

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

Alex Hernandez prepares sells a "torta de tamal" in his tamales stand at Baja California Avenue on April 17, 2020 in Mexico City, Mexico. After the government suspended nonessential activities to halt Covid-19 spread, the informal food street industry suffered a drastic reduction of customers, between 60% and 80%, according to merchants. (Photo: Manuel Velasquez/Getty Images)
The United Nations labor agency warned Wednesday that "1.6 billion workers in the informal economy--that is nearly half of the global workforce--stand in immediate danger of having their livelihoods destroyed" by the worldwide economic crisis created by the coronavirus pandemic.
"For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
--Guy Ryder, ILO
Lockdowns recommended by public health officials to stop the pandemic have meant business closures that have led to lost jobs and incomes. Global working hours fell 4.5%, the equivalent of 130 million full-time jobs, in the first quarter of 2020 compared with pre-crisis levels, according to the International Labor Organization (ILO).
The ILO's report (pdf) warns the world could see that decline hit 10.5% by mid-year, the equivalent of 305 million full-time jobs. The new numbers follow an early April report from agency detailing how lockdowns across the globe were already affecting almost 2.7 billion workers, around 81% of the world's workforce of 3.3 billion.
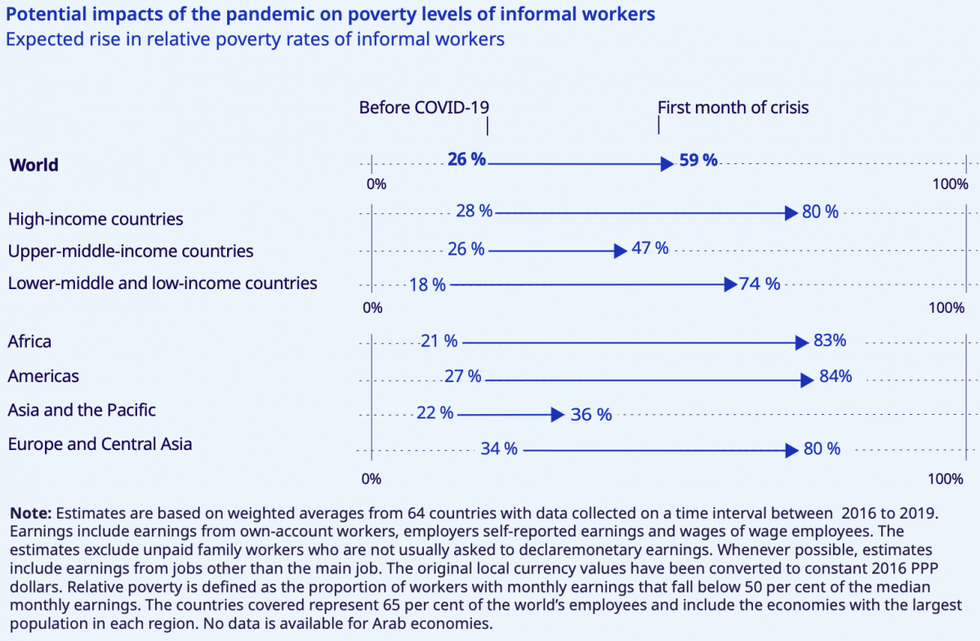
While the economic fallout of the crisis is expected to continue impacting the majority of global workers, that is especially true for those in the informal economy, which generally refers to workers whose employment conditions are "not recognized, registered, regulated, or protected under labor legislation and social protection."
As the new ILO report explains:
More than two billion people worldwide work in the informal economy in jobs that are characterized by a lack of basic protection, including social protection coverage. They often have poor access to healthcare services and have no income replacement in case of sickness or lockdown. Many of them have no possibility to work remotely from home. Staying home means losing their jobs, and without wages, they cannot eat.
As of 22 April 2020, close to 1.1 billion informal economy workers live and work in countries in full lockdown, and an additional 304 million in countries in partial lockdown
The agency estimates "almost 1.6 billion informal economy workers, accounting for 76% of informal employment worldwide, are significantly impacted by the lockdown measures and/or working in the hardest-hit sectors." The ILO projects income losses for these workers will be "massive" and further increase income inequality.
The sectors hardest hit by current global conditions are wholesale retail, trade and the repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles; manufacturing; accommodation and food services; and real estate, business, and administrative activities. Other significantly affected sectors include arts, entertainment, and recreation as well as transport, storage, and communication.
"Among informal economy workers significantly impacted by the crisis," the report notes, "women are overrepresented in high-risk sectors: 42% of women workers are working in those sectors, compared to 32% of men."
Given the new projections about how the pandemic-related economic crisis will affect workers worldwide, the ILO urges governments to pursue "urgent and significant policy responses to protect both enterprises, particularly smaller businesses, and workers, especially those operating in the informal economy."
The report reiterates the ILO's four-pillar policy framework to fight the economic impact of Covid-19 based on international labor standards: stimulating the economy and employment; supporting enterprises, jobs, and incomes; protecting workers in the workplace; and relying on social dialogue for solutions.
The ILO calls on governments to prioritize financial support for small businesses and informal economy workers, and to coordinate stimulus packages on a global scale. The report adds that "longer-term, large public investments are needed to boost employment and crowd in private investment."
In addition to detailing the need for longer-term financial aid, the report makes a case for the necessity of improving labor conditions as part of the recovery phase, noting that "the impact of the pandemic is likely to be uneven, adding significantly to existing vulnerabilities and inequalities."
"Greater attention should be paid to the strengthening of employment policies to support enterprises and workers," the report says, "along with strong labor market institutions and comprehensive and well-resourced social protection systems, including care policies and infrastructure, that kick in automatically and in an inclusive way as crises occur."
ILO Director-General Guy Ryder addressed the new report and the agency's current focus on the informal economy in a short video shared on Twitter Tuesday:
"As the pandemic and the jobs crisis evolve, the need to protect the most vulnerable becomes even more urgent," Ryder said in a statement. "For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
"Millions of businesses around the world are barely breathing," Ryder added. "They have no savings or access to credit. These are the real faces of the world of work. If we don't help them now, these enterprises will simply perish."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
The United Nations labor agency warned Wednesday that "1.6 billion workers in the informal economy--that is nearly half of the global workforce--stand in immediate danger of having their livelihoods destroyed" by the worldwide economic crisis created by the coronavirus pandemic.
"For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
--Guy Ryder, ILO
Lockdowns recommended by public health officials to stop the pandemic have meant business closures that have led to lost jobs and incomes. Global working hours fell 4.5%, the equivalent of 130 million full-time jobs, in the first quarter of 2020 compared with pre-crisis levels, according to the International Labor Organization (ILO).
The ILO's report (pdf) warns the world could see that decline hit 10.5% by mid-year, the equivalent of 305 million full-time jobs. The new numbers follow an early April report from agency detailing how lockdowns across the globe were already affecting almost 2.7 billion workers, around 81% of the world's workforce of 3.3 billion.
While the economic fallout of the crisis is expected to continue impacting the majority of global workers, that is especially true for those in the informal economy, which generally refers to workers whose employment conditions are "not recognized, registered, regulated, or protected under labor legislation and social protection."
As the new ILO report explains:
More than two billion people worldwide work in the informal economy in jobs that are characterized by a lack of basic protection, including social protection coverage. They often have poor access to healthcare services and have no income replacement in case of sickness or lockdown. Many of them have no possibility to work remotely from home. Staying home means losing their jobs, and without wages, they cannot eat.
As of 22 April 2020, close to 1.1 billion informal economy workers live and work in countries in full lockdown, and an additional 304 million in countries in partial lockdown
The agency estimates "almost 1.6 billion informal economy workers, accounting for 76% of informal employment worldwide, are significantly impacted by the lockdown measures and/or working in the hardest-hit sectors." The ILO projects income losses for these workers will be "massive" and further increase income inequality.
The sectors hardest hit by current global conditions are wholesale retail, trade and the repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles; manufacturing; accommodation and food services; and real estate, business, and administrative activities. Other significantly affected sectors include arts, entertainment, and recreation as well as transport, storage, and communication.
"Among informal economy workers significantly impacted by the crisis," the report notes, "women are overrepresented in high-risk sectors: 42% of women workers are working in those sectors, compared to 32% of men."
Given the new projections about how the pandemic-related economic crisis will affect workers worldwide, the ILO urges governments to pursue "urgent and significant policy responses to protect both enterprises, particularly smaller businesses, and workers, especially those operating in the informal economy."

The report reiterates the ILO's four-pillar policy framework to fight the economic impact of Covid-19 based on international labor standards: stimulating the economy and employment; supporting enterprises, jobs, and incomes; protecting workers in the workplace; and relying on social dialogue for solutions.
The ILO calls on governments to prioritize financial support for small businesses and informal economy workers, and to coordinate stimulus packages on a global scale. The report adds that "longer-term, large public investments are needed to boost employment and crowd in private investment."
In addition to detailing the need for longer-term financial aid, the report makes a case for the necessity of improving labor conditions as part of the recovery phase, noting that "the impact of the pandemic is likely to be uneven, adding significantly to existing vulnerabilities and inequalities."
"Greater attention should be paid to the strengthening of employment policies to support enterprises and workers," the report says, "along with strong labor market institutions and comprehensive and well-resourced social protection systems, including care policies and infrastructure, that kick in automatically and in an inclusive way as crises occur."
ILO Director-General Guy Ryder addressed the new report and the agency's current focus on the informal economy in a short video shared on Twitter Tuesday:
"As the pandemic and the jobs crisis evolve, the need to protect the most vulnerable becomes even more urgent," Ryder said in a statement. "For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
"Millions of businesses around the world are barely breathing," Ryder added. "They have no savings or access to credit. These are the real faces of the world of work. If we don't help them now, these enterprises will simply perish."
The United Nations labor agency warned Wednesday that "1.6 billion workers in the informal economy--that is nearly half of the global workforce--stand in immediate danger of having their livelihoods destroyed" by the worldwide economic crisis created by the coronavirus pandemic.
"For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
--Guy Ryder, ILO
Lockdowns recommended by public health officials to stop the pandemic have meant business closures that have led to lost jobs and incomes. Global working hours fell 4.5%, the equivalent of 130 million full-time jobs, in the first quarter of 2020 compared with pre-crisis levels, according to the International Labor Organization (ILO).
The ILO's report (pdf) warns the world could see that decline hit 10.5% by mid-year, the equivalent of 305 million full-time jobs. The new numbers follow an early April report from agency detailing how lockdowns across the globe were already affecting almost 2.7 billion workers, around 81% of the world's workforce of 3.3 billion.
While the economic fallout of the crisis is expected to continue impacting the majority of global workers, that is especially true for those in the informal economy, which generally refers to workers whose employment conditions are "not recognized, registered, regulated, or protected under labor legislation and social protection."
As the new ILO report explains:
More than two billion people worldwide work in the informal economy in jobs that are characterized by a lack of basic protection, including social protection coverage. They often have poor access to healthcare services and have no income replacement in case of sickness or lockdown. Many of them have no possibility to work remotely from home. Staying home means losing their jobs, and without wages, they cannot eat.
As of 22 April 2020, close to 1.1 billion informal economy workers live and work in countries in full lockdown, and an additional 304 million in countries in partial lockdown
The agency estimates "almost 1.6 billion informal economy workers, accounting for 76% of informal employment worldwide, are significantly impacted by the lockdown measures and/or working in the hardest-hit sectors." The ILO projects income losses for these workers will be "massive" and further increase income inequality.
The sectors hardest hit by current global conditions are wholesale retail, trade and the repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles; manufacturing; accommodation and food services; and real estate, business, and administrative activities. Other significantly affected sectors include arts, entertainment, and recreation as well as transport, storage, and communication.
"Among informal economy workers significantly impacted by the crisis," the report notes, "women are overrepresented in high-risk sectors: 42% of women workers are working in those sectors, compared to 32% of men."
Given the new projections about how the pandemic-related economic crisis will affect workers worldwide, the ILO urges governments to pursue "urgent and significant policy responses to protect both enterprises, particularly smaller businesses, and workers, especially those operating in the informal economy."

The report reiterates the ILO's four-pillar policy framework to fight the economic impact of Covid-19 based on international labor standards: stimulating the economy and employment; supporting enterprises, jobs, and incomes; protecting workers in the workplace; and relying on social dialogue for solutions.
The ILO calls on governments to prioritize financial support for small businesses and informal economy workers, and to coordinate stimulus packages on a global scale. The report adds that "longer-term, large public investments are needed to boost employment and crowd in private investment."
In addition to detailing the need for longer-term financial aid, the report makes a case for the necessity of improving labor conditions as part of the recovery phase, noting that "the impact of the pandemic is likely to be uneven, adding significantly to existing vulnerabilities and inequalities."
"Greater attention should be paid to the strengthening of employment policies to support enterprises and workers," the report says, "along with strong labor market institutions and comprehensive and well-resourced social protection systems, including care policies and infrastructure, that kick in automatically and in an inclusive way as crises occur."
ILO Director-General Guy Ryder addressed the new report and the agency's current focus on the informal economy in a short video shared on Twitter Tuesday:
"As the pandemic and the jobs crisis evolve, the need to protect the most vulnerable becomes even more urgent," Ryder said in a statement. "For millions of workers, no income means no food, no security, and no future."
"Millions of businesses around the world are barely breathing," Ryder added. "They have no savings or access to credit. These are the real faces of the world of work. If we don't help them now, these enterprises will simply perish."