

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
As I leave Baghdad, I carry a sense of Iraq’s resilience, the palpable scars of war, the warmth of its people, the hope for a better future, and the ongoing story of a nation rebuilding itself.
I arrived at the Taj Hotel in Baghdad's Jadriyah neighborhood at 6:00 am, worn thin by the long flight from Los Angeles. After sleeping until mid-afternoon, I stepped out into the 90°F heat on a simple mission: find falafel, fries, and a place to exchange money. A local bus picked me up and dropped me right across from a falafel shop—a small act of hospitality. Full and settled, I walked beside the Tigris River, watching construction cranes against the sky. Life was visibly moving forward. Yet the mental newsreel kept playing: bombs falling on these same banks 20 years earlier. I was a tourist now in a country I had once protested my own nation for invading. Needing to escape both the heat and the weight of those memories, I returned to the hotel for Nutella cake and Iraqi tea, yet deeply conscious of the complex layers beneath the surface.
The next day settled heavily. We started at Tahrir Monument and the roundabout where Saddam’s statue once stood—toppled in 2003 by US Marines in an image seen around the world. Today, no plaque marks the spot. Only election banners fluttered in the wind. From there, we traveled to the Arch of Ctesiphon, a soaring Persian vault from 540 AD. Nearby lay the relics of a different era: a derelict tourist complex and a museum designed by North Koreans, its walls scarred with bullet marks. Al-Mada’in, our guide remarked, had been a final stronghold against the invasion. It’s one thing to read about war and occupation, another to stand where it happened and touch the pockmarked concrete.
Just yards away, young boys kicked a soccer ball in the dust, a powerful scene of life insisting on moving forward. That contrast stayed with me: The tourist complex, once a thriving vacation spot with a luxurious pool, is now a place to store garbage. Aside from the enduring arch, the entire area lies in ruins, destroyed in the war and never rebuilt. Who knows if it ever will be. For some parts of Iraq, rebuilding only began around 2017, over a decade after the invasion. With elections approaching, I wondered about Iraq’s future—and what accountability looks like when destruction runs so deep.
A slower day followed, wandering through Old Baghdad: its bazaar, colonial facades, antique shops, Christian churches, and tea houses thick with the smoke of cigarettes. But I felt an unease seeing Saddam-era memorabilia, like old currency, sold as casual souvenirs. My time in Iraqi Kurdistan, at Amna Suraka and Halabja Memorial, had shown me the human cost of his brutal regime. Later, we passed the haunting cement skeleton of one of Saddam’s grand mosques, frozen mid-construction by the 2003 war. It stood empty, monumental yet abandoned, like a set from Dune—a stark metaphor for interrupted futures.
Now, as the world’s attention drifts to other conflicts, the weight of history here feels so obvious.
We traveled to Babylon. Before entering, we paused before one of the last remaining monuments to Saddam. His image is now outlawed; we gazed at the bullet marks and graffiti scoring the stone. Nearby, his palace loomed over the Euphrates—a hollow shell gazing across timeless dust. After roaming Babylon’s ruins, we crossed a low fence onto the palace grounds. Entering the space once occupied by a brutal dictator again filled me with unease. While others explored the looted, spray-painted halls, I was struck by the collision of histories here: ancient civilization, the US invasion, and the regime’s own atrocities against the Kurds.
From there, we journeyed to Karbala and the breathtaking Al-Abbas Holy Shrine. I wore an abaya to enter, humbled by the devotion, chanting, and crying that resonated in the air. The contrast stayed with me: between ransacked palaces of fallen power, land ravaged by war, and this enduring faith. We paused briefly at one of the world’s largest cemeteries in Najaf before visiting the Holy Shrine of Imam Ali. The long drive south to Nasiriyah that followed gave me space to hold all these layers: history, belief, silence, and dust.
A highlight came in the Mesopotamian Marshes. Gliding by water buffalo through vast wetlands, said to be the Garden of Eden, I felt a deep connection to this ancient ecosystem and the Indigenous communities who sustain it. The use of reeds to build entire homes felt like a quiet miracle. Later, we visited the Great Ziggurat of Ur—a stairway to a Sumerian sky. We moved through biblical landscapes that day, though in the distance stood an old American military base, now repurposed by the Iraqis. Someone showed me photos of US soldiers standing on those same Ziggurat steps.
As I leave Baghdad, I carry a sense of Iraq’s resilience, the palpable scars of war, the warmth of its people, the hope for a better future, and the ongoing story of a nation rebuilding itself. Now, as the world’s attention drifts to other conflicts, the weight of history here feels so obvious. The US footprint left in Iraq is deep—and as it threatens Iraq with sanctions, it is the last thing this country needs as it tries to move forward and heal.
The United Nations has now declared oil-rich Iraq, the land on which the Bush administration bet the future of our own country, to be the fifth most vulnerable to climate breakdown among its 193 member states.
It was one of the fabled rivers of history and the Marines needed to cross it.
In early April 2003, as American forces sought to wrap up their conquest of the Iraqi capital, Baghdad, and take strongholds to its north, the Marine Corps formed “Task Force Tripoli.” It was commanded by General John F. Kelly (who would later serve as Donald Trump’s White House chief of staff). His force was charged with capturing the city of Tikrit, the birthplace of dictator Saddam Hussein. The obvious eastern approach to it was blocked because a bridge over the Tigris River had been damaged. Since the Marines assembled the Task Force in northeastern Baghdad, its personnel needed to cross the treacherous, hard-flowing Tigris twice to advance on their target. Near Tikrit, while traversing the Swash Bridge, they came under fire from military remnants of Saddam’s regime.
Still, Tikrit fell on April 15 and, historically speaking, that double-crossing of the Tigris was a small triumph for American forces. After all, that wide, deep, swift-flowing waterway had traditionally posed logistical problems for any military force. It had, in fact, done so throughout recorded history, proving a daunting barrier for the militaries of Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon and the Achaemenid Cyrus the Great, for Alexander the Great and Roman Emperor Justinian, for the Mongols and the Safavid Iranians, for imperial British forces and finally General John H. Kelly. However, just as Kelly’s stature was diminished by his later collaboration with America’s only openly autocratic president, so, too, in this century the Tigris has been diminished in every sense and all too abruptly. No longer what the Kurds once called the Ava Mezin, “the Great Water,” it is now a shadow of its former self.
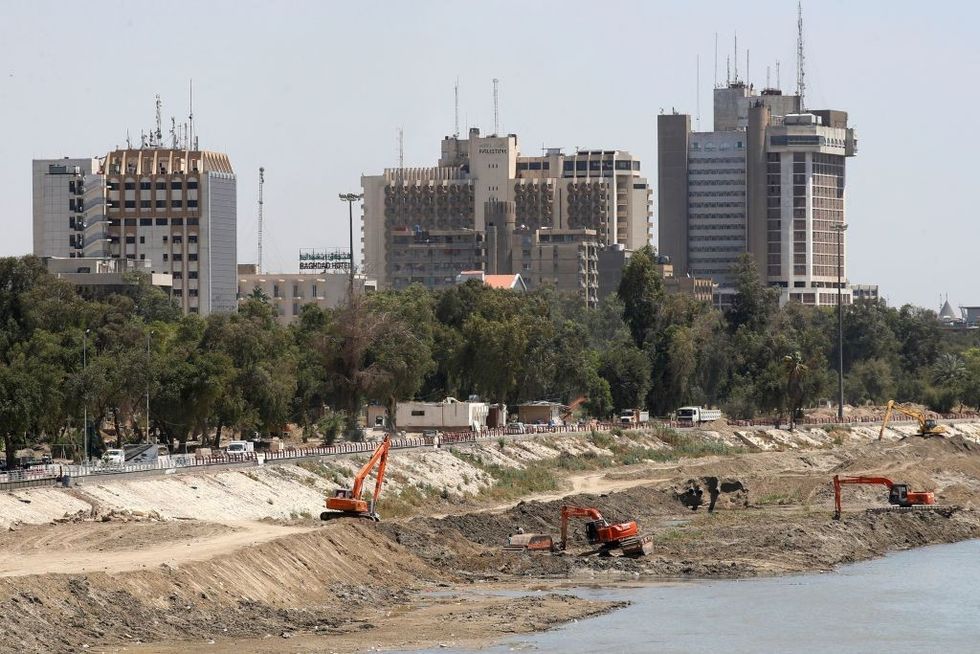

A picture taken on May 1, 2023, shows excavators working on the banks of the Tigris River in Baghdad, which is experiencing drought-induced drop in the water levels.
(Photo: Ahmad al-Rubaye/AFP via Getty Images)
Thanks at least in part to human-caused climate change, the Tigris and its companion river, the Euphrates, on which Iraqis still so desperately depend, have seen alarmingly low water flow in recent years. As Iraqi posts on social media now regularly observe in horror, at certain places, if you stand on the banks of those once mighty bodies of water, you can see through to their riverbeds. You can even, Iraqis report, ford them on foot in some spots, a previously unheard-of phenomenon.
Those two rivers no longer pose the military obstacle they used to. They were once synonymous with Iraq. The very word Mesopotamia, the premodern way of referring to what we now call Iraq, means “between rivers” in Greek, a reference, of course, to the Tigris and the Euphrates. Climate change and the damming of those waters in neighboring upriver countries are expected to cause the flow of the Euphrates to decline by 30% and of the Tigris by a whopping 60% by 2099, which would be a death sentence for many Iraqis.
There was a deep irony that haunted the decision to invade Iraq to (so to speak) liberate its oil exports. After all, burning gasoline in cars causes the earth to heat up.
Twenty years ago, with President George W. Bush and Vice President Dick Cheney, two oil men and climate-change denialists, in the White House and new petroleum finds dwindling, it seemed like the most natural thing in the world for them to use the 9/11 horror as an excuse to commit “regime change” in Baghdad (which had no role in taking down the World Trade Center in New York and part of the Pentagon in Washington, D.C.). They could thereby, they thought, create a friendly puppet regime and lift the U.S. and U.N. sanctions then in place on the export of Iraqi petroleum, imposed as a punishment for dictator Saddam Hussein’s 1990 invasion of Kuwait.
There was a deep irony that haunted the decision to invade Iraq to (so to speak) liberate its oil exports. After all, burning gasoline in cars causes the earth to heat up, so the very black gold that both Saddam Hussein and George W. Bush coveted turned out to be a Pandora’s box of the worst sort. Remember, we now know that, in Washington’s “war on terror” in Iraq, Afghanistan, and elsewhere, the U.S. military emitted at least 400 million metric tons of heat-trapping carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. And mind you, that fit into a great tradition. Since the 18th century, the U.S. has put 400 billion—yes, billion!—metric tons of CO2 into that same atmosphere, or twice as much as any other country, which means it has a double responsibility to climate victims like those in Iraq.
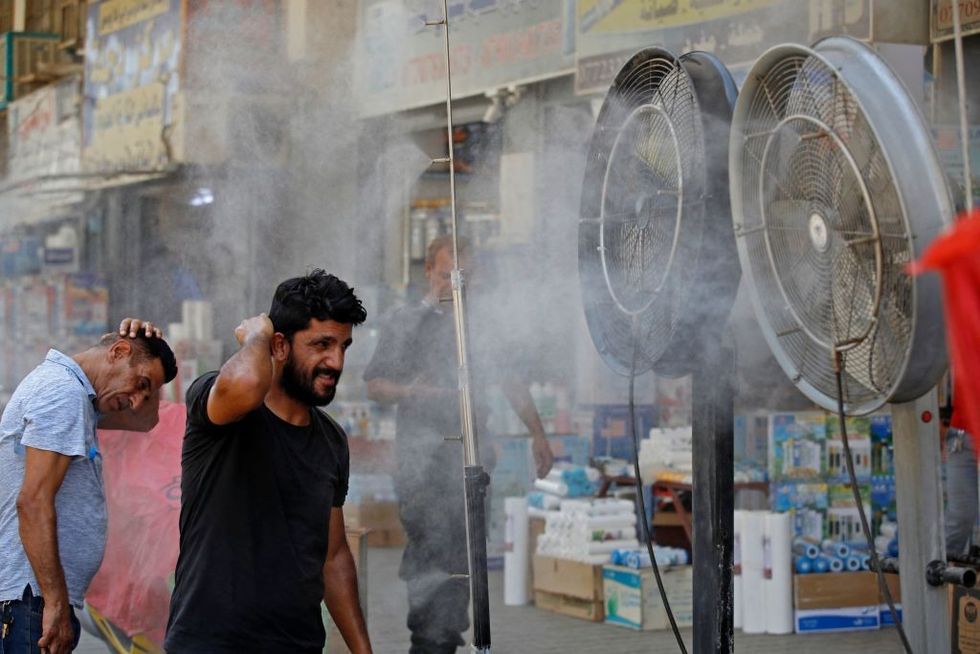
Iraqi men cool down in front of misting fans amid a heatwave in central Baghdad, on July 20, 2022.
(Photo: Ahmad al-Rubaye/AFP via Getty Images)
The United Nations has now declared oil-rich Iraq, the land on which the Bush administration bet the future of our own country, to be the fifth most vulnerable to climate breakdown among its 193 member states. Its future, the U.N. warns, will be one of “soaring temperatures, insufficient and diminishing rainfall, intensified droughts and water scarcity, frequent sand and dust storms, and flooding.” Sawa Lake, the “pearl of the south” in Muthanna governorate, has dried up, a victim of both the industrial overuse of aquifers and a climate-driven drought that has reduced precipitation by 30%.
“I’ve lived in Basra all my life. As a boy, the summer temperature never went much beyond 40°C (104°F) in summer. Today, it can surpass 50°C (122° F).”
Meanwhile, temperatures in that already hot land are now rising rapidly. As Adel Al-Attar, an Iraqi adviser to the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) on water and habitat, describes it, “I’ve lived in Basra all my life. As a boy, the summer temperature never went much beyond 40°C (104°F) in summer. Today, it can surpass 50°C (122° F).” The climate statistics bear him out. As early as July 22, 2017, the temperature in Basra reached 54°C (129.2°F), among the highest ever recorded in the eastern hemisphere. Iraqi temperatures are, in fact, two to seven times higher than average global temperatures, and that means greater dryness of soil, increased evaporation from rivers and reservoirs, decreasing rainfall, and a distinct loss of biodiversity, not to mention rising human health threats like heat stroke.
The American war did direct harm to Iraq’s farmers, who make up 18% of the country’s labor force. And when it was over, they had to deal with staggering numbers of explosives left in the countryside, including landmines, unexploded ordnance, and improvised explosive devices, many of which have since been dangerously covered by desert sands as a climate-driven drought worsens. An article in the journal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences observes that when it comes to military disruptions of waterways, “Displacement, explosions, and movement of heavy equipment increase dust that then settles on rivers and accumulates in reservoirs.” Worse yet, between 2014 and 2018 when the guerrillas of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, whom the American war helped bring into existence, took over parts of northern and western Iraq, they blew up dams and practiced scorched-earth tactics that did $600 million worth of damage to the country’s hydraulic infrastructure. Had the U.S. never invaded, there would have been no ISIL.
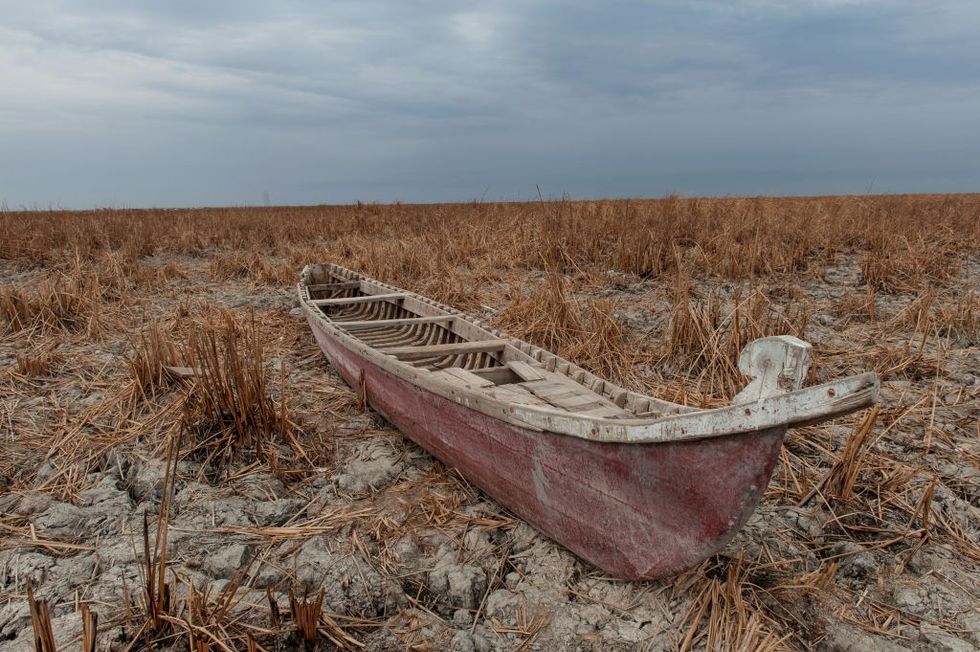

A traditional Marsh Arab boat seen laying idle on dry and cracked Marsh in the Central Marshes of Southern Iraq.
(Photo: John Wreford/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
As Al-Attar of the ICRC observed, “When there’s not enough rain or vegetation, the upper layers of earth become less compact, meaning the chance of dust or sandstorms increases. These weather events contribute to desertification. Fertile soil is turning into desert.” And that is part of Iraq’s post-invasion fate, which means ever more frequent dust- and sandstorms. In mid-June, the Iraqi government warned that particularly violent dust and thunderstorms in al-Anbar, Najaf, and Karbala provinces were uprooting ever more trees and flattening ever more farms. In late May in Kirkuk, a dust storm sent hundreds of Iraqis to the hospital. A year ago, the dust storms came so thick and fast, week after week, that visibility was often obscured in major cities and thousands were hospitalized with breathing problems. In the late 20th century, there already were, on average, 243 days annually with high particulate matter in the air. In the past 20 years, that number has reached 272. Climate scientists predict that it will hit 300 by 2050.
A little over half of Iraq’s farmed land relies on rain-fed agriculture, mostly in the north of the country. Iraqi journalist Sanar Hasan describes the impact of increasing drought and water scarcity in the northern province of Ninewah, where yields have shrunk considerably. Ninewah produced 5 million metric tons of wheat in 2020 but only 3.37 million in 2021 before plummeting by more than 50% to 1.34 million in 2022. Such declining yields pose a special problem in a world where wheat has only grown more expensive, thanks in part to the Russian war on Ukraine. Thousands of Iraqi farming families are being forced off their lands by water shortages. For example, Hasan quotes Yashue Yohanna, a Christian who worked all his life in agriculture but now can’t make ends meet, as saying, “When I leave the farm, what do you expect me to do next? I’m an old man. How will I afford the cost of living?”
Worse yet, southern Iraq’s marshlands are turning into classic dust bowls. The Environment Director of Maysan Governorate in southern Iraq recently announced that its al-Awda Marsh was 100% dried up.
“The drought ended our future. We have no hope, other than for a [government] job, which would be enough. Other work doesn’t fulfill our needs.”
The marshes at the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers have been storied for thousands of years. The world’s oldest epic, the Mesopotamian tale of Gilgamesh, is set there as it describes a hero journeying to an enchanted garden of the gods in search of immortality. (Echoes of that epic can be found in the biblical story of the garden of Eden.)
Our addiction to fossil fuels, however, has contributed significantly to the blighting of that very source of life and legend. It was there that marsh dwellers once hauled in a majority of the fish eaten by Iraqis, but the remaining wetlands are now experiencing increasingly high rates of evaporation. The Shatt al-Arab, created where the Tigris and Euphrates flow together into the Persian Gulf, has seen its water pressure drop, allowing an influx of salt water that has already destroyed 60,000 acres of farmland and some 30,000 trees.
Many of Iraq’s date palms have also died owing to war, neglect, soil salinization, and climate change. In the 1960s and 1970s, Iraq provided three-quarters of the world’s dates. Now, its date industry is tiny and on life support, while Marsh Arabs and southern farming families have been forced from their lands into cities where they have few of the skills needed to make a living. Journalist Ahmed Saeed and his colleagues at Reuters quote Hasan Moussa, a former fisherman who now drives a taxi, as saying, “The drought ended our future. We have no hope, other than for a [government] job, which would be enough. Other work doesn’t fulfill our needs.”
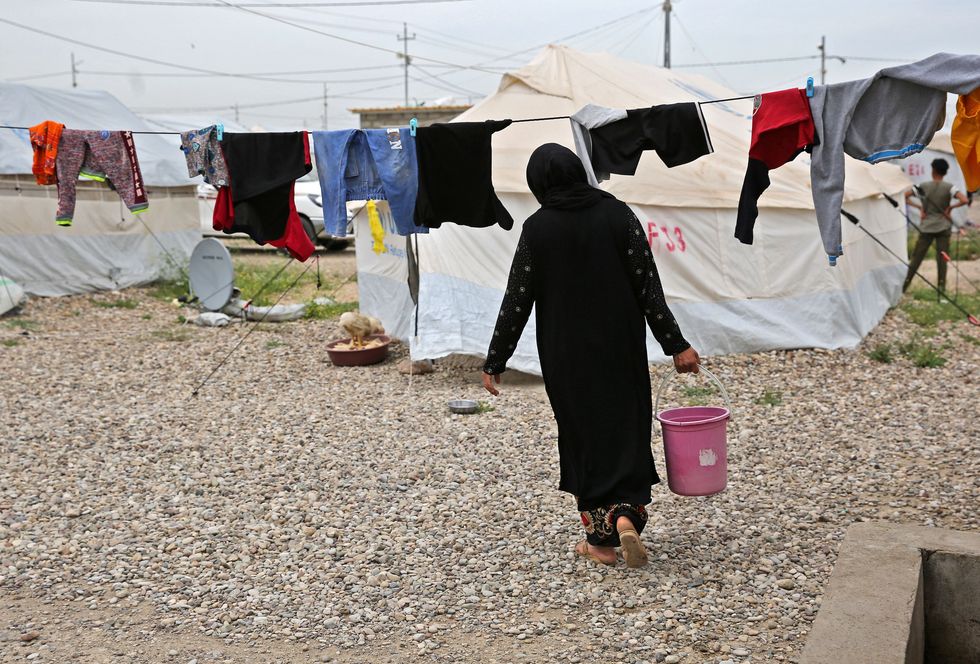

A woman walks with a pail of water at Laylan camp for the displaced about 25 kilometres east of the northern multi-ethnic Iraqi city of Kirkuk on May 9, 2019.
(Photo: Ahmad aL-Rubaye/AFP via Getty Images)
Although it was mostly men who planned out Iraq’s ruinous wars of the past half-century and set their sights on burning as much petroleum, coal, and natural gas as possible for profit and power, Iraq’s women have borne the brunt of the climate crisis. Few of them are in the formal job market, though many do work on farms. Because they are at home, they have often been given responsibility for providing water. Because of the present drought conditions, many women already spend at least three hours a day trying to get water from reservoirs and bring it home. Water foraging is becoming so difficult and time-consuming that some girls are dropping out of secondary school to focus on it.
At home, women are dependent on tap water, which is often contaminated. Men who work outside the home often gain access to water purified for Iraqi industry and its cities. As farms fail owing to drought, men are emigrating to those very cities for work, often leaving the women of the household in rural villages scrambling to raise enough food in arid circumstances to feed themselves and their children.
If, instead of invading Iraq, the American government had swung into action in the spring of 2003 to cut carbon dioxide output..., the emission of hundreds of billions of tons of CO2 might have been avoided.
Last fall, the International Organization for Migration at the United Nations estimated that 62,000 Iraqis living in the center and the south of the country had been displaced from their homes by drought over the previous four years and anticipated that many more would follow. Just as people from Oklahoma fled to California in droves during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s, so now Iraqis are facing the prospect of dealing with their own dustbowl. It is, however, unlikely to be a mere episode like the American one. Instead, it looms as the long-term fate of their country.
If, instead of invading Iraq, the American government had swung into action in the spring of 2003 to cut carbon dioxide output, as one of our foremost climate scientists, Michael Mann, was suggesting at the time, the emission of hundreds of billions of tons of CO2 might have been avoided. Humanity would have had an extra two decades to make the transition to a zero-carbon world. In the end, after all, the stakes are as high for Americans as they are for Iraqis.
If humanity doesn’t reach zero carbon emissions by 2050, we are likely to outrun our “carbon budget,” the ocean’s ability to absorb CO2, and the climate will undoubtedly go chaotic. What has already happened in Iraq, not to speak of the dire climate impacts that have recently left Canada constantly aflame, U.S. cities smoking, and Texans broiling in a record fashion would then seem like child’s play.
At that point, in short, we would have invaded ourselves.
"It should not be forgotten that this debacle of death and destruction was not only a profound error of policymaking; it was the result of a carefully executed crusade of disinformation and lies," said one prominent critic.
As the world this week mark the 20th anniversary of the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq, journalism experts weighed in on the corporate media's complicity in amplifying the Bush administration's lies, including ones about former Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein's nonexistent nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons upon which the war was waged.
"Twenty years ago, this country's mainstream media—with one notable exception—bought into phony Bush administration claims about Hussein's stockpiles of weapons of mass destruction, helping cheerlead our nation into a conflict that ended the lives of thousands of Americans and hundreds of thousands of Iraqis," Los Angeles Times columnist Robin Abcarian wrote Sunday.
That "one notable exception" was a group of journalists at the Washington, D.C. bureau of Knight Ridder—which was acquired by McClatchy in 2006—who published dozens of articles in several of the company's papers debunking and criticizing the Bush administration's dubious claims about Iraq and its WMDs. Their efforts were the subject of the 2017 Rob Reiner film Shock and Awe, starring Woody Harrelson.
"The war—along with criminally poor post-war planning on the part of Bush administration officials—also unleashed horrible sectarian strife, led to the emergence of ISIS, and displaced more than 1 million Iraqis," Abcarian noted.
She continued:
That sad chapter in American history produced its share of jingoistic buzzwords and phrases: "WMD," "the axis of evil," "regime change," "yellowcake uranium," "the coalition of the willing," and a cheesy but terrifying refrain, repeated ad nauseam by Bush administration officials such as then-National Security Adviser Condoleezza Rice: "We don't want the smoking gun to be a mushroom cloud."
"Of course," wrote Abcarian, "there was never any smoking gun, mushroom-shaped or not."
According to the Center for Public Integrity, a Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit investigative journalism organization, Bush and top administration officials—including then-Vice President Dick Cheney, Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld, Secretary of State Colin Powell, and Rice—"made at least 935 false statements in the two years following September 11, 2001, about the national security threat posed by Saddam Hussein's Iraq."
Those lies were dutifully repeated by most U.S. corporate mainstream media in what the center called "part of an orchestrated campaign that effectively galvanized public opinion and, in the process, led the nation to war under decidedly false pretenses."
"It should not be forgotten that this debacle of death and destruction was not only a profound error of policymaking; it was the result of a carefully executed crusade of disinformation and lies," David Corn, the Washington, D.C. bureau chief for Mother Jones, asserted Monday.
Far from paying a price for amplifying the Bush administration's Iraq lies, many of the media hawks who acted more like lapdogs than watchdogs 20 years ago are today ensconced in prestigious and well-paying positions in media, public policy, and academia.
In a where-are-they-now piece for The Real News Network, media critic Adam Johnson highlighted how the careers of several media and media-related government professionals "blossomed" after their lie-laden selling of the Iraq War:
"The almost uniform success of all the Iraq War cheerleaders provides the greatest lesson about what really helps one get ahead in public life: It's not being right, doing the right thing, or challenging power, but going with prevailing winds and mocking anyone who dares to do the opposite," wrote Johnson.
In an interview with the Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft—which is hosting a discussion Wednesday about the media's role in war and peace—Middle East expert Assal Rad noted:
Rather than challenging the narrative of the state, calling for evidence, or even humanizing the would-be victims of the war, the Iraqi people, reporters such as Thomas Friedman with significant platforms like The New York Times most often parroted the talking points of U.S. officials. There was little critical journalism to question the existence of WMDs and little reflection on important issues, such as the U.S. role in supporting Saddam Hussein in the 1980s against Iran, international law, or the humanity of Iraqis.
While there was some contrition from outlets including the Times as the Iraq occupation continued for years and not the "five days or five weeks or five months" promised by Rumsfeld, journalist Jon Schwarz of The Intercept noted that media lies and distortions about the war continue to this day.
"Perhaps the most telling instance of the media's acquiescence was a year after the Iraq invasion," said Rad, "when President Bush's joke at the White House Correspondents' dinner about finding no weapons of mass destruction was met with uproarious laughter from an audience of journalists."