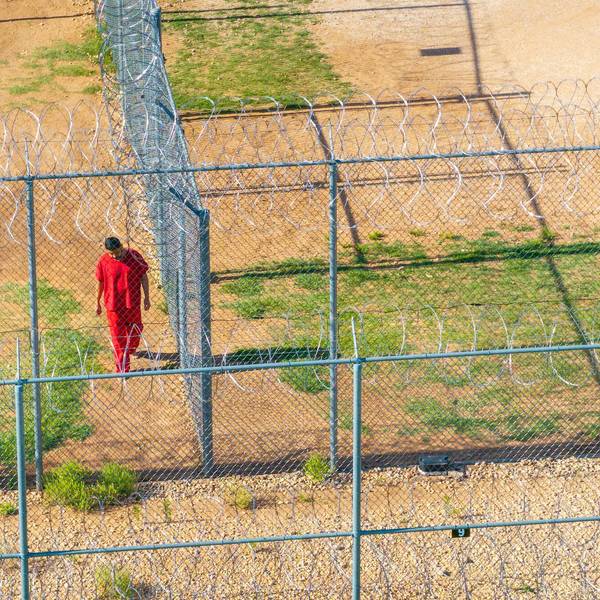
The legal action was brought by the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission against RACE, which stands for Radiological Assistance, Consulting and Engineering. The company, which processes radioactive waste from hospitals, laboratories and nuclear power plants, was purchased [pdf] in 2006 by the Swedish waste processor Studsvik, which points out that alleged incidents occurred prior to the sale.
"Some of the discrimination alleged in this case is unusually extreme because of the physical danger it created for African American employees," said EEOC Acting Chair Stuart J. Ishimaru. "It is deeply disturbing that this kind of race-based discrimination could be inflicted upon innocent workers."
Carson Owen, a senior EEOC trial attorney, told the Memphis Commercial Appeal newspaper that the health risk to the employees made the case the most serious he has seen in his 30 years with the agency.
According to the EEOC lawsuit, white managers at RACE subjected African-American employees to excessive radiation exposure -- more than their white co-workers. The company allegedly assigned black workers to the shop with radioactive waste while white employees worked elsewhere, and it manipulated the dosimeters that measure radiation exposure to mask the actual levels that black workers received.
Courtney Britton, the lead worker in the shop, and other African-American employees were also subjected to racist comments by white supervisors. The complaint said that Britton's boss referred to him and other black employees with the N-word and other derogatory slurs such as "boy." When he finally complained about the racial harassment, Britton was suspended for 15 days and then laid off.
"Mr. Britton and other African-American employees endured the abuse because they needed to work to support their families," said Attorney Faye Williams of the EEOC's Memphis district, which covers Tennessee, Arkansas and northern Mississippi.
Besides providing for the payment of $650,000 to 23 African-American employees, the three-year consent decree issued in the case also prohibits Studsvik from discriminating against or assigning employees based on their race and from retaliating against workers who assert their rights. In addition, Studsvik agreed to adopt an anti-discrimination policy and provide mandatory training about the policy to employees.