

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.
5
#000000
#FFFFFF
To donate by check, phone, or other method, see our More Ways to Give page.


Daily news & progressive opinion—funded by the people, not the corporations—delivered straight to your inbox.

The report--Gun Ownership and Firearm-related Deaths (pdf)--which looks closely at the correlation between gun ownership figures and gun violence mortality rates in 27 countries, firmly debunks the endlessly repeatedly claims by the gun industry lobby and right-wing advocacy groups like the National Rifle Association that claim "guns make a nation safer."
Released just two days after another mass shooting in the U.S., its scheduled publication was pushed up after a man killed twelve people at a naval yard in Washington, DC. Controlling for the prevalence of mental illness in a society, the study found the "correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate off firearm-related deaths" was striking and impossible to ignore.
According to the report:
The number of guns per capita per country was a strong and independent predictor of firearm-related death in a given country, whereas the predictive power of the mental illness burden was of borderline significance in a multivariable model. Regardless of exact cause and effect, however, the current study debunks the widely quoted hypothesis that guns make a nation safer.
"Although correlation is not the same as causation, it seems conceivable that abundant gun availability facilitates firearm-related deaths," said the authors of the study, Sripal Bangalore of NYU Langone Medical Center, and Franz H Messerli of St Luke's Roosevelt hospital at Columbia University.
Though they allowed that "high crime rates may instigate widespread anxiety and fear, thereby motivating people to arm themselves and give rise to increased gun ownership" they said this "resulting vicious cycle" would also help explain the "polarized status that is now the case with the US" where even as a majority segment of the population wants tougher gun safety laws, a powerful minority is able to successfully lobby against it.
Either way, what the report attempted to do was test the claims by pro-gun interests who repeatedly make claims unsupported by objective analysis.
For example, as many critics of their argument point out, gun industry lobbyists have tried to deflect responsibility for mass shootings by claiming that mental illness is the true culprit, not the easy access to guns that perpetrators have.
As the report notes:
There is little question that the combination of mental illness and easy access to guns may prove to be synergistic in their lethality, as was seen in the shootings in Aurora, Tucson, at Virginia Tech, in Oak Creek, and other places in recent years. On the opposite end stands the contention that fewer firearms would reduce crime rates and overall lead to greater safety. Yet many of these arguments from both sides are based on little or no evidence. We sought to evaluate the relationship between prevalence of gun ownership and mental illness on firearm-related death in a given country.
Looking at international data, here's what they found:
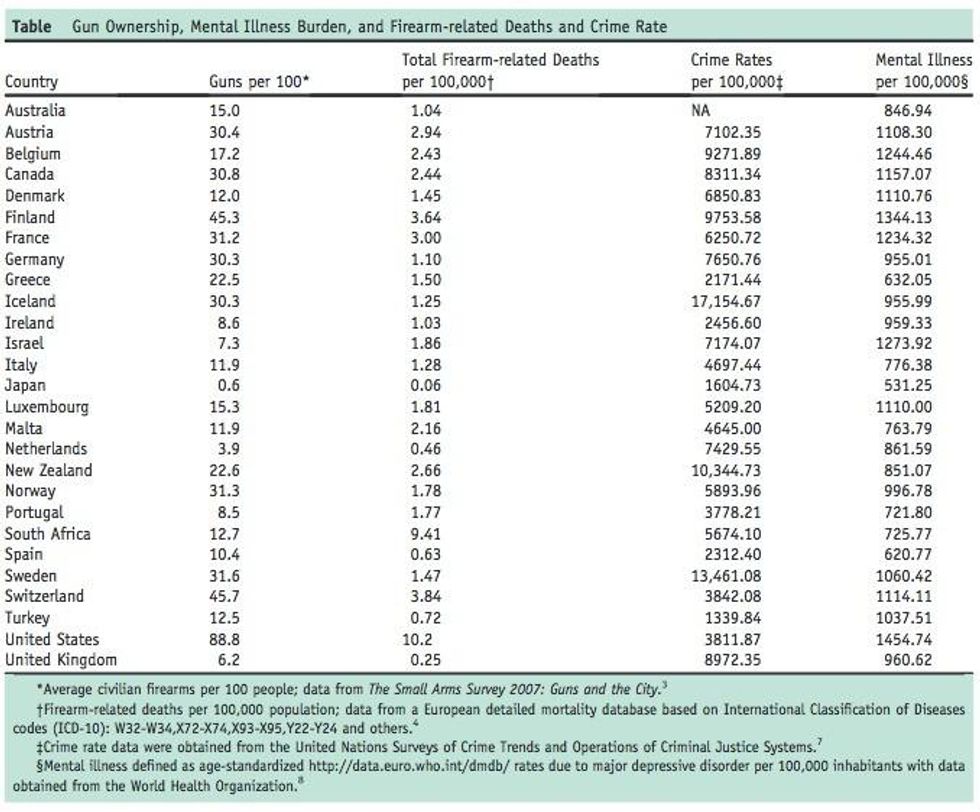
In having almost as many guns as it has people, prevalence of private gun ownership was the highest in the US among both developed and developing countries. Japan, on the other end, had an extremely low gun ownership rate (see Table below). Similarly, South Africa (9.4 per 100,000) and the US (10.2 per 100,000) had extremely high firearm-related deaths, whereas the United Kingdom (0.25 per 100,000) had an extremely low rate of firearm-related deaths. There was a significant positive correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate of firearm-related deaths ( r 1/4 0.80; P < .0001) ( Figure, A ), with Japan being on one end of the spectrum and the US being on the other. In this correlation, South Africa was the only outlier in that the observed firearms-related death rate was several times higher than expected from gun ownership.
The study has been underway for sometime, but its release was expedited following Monday's workplace massacre in Washington, DC.
As The Guardian reports:
The journal has fast-tracked publication of the study because of the shootings at the Washington navy yard. It was originally scheduled for later this week.
It follows an emotional appeal from a doctor at the trauma center in Washington where the victims of Aaron Alexis' random violence were taken. "I would like you to put my trauma center out of business," Janis Orlowski, chief medical officer at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, told reporters in the aftermath of the massacre. "I would like to not be an expert on gunshots. Let's get rid of this. This is not America."
As it turns out, according to this study, the massacre in Washington, DC on Monday--like the many that came before it and those sure to follow--was very American, indeed.
________________________________
Dear Common Dreams reader, The U.S. is on a fast track to authoritarianism like nothing I've ever seen. Meanwhile, corporate news outlets are utterly capitulating to Trump, twisting their coverage to avoid drawing his ire while lining up to stuff cash in his pockets. That's why I believe that Common Dreams is doing the best and most consequential reporting that we've ever done. Our small but mighty team is a progressive reporting powerhouse, covering the news every day that the corporate media never will. Our mission has always been simple: To inform. To inspire. And to ignite change for the common good. Now here's the key piece that I want all our readers to understand: None of this would be possible without your financial support. That's not just some fundraising cliche. It's the absolute and literal truth. We don't accept corporate advertising and never will. We don't have a paywall because we don't think people should be blocked from critical news based on their ability to pay. Everything we do is funded by the donations of readers like you. Will you donate now to help power the nonprofit, independent reporting of Common Dreams? Thank you for being a vital member of our community. Together, we can keep independent journalism alive when it’s needed most. - Craig Brown, Co-founder |

The report--Gun Ownership and Firearm-related Deaths (pdf)--which looks closely at the correlation between gun ownership figures and gun violence mortality rates in 27 countries, firmly debunks the endlessly repeatedly claims by the gun industry lobby and right-wing advocacy groups like the National Rifle Association that claim "guns make a nation safer."
Released just two days after another mass shooting in the U.S., its scheduled publication was pushed up after a man killed twelve people at a naval yard in Washington, DC. Controlling for the prevalence of mental illness in a society, the study found the "correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate off firearm-related deaths" was striking and impossible to ignore.
According to the report:
The number of guns per capita per country was a strong and independent predictor of firearm-related death in a given country, whereas the predictive power of the mental illness burden was of borderline significance in a multivariable model. Regardless of exact cause and effect, however, the current study debunks the widely quoted hypothesis that guns make a nation safer.
"Although correlation is not the same as causation, it seems conceivable that abundant gun availability facilitates firearm-related deaths," said the authors of the study, Sripal Bangalore of NYU Langone Medical Center, and Franz H Messerli of St Luke's Roosevelt hospital at Columbia University.
Though they allowed that "high crime rates may instigate widespread anxiety and fear, thereby motivating people to arm themselves and give rise to increased gun ownership" they said this "resulting vicious cycle" would also help explain the "polarized status that is now the case with the US" where even as a majority segment of the population wants tougher gun safety laws, a powerful minority is able to successfully lobby against it.
Either way, what the report attempted to do was test the claims by pro-gun interests who repeatedly make claims unsupported by objective analysis.
For example, as many critics of their argument point out, gun industry lobbyists have tried to deflect responsibility for mass shootings by claiming that mental illness is the true culprit, not the easy access to guns that perpetrators have.
As the report notes:
There is little question that the combination of mental illness and easy access to guns may prove to be synergistic in their lethality, as was seen in the shootings in Aurora, Tucson, at Virginia Tech, in Oak Creek, and other places in recent years. On the opposite end stands the contention that fewer firearms would reduce crime rates and overall lead to greater safety. Yet many of these arguments from both sides are based on little or no evidence. We sought to evaluate the relationship between prevalence of gun ownership and mental illness on firearm-related death in a given country.
Looking at international data, here's what they found:
In having almost as many guns as it has people, prevalence of private gun ownership was the highest in the US among both developed and developing countries. Japan, on the other end, had an extremely low gun ownership rate (see Table below). Similarly, South Africa (9.4 per 100,000) and the US (10.2 per 100,000) had extremely high firearm-related deaths, whereas the United Kingdom (0.25 per 100,000) had an extremely low rate of firearm-related deaths. There was a significant positive correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate of firearm-related deaths ( r 1/4 0.80; P < .0001) ( Figure, A ), with Japan being on one end of the spectrum and the US being on the other. In this correlation, South Africa was the only outlier in that the observed firearms-related death rate was several times higher than expected from gun ownership.

The study has been underway for sometime, but its release was expedited following Monday's workplace massacre in Washington, DC.
As The Guardian reports:
The journal has fast-tracked publication of the study because of the shootings at the Washington navy yard. It was originally scheduled for later this week.
It follows an emotional appeal from a doctor at the trauma center in Washington where the victims of Aaron Alexis' random violence were taken. "I would like you to put my trauma center out of business," Janis Orlowski, chief medical officer at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, told reporters in the aftermath of the massacre. "I would like to not be an expert on gunshots. Let's get rid of this. This is not America."
As it turns out, according to this study, the massacre in Washington, DC on Monday--like the many that came before it and those sure to follow--was very American, indeed.
________________________________

The report--Gun Ownership and Firearm-related Deaths (pdf)--which looks closely at the correlation between gun ownership figures and gun violence mortality rates in 27 countries, firmly debunks the endlessly repeatedly claims by the gun industry lobby and right-wing advocacy groups like the National Rifle Association that claim "guns make a nation safer."
Released just two days after another mass shooting in the U.S., its scheduled publication was pushed up after a man killed twelve people at a naval yard in Washington, DC. Controlling for the prevalence of mental illness in a society, the study found the "correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate off firearm-related deaths" was striking and impossible to ignore.
According to the report:
The number of guns per capita per country was a strong and independent predictor of firearm-related death in a given country, whereas the predictive power of the mental illness burden was of borderline significance in a multivariable model. Regardless of exact cause and effect, however, the current study debunks the widely quoted hypothesis that guns make a nation safer.
"Although correlation is not the same as causation, it seems conceivable that abundant gun availability facilitates firearm-related deaths," said the authors of the study, Sripal Bangalore of NYU Langone Medical Center, and Franz H Messerli of St Luke's Roosevelt hospital at Columbia University.
Though they allowed that "high crime rates may instigate widespread anxiety and fear, thereby motivating people to arm themselves and give rise to increased gun ownership" they said this "resulting vicious cycle" would also help explain the "polarized status that is now the case with the US" where even as a majority segment of the population wants tougher gun safety laws, a powerful minority is able to successfully lobby against it.
Either way, what the report attempted to do was test the claims by pro-gun interests who repeatedly make claims unsupported by objective analysis.
For example, as many critics of their argument point out, gun industry lobbyists have tried to deflect responsibility for mass shootings by claiming that mental illness is the true culprit, not the easy access to guns that perpetrators have.
As the report notes:
There is little question that the combination of mental illness and easy access to guns may prove to be synergistic in their lethality, as was seen in the shootings in Aurora, Tucson, at Virginia Tech, in Oak Creek, and other places in recent years. On the opposite end stands the contention that fewer firearms would reduce crime rates and overall lead to greater safety. Yet many of these arguments from both sides are based on little or no evidence. We sought to evaluate the relationship between prevalence of gun ownership and mental illness on firearm-related death in a given country.
Looking at international data, here's what they found:
In having almost as many guns as it has people, prevalence of private gun ownership was the highest in the US among both developed and developing countries. Japan, on the other end, had an extremely low gun ownership rate (see Table below). Similarly, South Africa (9.4 per 100,000) and the US (10.2 per 100,000) had extremely high firearm-related deaths, whereas the United Kingdom (0.25 per 100,000) had an extremely low rate of firearm-related deaths. There was a significant positive correlation between guns per capita per country and the rate of firearm-related deaths ( r 1/4 0.80; P < .0001) ( Figure, A ), with Japan being on one end of the spectrum and the US being on the other. In this correlation, South Africa was the only outlier in that the observed firearms-related death rate was several times higher than expected from gun ownership.

The study has been underway for sometime, but its release was expedited following Monday's workplace massacre in Washington, DC.
As The Guardian reports:
The journal has fast-tracked publication of the study because of the shootings at the Washington navy yard. It was originally scheduled for later this week.
It follows an emotional appeal from a doctor at the trauma center in Washington where the victims of Aaron Alexis' random violence were taken. "I would like you to put my trauma center out of business," Janis Orlowski, chief medical officer at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, told reporters in the aftermath of the massacre. "I would like to not be an expert on gunshots. Let's get rid of this. This is not America."
As it turns out, according to this study, the massacre in Washington, DC on Monday--like the many that came before it and those sure to follow--was very American, indeed.
________________________________