

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
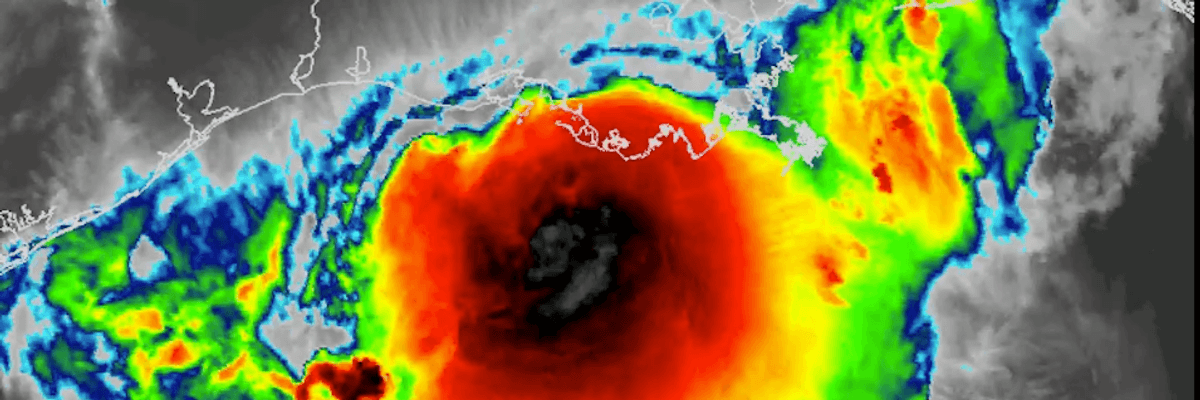
Infrared captures Hurricane Barry on Saturday morning ahead of making landfall. Barry was downgraded to a tropical storm after hitting the Louisiana coast. (Image: NWS Memphis, cc)
The climate crisis is making tropical storms worse, experts warned as Louisiana faced flooding threats from a powerful storm that made landfall Saturday at midday.
"The real increased threat from a warming climate is an atmosphere that's capable of producing higher intensity precipitation events," Jill Trepanier, an extreme climatic and weather events expert, told Al Jazeera on Friday.
Tropical storm Barry was downgraded from a hurricane after making landfall, but the threat from excessive rainfall and winds is still real for Louisiana residents in the cyclone's path.
Barry hit the Louisiana coast at about 1pm ET, drenching towns along the Gulf of Mexico with rainfall as it moved inland. Some parts of Louisiana could receive up to 25 inches of rain, according to some estimates.
The city of New Orleans was under a shelter in place advisory Saturday. The Mississippi River, which threatened to overtop its levees after up to 10 inches of rain fell on the city Thursday, is no longer a threat to flood, but the city remains watchful.
The rainfall, studies show, is one of the major threats going forward of the climate crisis. As the weather warms the ocean, more water goes into the air--leading in turn to higher levels of precipitation.
"When the air is warmer, it can hold more water vapor," climatologist Mark Risser told BuzzFeed News. "So that when a storm moves through an area that has warmer, wetter air, there's more of a source for the precipitation."
Risser, who wrote a study in 2017 about Hurricane Harvey's record rainfall for the science journal Geophysical Research Letters, has seen his predictions confirmed in subsequent studies. Barry's rainfall, climate researcher Katharine Hayhoe said in an email to BuzzFeed, is part of that trend.
"Barry appears to be playing out very much in the same direction, with the added impact of pre-storm flooding," said Hayhoe. "Though the formal attribution remains to be done, is likely related to the observed increase in heavy precipitation."
That, combined with Barry's slow movement, poses the real danger. Even after Barry, future such storms are expected to be at least as intense. The climate crisis will see to that, climate scientist Andrew Dessler told Reuters.
"We might have four or five times as much warming over the coming century as the last," said Dessler, "so these kinds of weather events are likely to get much, much worse."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
The climate crisis is making tropical storms worse, experts warned as Louisiana faced flooding threats from a powerful storm that made landfall Saturday at midday.
"The real increased threat from a warming climate is an atmosphere that's capable of producing higher intensity precipitation events," Jill Trepanier, an extreme climatic and weather events expert, told Al Jazeera on Friday.
Tropical storm Barry was downgraded from a hurricane after making landfall, but the threat from excessive rainfall and winds is still real for Louisiana residents in the cyclone's path.
Barry hit the Louisiana coast at about 1pm ET, drenching towns along the Gulf of Mexico with rainfall as it moved inland. Some parts of Louisiana could receive up to 25 inches of rain, according to some estimates.
The city of New Orleans was under a shelter in place advisory Saturday. The Mississippi River, which threatened to overtop its levees after up to 10 inches of rain fell on the city Thursday, is no longer a threat to flood, but the city remains watchful.
The rainfall, studies show, is one of the major threats going forward of the climate crisis. As the weather warms the ocean, more water goes into the air--leading in turn to higher levels of precipitation.
"When the air is warmer, it can hold more water vapor," climatologist Mark Risser told BuzzFeed News. "So that when a storm moves through an area that has warmer, wetter air, there's more of a source for the precipitation."
Risser, who wrote a study in 2017 about Hurricane Harvey's record rainfall for the science journal Geophysical Research Letters, has seen his predictions confirmed in subsequent studies. Barry's rainfall, climate researcher Katharine Hayhoe said in an email to BuzzFeed, is part of that trend.
"Barry appears to be playing out very much in the same direction, with the added impact of pre-storm flooding," said Hayhoe. "Though the formal attribution remains to be done, is likely related to the observed increase in heavy precipitation."
That, combined with Barry's slow movement, poses the real danger. Even after Barry, future such storms are expected to be at least as intense. The climate crisis will see to that, climate scientist Andrew Dessler told Reuters.
"We might have four or five times as much warming over the coming century as the last," said Dessler, "so these kinds of weather events are likely to get much, much worse."
The climate crisis is making tropical storms worse, experts warned as Louisiana faced flooding threats from a powerful storm that made landfall Saturday at midday.
"The real increased threat from a warming climate is an atmosphere that's capable of producing higher intensity precipitation events," Jill Trepanier, an extreme climatic and weather events expert, told Al Jazeera on Friday.
Tropical storm Barry was downgraded from a hurricane after making landfall, but the threat from excessive rainfall and winds is still real for Louisiana residents in the cyclone's path.
Barry hit the Louisiana coast at about 1pm ET, drenching towns along the Gulf of Mexico with rainfall as it moved inland. Some parts of Louisiana could receive up to 25 inches of rain, according to some estimates.
The city of New Orleans was under a shelter in place advisory Saturday. The Mississippi River, which threatened to overtop its levees after up to 10 inches of rain fell on the city Thursday, is no longer a threat to flood, but the city remains watchful.
The rainfall, studies show, is one of the major threats going forward of the climate crisis. As the weather warms the ocean, more water goes into the air--leading in turn to higher levels of precipitation.
"When the air is warmer, it can hold more water vapor," climatologist Mark Risser told BuzzFeed News. "So that when a storm moves through an area that has warmer, wetter air, there's more of a source for the precipitation."
Risser, who wrote a study in 2017 about Hurricane Harvey's record rainfall for the science journal Geophysical Research Letters, has seen his predictions confirmed in subsequent studies. Barry's rainfall, climate researcher Katharine Hayhoe said in an email to BuzzFeed, is part of that trend.
"Barry appears to be playing out very much in the same direction, with the added impact of pre-storm flooding," said Hayhoe. "Though the formal attribution remains to be done, is likely related to the observed increase in heavy precipitation."
That, combined with Barry's slow movement, poses the real danger. Even after Barry, future such storms are expected to be at least as intense. The climate crisis will see to that, climate scientist Andrew Dessler told Reuters.
"We might have four or five times as much warming over the coming century as the last," said Dessler, "so these kinds of weather events are likely to get much, much worse."