

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

Traders work during the opening bell at the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) on March 19, 2020, at Wall Street in New York City. Wall Street stocks fell again early Thursday as central banks unveiled new stimulus measures and U.S. jobless claims showed an initial hit from the slowdown generated by the coronavirus outbreak. (Photo: Johannes Eisele/AFP via Getty Images)
A new analysis released Tuesday shows that more U.S. workers filed unemployment claims last week than during any other week in the nation's history.
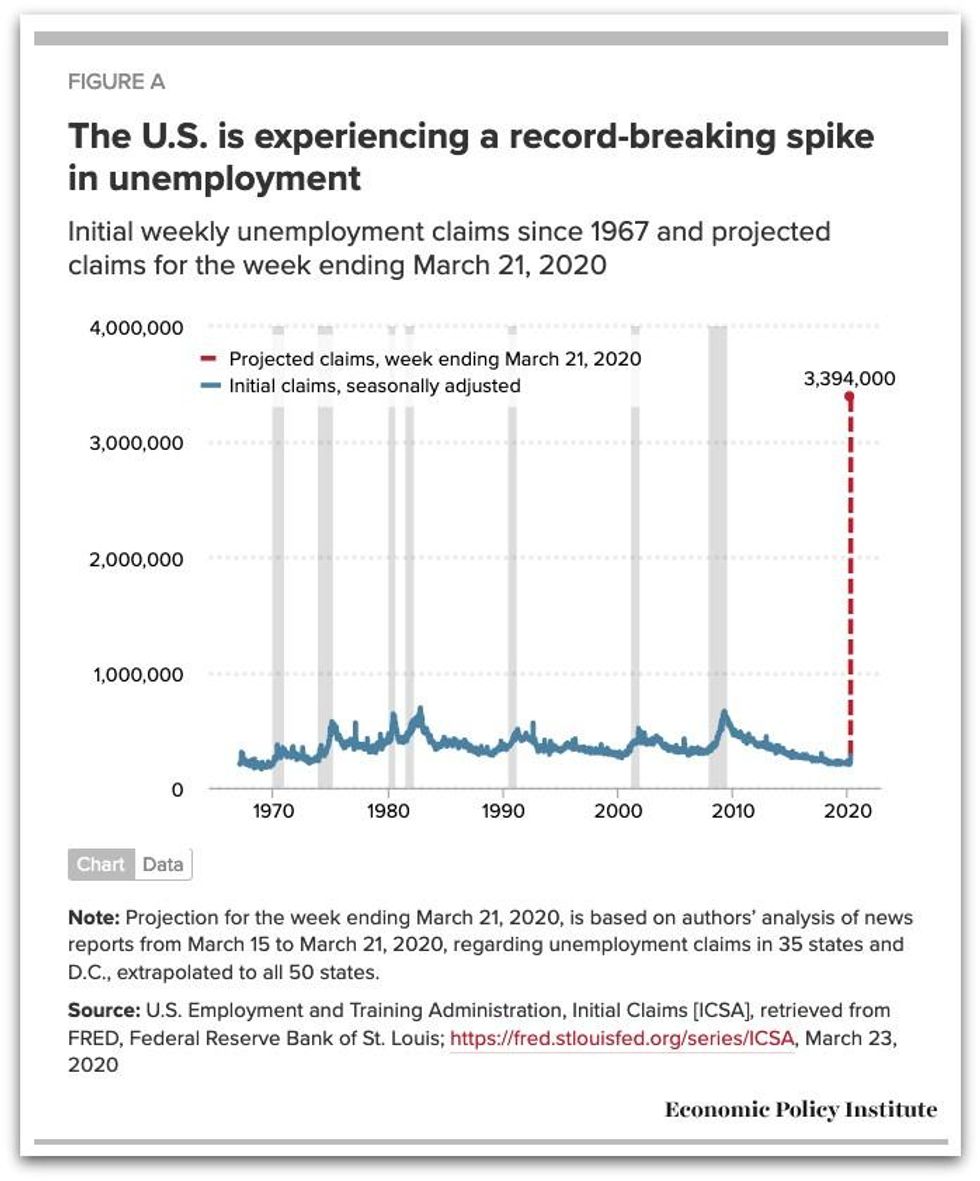
An estimated 3.4 million Americans filed such claims for the week ending March 21, according to the findings from the Economic Policy Institute (EPI).
"This will dwarf every other week in history," wrote EPI's Aaron Sojourner and Paul Goldsmith-Pinkham, adding, "The true impacts are undoubtedly of larger scale than described here."
The startling calculation--based on claims in 35 states and Washington, D.C. and extrapolated to the other 15 states--comes as the nation continues to experience a rise in cases of the novel coronavirus--with over 46,000 confirmed as of Tuesday--and as ordinary Americans feel the economic and societal impacts of the crisis, with schools, stores, and work places temporarily shuttered, varying degrees of lockdowns in place, and households and frontline workers still wondering if lawmakers will put their urgent needs above those of corporate America.
A graph accompanying the new EPI analysis, which is based on data from news reports from March 15 to March 21, illustrates the enormous jump in unemployment claims--even if the actual figure ends up being on the analysts' low-end projection of 3 million claims. At no other point in the timeline shown does the figure even scrape 1 million.
Reaction to the findings was stark:
Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham, both research associates at EPI, put the projection into the context of the nation's unemployment rate:
For scale, consider that 3.4 million Americans moving from employment to unemployment would raise the number of the unemployed from 5.7 million to 9.1 million. This alone would raise the unemployment rate by more than half, by 2 percentage points from 3.5% to 5.5%, moving back to 2015 levels in just one week. This spike represents 2.2% of all jobs in the economy. The largest monthly rise in the unemployment rate in American history was plus 1.3 percentage points in October 1949.
Grim as the scenario painted by the analsis is, reality may be even worse. The researchers wrote that the actual tally of claims "could be substantially higher." Not all unemployed workers are able to file unemployment insurance claims either, and for those that do, they'll get about half--or less--of their regular income. The end of the coronavirus crisis is also not in the immediate future.
All that points to the need for the federal government to provide states with more aid.
"American working families are paying a large price through no fault of their own," wrote Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham. "But there is no shortcutting public health to get the American economy back to work. A healthy economy requires public health."
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |
A new analysis released Tuesday shows that more U.S. workers filed unemployment claims last week than during any other week in the nation's history.
An estimated 3.4 million Americans filed such claims for the week ending March 21, according to the findings from the Economic Policy Institute (EPI).
"This will dwarf every other week in history," wrote EPI's Aaron Sojourner and Paul Goldsmith-Pinkham, adding, "The true impacts are undoubtedly of larger scale than described here."
The startling calculation--based on claims in 35 states and Washington, D.C. and extrapolated to the other 15 states--comes as the nation continues to experience a rise in cases of the novel coronavirus--with over 46,000 confirmed as of Tuesday--and as ordinary Americans feel the economic and societal impacts of the crisis, with schools, stores, and work places temporarily shuttered, varying degrees of lockdowns in place, and households and frontline workers still wondering if lawmakers will put their urgent needs above those of corporate America.
A graph accompanying the new EPI analysis, which is based on data from news reports from March 15 to March 21, illustrates the enormous jump in unemployment claims--even if the actual figure ends up being on the analysts' low-end projection of 3 million claims. At no other point in the timeline shown does the figure even scrape 1 million.

Reaction to the findings was stark:
Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham, both research associates at EPI, put the projection into the context of the nation's unemployment rate:
For scale, consider that 3.4 million Americans moving from employment to unemployment would raise the number of the unemployed from 5.7 million to 9.1 million. This alone would raise the unemployment rate by more than half, by 2 percentage points from 3.5% to 5.5%, moving back to 2015 levels in just one week. This spike represents 2.2% of all jobs in the economy. The largest monthly rise in the unemployment rate in American history was plus 1.3 percentage points in October 1949.
Grim as the scenario painted by the analsis is, reality may be even worse. The researchers wrote that the actual tally of claims "could be substantially higher." Not all unemployed workers are able to file unemployment insurance claims either, and for those that do, they'll get about half--or less--of their regular income. The end of the coronavirus crisis is also not in the immediate future.
All that points to the need for the federal government to provide states with more aid.
"American working families are paying a large price through no fault of their own," wrote Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham. "But there is no shortcutting public health to get the American economy back to work. A healthy economy requires public health."
A new analysis released Tuesday shows that more U.S. workers filed unemployment claims last week than during any other week in the nation's history.
An estimated 3.4 million Americans filed such claims for the week ending March 21, according to the findings from the Economic Policy Institute (EPI).
"This will dwarf every other week in history," wrote EPI's Aaron Sojourner and Paul Goldsmith-Pinkham, adding, "The true impacts are undoubtedly of larger scale than described here."
The startling calculation--based on claims in 35 states and Washington, D.C. and extrapolated to the other 15 states--comes as the nation continues to experience a rise in cases of the novel coronavirus--with over 46,000 confirmed as of Tuesday--and as ordinary Americans feel the economic and societal impacts of the crisis, with schools, stores, and work places temporarily shuttered, varying degrees of lockdowns in place, and households and frontline workers still wondering if lawmakers will put their urgent needs above those of corporate America.
A graph accompanying the new EPI analysis, which is based on data from news reports from March 15 to March 21, illustrates the enormous jump in unemployment claims--even if the actual figure ends up being on the analysts' low-end projection of 3 million claims. At no other point in the timeline shown does the figure even scrape 1 million.

Reaction to the findings was stark:
Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham, both research associates at EPI, put the projection into the context of the nation's unemployment rate:
For scale, consider that 3.4 million Americans moving from employment to unemployment would raise the number of the unemployed from 5.7 million to 9.1 million. This alone would raise the unemployment rate by more than half, by 2 percentage points from 3.5% to 5.5%, moving back to 2015 levels in just one week. This spike represents 2.2% of all jobs in the economy. The largest monthly rise in the unemployment rate in American history was plus 1.3 percentage points in October 1949.
Grim as the scenario painted by the analsis is, reality may be even worse. The researchers wrote that the actual tally of claims "could be substantially higher." Not all unemployed workers are able to file unemployment insurance claims either, and for those that do, they'll get about half--or less--of their regular income. The end of the coronavirus crisis is also not in the immediate future.
All that points to the need for the federal government to provide states with more aid.
"American working families are paying a large price through no fault of their own," wrote Sojourner and Goldsmith-Pinkham. "But there is no shortcutting public health to get the American economy back to work. A healthy economy requires public health."