colorado River and the Imperial Valley.
The California Fish and Game Commission rejected the 2003 petition following a highly controversial assessment by the Department of Fish and Game. After the vote, it was revealed that agency biologists evaluating the petition concluded that the burrowing owl should be protected as a "candidate" species and considered for endangered or threatened status, but the Department suppressed their report and recommended against listing.
Burrowing owls face multiple significant threats, including habitat loss and fragmentation by urban development, elimination of burrowing rodents and destruction of burrows, pesticides, predation by nonnative species, vehicle strikes, collisions with wind turbines and shooting. The state has allowed landowners to evict and "passively relocate" owls from development sites, with inadequate mitigation and no assurances that relocated owls are able to survive.
It is unknown what is causing the Imperial owl decline, but loss of suitable foraging areas from fallowing of agricultural fields due to water transfers and ground-squirrel eradication programs may play a role. There is no evidence that the Imperial owls are moving elsewhere in California.
The information about Imperial Valley burrowing owl declines is buried in a 2009 annual report by the Imperial Irrigation District to the State Water Resources Control Board that can be found at https://www.iid.com/Media/2009-Report.pdf on page 176. The significant decline in the Imperial Valley has not been publicized by the Department of Fish and Game, which is currently preparing a state burrowing owl "Conservation Strategy" designed to prevent listing, and will rely primarily on voluntary measures and provide no effective legal protection for owl habitat.
Background
The western burrowing owl (Athene cunicularia hypugaea) is a small, ground-nesting bird of prairie and grassland habitats. Its breeding range is west of the Mississippi River to the Pacific, north into Canada and south to Mexico. The species has declined significantly throughout North America, is listed as endangered in Canada and threatened in Mexico, and is state-listed as endangered in Minnesota and threatened in Colorado. Many other states, including California, list it as a state "species of special concern." California supports the largest remaining breeding and wintering populations of western burrowing owls. There are no state or federal laws that protect burrowing owl habitat, which is rarely purchased by agencies to conserve the owl or other grassland-dependent species. An estimated 91 percent of all burrowing owls in California occur on private land, much of which is threatened by future development.
Early accounts of the burrowing owl in California described it as one of the state's most common birds in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Owl numbers have dropped steadily since the 1940s; by the mid-1990s surveys estimated 9,450 owl nesting pairs in the primary range of California burrowing owls, with 5,600 pairs thought to nest in the Imperial Valley. The number of breeding owl colonies in the survey area declined by nearly 60 percent from the 1980s to the early 1990s, and the statewide number of owls is now thought to be continuing to decline by about 8 percent per year due to urban development. The Institute for Bird Populations conducted a follow-up statewide survey in 2007 and 2008, and preliminary data indicates owl populations continue to decline in most areas of the state. Breeding owls have been largely eliminated from Sonoma, Napa, Marin, western Contra Costa, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Cruz, Monterey, San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, Orange and San Diego counties.
Most of the state's remaining breeding owls are concentrated in the Imperial Valley, an area that makes up only 2.5 percent of the state's land area. These owls face threats from conversion of agricultural lands to urban development, plans to line earthen canals with concrete, and ground-squirrel eradication. Throughout the vast majority of the owl's range in California, breeding owls persist in only small, declining populations of birds that are highly susceptible to extirpation.
The Department's conclusions regarding the burrowing owl listing petition were widely criticized by owl experts as fraught with inaccuracies, speculation and inconsistencies. The agency's reasoning that listing of the burrowing owl was not warranted relied on erroneous premises: that there was insufficient information on the historic range and abundance of the species; that a shift in owl population density has occurred, with increased densities appearing in the Imperial Valley balancing out reduced densities elsewhere in the state; that significant exchange occurs between regional populations; and that the Imperial Valley and other larger populations can maintain the species by augmenting declining populations elsewhere.
But banding data on owls in California shows little evidence of connectivity between regional populations, and larger southern populations have never been shown to serve as source populations for declining owl colonies elsewhere. The recent decline in the Imperial Valley undermines the Department's arguments about a stable overall state population. Significant breeding-owl declines have been shown in almost every part of the state; the species is threatened in a significant portion of its range.
At the Center for Biological Diversity, we believe that the welfare of human beings is deeply linked to nature — to the existence in our world of a vast diversity of wild animals and plants. Because diversity has intrinsic value, and because its loss impoverishes society, we work to secure a future for all species, great and small, hovering on the brink of extinction. We do so through science, law and creative media, with a focus on protecting the lands, waters and climate that species need to survive.
(520) 623-5252"The only beneficiaries will be polluting industries, many of which are among President Trump’s largest donors,” the lawmakers wrote.
A group of 31 Democratic senators has launched an investigation into a new Trump administration policy that they say allows the Environmental Protection Agency to "disregard" the health impacts of air pollution when passing regulations.
Plans for the policy were first reported on last month by the New York Times, which revealed that the EPA was planning to stop tallying the financial value of health benefits caused by limiting fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone when regulating polluting industries and instead focus exclusively on the costs these regulations pose to industry.
On December 11, the Times reported that the policy change was being justified based on the claim that the exact benefits of curbing these emissions were “uncertain."
"Historically, the EPA’s analytical practices often provided the public with false precision and confidence regarding the monetized impacts of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone," said an email written by an EPA supervisor to his employees on December 11. “To rectify this error, the EPA is no longer monetizing benefits from PM2.5 and ozone.”
The group of senators, led by Sen. Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI), rebuked this idea in a letter sent Thursday to EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin.
"EPA’s new policy is irrational. Even where health benefits are 'uncertain,' what is certain is that they are not zero," they said. "It will lead to perverse outcomes in which EPA will reject actions that would impose relatively minor costs on polluting industries while resulting in massive benefits to public health—including in saved lives."
"It is contrary to Congress’s intent and directive as spelled out in the Clean Air Act. It is legally flawed," they continued. "The only beneficiaries will be polluting industries, many of which are among President [Donald] Trump’s largest donors."
Research published in 2023 in the journal Science found that between 1999 and 2020, PM2.5 pollution from coal-fired power plants killed roughly 460,000 people in the United States, making it more than twice as deadly as other kinds of fine particulate emissions.
While this is a staggering loss of life, the senators pointed out that the EPA has also been able to put a dollar value on the loss by noting quantifiable results of increased illness and death—heightened healthcare costs, missed school days, and lost labor productivity, among others.
Pointing to EPA estimates from 2024, they said that by disregarding human health effects, the agency risks costing Americans “between $22 and $46 billion in avoided morbidities and premature deaths in the year 2032."
Comparatively, they said, “the total compliance cost to industry, meanwhile, [would] be $590 million—between one and two one-hundredths of the estimated health benefit value."
They said the plan ran counter to the Clean Air Act's directive to “protect and enhance the quality of the Nation’s air resources so as to promote the public health and welfare,” and to statements made by Zeldin during his confirmation hearing, where he said "the end state of all the conversations that we might have, any regulations that might get passed, any laws that might get passed by Congress” is to “have the cleanest, healthiest air, [and] drinking water.”
The senators requested all documents related to the decision, including any information about cost-benefit modeling and communications with industry representatives.
"That EPA may no longer monetize health benefits when setting new clean air standards does not mean that those health benefits don’t exist," the senators said. "It just means that [EPA] will ignore them and reject safer standards, in favor of protecting corporate interests."
"An unmistakable majority wants a party that will fight harder against the corporations and rich people they see as responsible for keeping them down," wrote the New Republic's editorial director.
Democratic voters overwhelmingly want a leader who will fight the superrich and corporate America, and they believe Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez is the person to do it, according to a poll released this week.
While Democrats are often portrayed as squabbling and directionless, the poll conducted last month by the New Republic with Embold Research demonstrated a remarkable unity among the more than 2,400 Democratic voters it surveyed.
This was true with respect to policy: More than 9 in 10 want to raise taxes on corporations and on the wealthiest Americans, while more than three-quarters want to break up tech monopolies and believe the government should conduct stronger oversight of business.
But it was also reflected in sentiments that a more confrontational governing philosophy should prevail and general agreement that the party in its current form is not doing enough to take on its enemies.
Three-quarters said they wanted Democrats to "be more aggressive in calling out Republicans," while nearly 7 in 10 said it was appropriate to describe their party as "weak."
This appears to have translated to support for a more muscular view of government. Where the label once helped to sink Sen. Bernie Sanders' (I-Vt.) two runs for president, nearly three-quarters of Democrats now say they are either unconcerned with the label of "socialist" or view it as an asset.
Meanwhile, 46% said they want to see a "progressive" at the top of the Democratic ticket in 2028, higher than the number who said they wanted a "liberal" or a "moderate."
It's an environment that appears to be fertile ground for Ocasio-Cortez, who pitched her vision for a "working-class-centered politics" at this week's Munich summit in what many suspected was a soft-launch of her presidential candidacy in 2028.
With 85% favorability, Bronx congresswoman had the highest approval rating of any Democratic figure in the country among the voters surveyed.
It's a higher mark than either of the figures who head-to-head polls have shown to be presumptive favorites for the nomination: Former Vice President Kamala Harris and California Gov. Gavin Newsom.
Early polls show AOC lagging considerably behind these top two. However, there are signs in the New Republic's poll that may give her supporters cause for hope.
While Harris is also well-liked, 66% of Democrats surveyed said they believe she's "had her shot" at the presidency and should not run again after losing to President Donald Trump in 2024.
Newsom does not have a similar electoral history holding him back and is riding high from the passage of Proposition 50, which will allow Democrats to add potentially five more US House seats this November.
But his policy approach may prove an ill fit at a time when Democrats overwhelmingly say their party is "too timid" about taxing the rich and corporations and taking on tech oligarchs.
As labor unions in California have pushed for a popular proposal to introduce a billionaire's tax, Newsom has made himself the chiseled face of the resistance to this idea, joining with right-wing Silicon Valley barons in an aggressive campaign to kill it.
While polls can tell us little two years out about what voters will do in 2028, New Republic editorial director Emily Cooke said her magazine's survey shows an unmistakable pattern.
"It’s impossible to come away from these results without concluding that economic populism is a winning message for loyal Democrats," she wrote. "This was true across those who identify as liberals, moderates, or progressives: An unmistakable majority wants a party that will fight harder against the corporations and rich people they see as responsible for keeping them down."
In some cases, the administration has kept immigrants locked up even after a judge has ordered their release, according to an investigation by Reuters.
Judges across the country have ruled more than 4,400 times since the start of October that US Immigration and Customs Enforcement has illegally detained immigrants, according to a Reuters investigation published Saturday.
As President Donald Trump carries out his unprecedented "mass deportation" crusade, the number of people in ICE custody ballooned to 68,000 this month, up 75% from when he took office.
Midway through 2025, the administration had begun pushing for a daily quota of 3,000 arrests per day, with the goal of reaching 1 million per year. This has led to the targeting of mostly people with no criminal records rather than the "worst of the worst," as the administration often claims.
Reuters' reporting suggests chasing this number has also resulted in a staggering number of arrests that judges have later found to be illegal.
Since the beginning of Trump's term, immigrants have filed more than 20,200 habeas corpus petitions, claiming they were held indefinitely without trial in violation of the Constitution.
In at least 4,421 cases, more than 400 federal judges have ruled that their detentions were illegal.
Last month, more than 6,000 habeas petitions were filed. Prior to the second Trump administration, no other month dating back to 2010 had seen even 500.
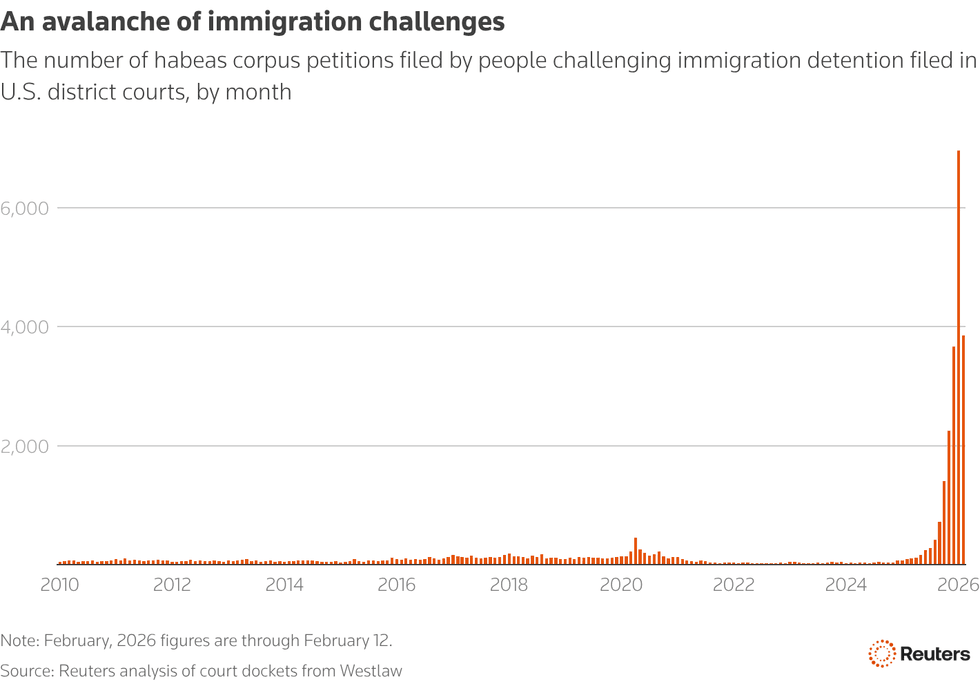
In part due to the sheer volume of legal challenges, the Trump administration has often failed to comply with court rulings, leaving people locked up even after judges ordered them to be released.
Reuters' new report is the most comprehensive examination to date of the administration's routine violation of the law with respect to immigration enforcement. But the extent to which federal immigration agencies have violated the law under Trump is hardly new information.
In a ruling last month, Chief Judge Patrick J. Schiltz of the US District Court in Minnesota—a conservative jurist appointed by former President George W. Bush—provided a list of nearly 100 court orders ICE had violated just that month while deployed as part of Trump's Operation Metro Surge.
The report of ICE's systemic violation of the law comes as the agency faces heightened scrutiny on Capitol Hill, with leaders of the agency called to testify and Democrats attempting to hold up funding in order to force reforms to ICE's conduct, which resulted in a partial shutdown beginning Saturday.
Following the release of Reuters' report, Rep. Ted Lieu (D-Calif.) directed a pointed question over social media to Kristi Noem, the secretary of the Department of Homeland Security, which oversees ICE.
"Why do your out-of-control agents keep violating federal law?" he said. "I look forward to seeing you testify under oath at the House Judiciary Committee in early March."